Effects of tachyplesin and n-sodium butyrate on proliferation and gene expression of human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line BGC-823 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Effects of tachyplesin and n-sodium butyrate on proliferation and gene expression of human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line BGC-823
Song-Lin Shi et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2006.
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of tachyplesin and n-sodium butyrate on proliferation and gene expression of human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line BGC-823.
Methods: Effects of tachyplesin and n-sodium butyrate on proliferation of BGC-823 cells were determined with trypan blue dye exclusion test and HE staining. Effects of tachyplesin and n-sodium butyrate on cell cycle were detected by flow cytometry. Protein levels of c-erbB-2, c-myc, p53 and p16 were examined by immunocytochemistry.
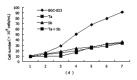
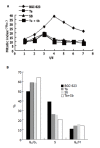
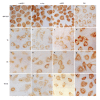
Results: The inhibiting effects were similar after 2.0 mg/L tachyplesin and 2.0 mmol/L n-sodium butyrate treatment, the inhibitory rate of cellular growth was 62.66% and 60.19% respectively, and the respective maximum mitotic index was decreased by 49.35% and 51.69% respectively. Tachyplesin and n-sodium butyrate treatment could markedly increase the proportion of cells at G(0)/G(1) phase and decrease the proportion at S phase. The expression levels of oncogene c-erbB-2, c-myc, and mtp53 proteins were down-regulated while the expression level of tumor suppressor gene p16 protein was up-regulated after the treatment with tachyplesin or n-sodium butyrate. The effects of 1.0 mg/L tachyplesin in combination with 1.0 mmol/L n-sodium butyrate were obviously superior to their individual treatment in changing cell cycle distribution and expression of c-erbB-2, c-myc, mtp53 and p16 protein. The inhibitory rate of cellular growth of BGC-823 cells after combination treatment was 62.29% and the maximum mitotic index was decreased by 51.95%.
Conclusion: Tachyplesin as a differentiation inducer of tumor cells has similar effects as n-sodium butyrate on proliferation of tumor cells, expression of correlative oncogene and tumor suppressor gene. It also has a synergistic effect on differentiation of tumor cells.
Figures
Figure 1
Cell growth inhibition in BGC-823 cells after tachyplesin, n-sodium butyrate and their combination treatment (×104 cells/mL).
Figure 2
Influence of tachyplesin, n-sodium butyrate and their combination on mitotic index (A) and cell cycle (B) of BGC-823 cells.
Figure 3
Expression of c-erbB-2 (A-D), c-myc (E-H), p53 (I-L), and p16 (M-R) in BGC-823 cells, tachyplesin-treated cells, n-sodium butyrate-treated cells, and tachyplesin + n-sodium butyrate-treated cells. ×536.
Similar articles
- Effects of tachyplesin on proliferation and differentiation of human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells.
Ouyang GL, Li QF, Peng XX, Liu QR, Hong SG. Ouyang GL, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Dec;8(6):1053-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.1053. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 12439924 Free PMC article. - [Effects of sodium butyrate on proliferation of human gastric cancer cells and expression of p16 gene].
Shen WJ, Dai DQ, Teng Y, Liu J. Shen WJ, et al. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Apr 29;88(17):1192-6. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18844115 Chinese. - Effects of tachyplesin on the regulation of cell cycle in human hepatocarcinoma SMMC-7721 cells.
Li QF, Ou-Yang GL, Peng XX, Hong SG. Li QF, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Mar;9(3):454-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i3.454. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12632496 Free PMC article. - [Genetic alterations and expression changes in breast cancers].
Terada K, Ushijima T. Terada K, et al. Nihon Rinsho. 2007 Jun 28;65 Suppl 6:113-9. Nihon Rinsho. 2007. PMID: 17682148 Review. Japanese. No abstract available. - Tachyplesin I and its derivatives: A pharmaco-chemical perspective on their antimicrobial and antitumor potential.
Lu S, Lin J, Jin J, Zhang L, Guan Y, Chen H, Wu Y, Zhang W, Luan X. Lu S, et al. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2022 Dec;17(12):1407-1423. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2023.2157402. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 36503335 Review.
Cited by
- Examination of the molecular control of ruminal epithelial function in response to dietary restriction and subsequent compensatory growth in cattle.
O'Shea E, Waters SM, Keogh K, Kelly AK, Kenny DA. O'Shea E, et al. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2016 Sep 15;7:53. doi: 10.1186/s40104-016-0114-8. eCollection 2016. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27651894 Free PMC article. - Identifying anticancer peptides by using improved hybrid compositions.
Li FM, Wang XQ. Li FM, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 27;6:33910. doi: 10.1038/srep33910. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27670968 Free PMC article. - Aberrant expression of nuclear matrix proteins during HMBA-induced differentiation of gastric cancer cells.
Jing GJ, Xu DH, Shi SL, Li QF, Wang SY, Wu FY, Kong HY. Jing GJ, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2010 May 7;16(17):2176-82. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2176. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20440860 Free PMC article. - Pathway analysis identifies perturbation of genetic networks induced by butyrate in a bovine kidney epithelial cell line.
Li CJ, Li RW, Wang YH, Elsasser TH. Li CJ, et al. Funct Integr Genomics. 2007 Jul;7(3):193-205. doi: 10.1007/s10142-006-0043-2. Epub 2006 Dec 21. Funct Integr Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17186197 - Transcriptome characterization by RNA-seq unravels the mechanisms of butyrate-induced epigenomic regulation in bovine cells.
Wu S, Li RW, Li W, Li CJ. Wu S, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036940. Epub 2012 May 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22615851 Free PMC article.
References
- Iwanaga S, Kawabata S, Muta T. New types of clotting factors and defense molecules found in horseshoe crab hemolymph: their structures and functions. J Biochem. 1998;123:1–15. - PubMed
- Witt O, Schulze S, Kanbach K, Roth C, Pekrun A. Tumor cell differentiation by butyrate and environmental stress. Cancer Lett. 2001;171:173–182. - PubMed
- Nakamura T, Furunaka H, Miyata T, Tokunaga F, Muta T, Iwanaga S, Niwa M, Takao T, Shimonishi Y. Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). Isolation and chemical structure. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:16709–16713. - PubMed
- Li QF, Wang DY, The differentiation of human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line MGC80-3 induced by dibutyryl cAMP in vitro. Shiyan Shengwu Xuebao. 1990;23:167–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous