Quantitative real-time PCR protocol for analysis of nuclear receptor signaling pathways - PubMed (original) (raw)
Quantitative real-time PCR protocol for analysis of nuclear receptor signaling pathways
Angie L Bookout et al. Nucl Recept Signal. 2003.
Abstract
A major goal of the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas (NURSA) is to elucidate the biochemical and physiological roles of nuclear receptors in vivo. Characterizing the tissue expression pattern of individual receptors and their target genes in whole animals under various pharmacological conditions and genotypes is an essential component of this aim. Here we describe a high-throughput quantitative, real-time, reverse-transcription PCR (QPCR) method for the measurement of both the relative level of expression of a particular transcript in a given tissue or cell type, and the relative change in expression of a particular transcript after pharmacologic or genotypic manipulation. This method is provided as a standardized protocol for those in the nuclear receptor field. It is meant to be a simplified, easy to use protocol for the rapid, high-throughput measurement of transcript levels in a large number of samples. A subsequent report will provide validated primer and probe sequence information for the entire mouse and human nuclear receptor superfamily.
Figures
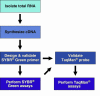
Figure 1. Typical work-flow for designing and implementing Real-Time PCR assays.
See text for more details
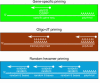
Figure 2. Representation of RNA priming for reverse transcription.
See text for more details
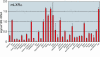
Figure 3. Primer set validation.
(a) Example of a valid primer set for mouse LXR- α using SYBR® Green. The presence of a single peak in the dissociation curve and the -3.3 slope and 0.99 R2 value of the standard curve plot are indicative of a good set of primers. (b) Example of an invalid primer set for mouse HSD due to the amplification of non-specific products, as indicated by the presence of multiple peaks in the dissociation curve. This may be an effect of non-specific priming or primer dimerization. Note that the slope of the standard curve plot (-3.2) is within the acceptable range of a valid primer set, but the dissociation curve renders this set of primers unacceptable. (c) Example of an invalid primer set for mouse PNR due to poor amplification. Note the unacceptable slope (-2.28) in the standard curve plot, and the presence of multiple peaks in the dissociation curve.
Figure 4. Formulas for Q-PCR calculations
See text for more details.
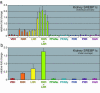
Figure 5. Expression profile for mouse LXR- α generated using the standard curve method.
The relative levels of the mRNA transcript are shown (S.D. (from triplicate readings). 18S rRNA was used as the normalizer gene so that the level of LXR- α may be compared between tissue types.
Figure 6. Typical experiment in which wild-type male mice were treated with several different nuclear receptor agonists.
The relative changes in mRNA expression for known receptor target genes, in this case SREBP-1c, an LXR target gene, were measured using the comparative Ct method. (a) SREBP-1c expression plotted for each of the animals (S.D. Each color represents a different experimental group (n=4 animals). (b) SREBP-1c expression plotted as averages of the fold changes for the 4 animals in each treatment group shown in (a) (SEM. Note that the SREBP-1c transcript increases relative to control (VEH) in the animals treated with an RXR agonist (LG268), an LXR agonist (T1317), or both LG269 and T1317 together (T+LG). Note that ligands for PPAR- α (fenofibrate), PPAR- γ (troglitazone), FXR (CDCA), PXR (PCN), and CAR (TCPOBOB) have no effect on the level of the SREBP-1c message relative to control.
Similar articles
- Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas (www.nursa.org): hyperlinking the nuclear receptor signaling community.
Lanz RB, Jericevic Z, Zuercher WJ, Watkins C, Steffen DL, Margolis R, McKenna NJ. Lanz RB, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D221-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj029. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16381851 Free PMC article. - Minireview: Evolution of NURSA, the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas.
McKenna NJ, Cooney AJ, DeMayo FJ, Downes M, Glass CK, Lanz RB, Lazar MA, Mangelsdorf DJ, Moore DD, Qin J, Steffen DL, Tsai MJ, Tsai SY, Yu R, Margolis RN, Evans RM, O'Malley BW. McKenna NJ, et al. Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jun;23(6):740-6. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0135. Epub 2009 May 7. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19423650 Free PMC article. Review. - The Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas: development of a functional atlas of nuclear receptors.
Margolis RN, Evans RM, O'Malley BW; NURSA Atlas Consortium. Margolis RN, et al. Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Oct;19(10):2433-6. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0461. Epub 2005 Jul 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 16051673 - Nuclear receptor atlas of female mouse liver parenchymal, endothelial, and Kupffer cells.
Li Z, Kruijt JK, van der Sluis RJ, Van Berkel TJ, Hoekstra M. Li Z, et al. Physiol Genomics. 2013 Apr 1;45(7):268-75. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00151.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Physiol Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23362145 - [Quantitative PCR in the diagnosis of Leishmania].
Mortarino M, Franceschi A, Mancianti F, Bazzocchi C, Genchi C, Bandi C. Mortarino M, et al. Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):163-7. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305709 Review. Italian.
Cited by
- Bulk and single-cell transcriptomics identify gene signatures of stem cell-derived NK cell donors with superior cytolytic activity.
van Vliet AA, van den Hout MGCN, Steenmans D, Duru AD, Georgoudaki AM, de Gruijl TD, van IJcken WFJ, Spanholtz J, Raimo M. van Vliet AA, et al. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Sep 2;32(4):200870. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200870. eCollection 2024 Dec 19. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39346765 Free PMC article. - Green (Ulva fenestrata) and Brown (Saccharina latissima) Macroalgae Similarly Modulate Inflammatory Signaling by Activating NF-_κ_B and Dampening IRF in Human Macrophage-Like Cells.
Mildenberger J, Rebours C. Mildenberger J, et al. J Immunol Res. 2024 May 17;2024:8121284. doi: 10.1155/2024/8121284. eCollection 2024. J Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38799117 Free PMC article. - The combined application of rutin and silicon alleviates osmotic stress in maize seedlings by triggering accumulation of osmolytes and antioxidants' defense mechanisms.
Altansambar N, Sezgin Muslu A, Kadıoglu A. Altansambar N, et al. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2024 Mar;30(3):513-525. doi: 10.1007/s12298-024-01430-z. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2024. PMID: 38633275 Free PMC article. - Gene-edited Mtsoc1 triple mutant Medicago plants do not flower.
Poulet A, Zhao M, Peng Y, Tham F, Jaudal M, Zhang L, van Wolfswinkel JC, Putterill J. Poulet A, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 26;15:1357924. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1357924. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38469328 Free PMC article. - Effect of herbivore stress on transgene behaviour in maize crosses with different genetic backgrounds: cry1Ab transgene transcription, insecticidal protein expression and bioactivity against insect pests.
Lohn AF, Trtikova M, Chapela I, van den Berg J, du Plessis H, Hilbeck A. Lohn AF, et al. Environ Sci Eur. 2023;35(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12302-023-00815-3. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Environ Sci Eur. 2023. PMID: 38037561 Free PMC article.
References
- Technotes Newsletter. Vol. 8. Ambion; 2001. The Top 10 Most common quantitative PCR pitfalls.
- Applied Biosystems: 1997. Relative Quantitation Of Gene Expression: ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: User Bulletin #2: Rev B.
- Applied Biosystems: 2001. ABI Prism 7900HT User Manual.
- Applied Biosystems; 2003. Essentials of Real Time PCR.
- Morrison T. B., Weis J. J., Wittwer C. T. Quantification of low-copy transcripts by continuous SYBR Green I monitoring during amplification. Biotechniques. 1998;24:954–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources