Trends in production, trafficking, and consumption of methamphetamine and cocaine in Mexico - PubMed (original) (raw)
Trends in production, trafficking, and consumption of methamphetamine and cocaine in Mexico
Kimberly C Brouwer et al. Subst Use Misuse. 2006.
Abstract
Over the past decade, Mexico has experienced a significant increase in trafficking of cocaine and trafficking and production of methamphetamine. An estimated 70% of United States cocaine originating in South America passes through the Central America-Mexico corridor. Mexico-based groups are now believed to control 70%-90% of methamphetamine production and distribution in the United States. Increased availability of these drugs at reduced prices has led to a parallel rise in local drug consumption. Methamphetamine abuse is now the primary reason for seeking drug abuse treatment in a number of cities, primarily in northwestern Mexico. Although cocaine and methamphetamine use have been linked with the sex trade and high-risk behaviors, such as shooting gallery attendance and unprotected sex in other settings, comparatively little is known about the risk behaviors associated with use of these drugs in Mexico, especially for methamphetamines. We review historical aspects and current trends in cocaine and methamphetamine production, trafficking, and consumption in Mexico, with special emphasis on the border cities of Ciudad Juarez and Tijuana. Additionally, we discuss the potential public health consequences of cocaine use and the recent increase in methamphetamine use, especially in regards to the spread of bloodborne and other infections, in an effort to inform appropriate public health interventions.
Figures
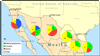
Figure 1. Map of drug user treatment admissions in Mexican states bordering the U.S
Pie charts above each of the six Mexican states bordering the U.S. show the percent of drug user treatment admissions by primary drug used. Data was compiled based on the Mexican Addiction Epidemiologic Surveillance System or SISVEA (Maxwell et al., 2005). The “Other” category includes marijuana, inhalants, alcohol, tobacco, and a variety of veterinary products.
Similar articles
- At the borders, on the edge: use of injected methamphetamine in Tijuana and Ciudad Juarez, Mexico.
Case P, Ramos R, Brouwer KC, Firestone-Cruz M, Pollini RA, Fraga MA, Patterson TL, Strathdee SA. Case P, et al. J Immigr Minor Health. 2008 Feb;10(1):23-33. doi: 10.1007/s10903-007-9051-0. J Immigr Minor Health. 2008. PMID: 17516170 Free PMC article. - Comparison of sexual and drug use behaviors between female sex workers in Tijuana and Ciudad Juarez, Mexico.
Patterson TL, Semple SJ, Fraga M, Bucardo J, de la Torre A, Salazar J, Orozovich P, Staines H, Amaro H, Magis-Rodríguez C, Strathdee SA. Patterson TL, et al. Subst Use Misuse. 2006;41(10-12):1535-49. doi: 10.1080/10826080600847852. Subst Use Misuse. 2006. PMID: 17002992 - Historical trends in the production and consumption of illicit drugs in Mexico: implications for the prevention of blood borne infections.
Bucardo J, Brouwer KC, Magis-Rodríguez C, Ramos R, Fraga M, Perez SG, Patterson TL, Strathdee SA. Bucardo J, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2005 Sep 1;79(3):281-93. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2005.02.003. Epub 2005 Apr 1. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2005. PMID: 16102372 Free PMC article. Review. - An evolving problem: methamphetamine production and trafficking in the United States.
Shukla RK, Crump JL, Chrisco ES. Shukla RK, et al. Int J Drug Policy. 2012 Nov;23(6):426-35. doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2012.07.004. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Int J Drug Policy. 2012. PMID: 22943831 Review.
Cited by
- Prevalence of hepatitis C virus and HIV infection among injection drug users in two Mexican cities bordering the U.S.
White EF, Garfein RS, Brouwer KC, Lozada R, Ramos R, Firestone-Cruz M, Pérez SG, Magis-Rodríguez C, Conde-Glez CJ, Strathdee SA. White EF, et al. Salud Publica Mex. 2007 May-Jun;49(3):165-72. doi: 10.1590/s0036-36342007000300001. Salud Publica Mex. 2007. PMID: 17589770 Free PMC article. - Managing la malilla: Exploring drug treatment experiences among injection drug users in Tijuana, Mexico, and their implications for drug law reform.
Syvertsen J, Pollini RA, Lozada R, Vera A, Rangel G, Strathdee SA. Syvertsen J, et al. Int J Drug Policy. 2010 Nov;21(6):459-65. doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2010.06.006. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Int J Drug Policy. 2010. PMID: 20800464 Free PMC article. - Crystal methamphetamine use among female street-based sex workers: Moving beyond individual-focused interventions.
Shannon K, Strathdee S, Shoveller J, Zhang R, Montaner J, Tyndall M. Shannon K, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011 Jan 1;113(1):76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2010.07.011. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011. PMID: 20810223 Free PMC article. - A comparison of registered and unregistered female sex workers in Tijuana, Mexico.
Sirotin N, Strathdee SA, Lozada R, Nguyen L, Gallardo M, Vera A, Patterson TL. Sirotin N, et al. Public Health Rep. 2010 Jul-Aug;125 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):101-9. doi: 10.1177/00333549101250S414. Public Health Rep. 2010. PMID: 20626197 Free PMC article. - Intimate Partner Violence Among Female Sex Workers and Their Noncommercial Male Partners in Mexico: A Mixed-Methods Study.
Ulibarri MD, Salazar M, Syvertsen JL, Bazzi AR, Rangel MG, Orozco HS, Strathdee SA. Ulibarri MD, et al. Violence Against Women. 2019 Apr;25(5):549-571. doi: 10.1177/1077801218794302. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Violence Against Women. 2019. PMID: 30156143 Free PMC article.
References
- Astorga LA. Drug trafficking in Mexico: a first general assessment. Management of Social Transformations - Discussion Paper No. 36. 1999. [Accessed December 12, 2004]. from http://www.unesco.org/most/astorga.htm.
- Badillo AR, Magis-Rodríguez C, Ortiz-Mondragon R, Lozada-Romero R, Uribe-Zúñiga PE. Int Conf AIDS. Geneva, Switzerland: 1998. Persons who injecting drug in treatment and prisoners in Tijuana, Baja California, Mexico.
- Bruneau J, Brogly SB, Tyndall MW, Lamothe F, Franco EL. Intensity of drug injection as a determinant of sustained injection cessation among chronic drug users: the interface with social factors and service utilization. Addiction. 2004;99(6):727–737. - PubMed
- Bruneau J, Lamothe F, Franco E, Lachance N, Desy M, Soto J, Vincelette J. High rates of HIV infection among injection drug users participating in needle exchange programs in Montreal: results of a cohort study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997;146(12):994–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH061146/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA09225-S11/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007384-14/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA020364/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA023877/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007384/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH61146/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12116/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI36214-06/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062554/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA009225-10S1/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062554-05/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01DA020364/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012116-05/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA009225/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA020364-01/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MH62554/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012116/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 AI07384/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061146-05/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous