Multivariable risk prediction can greatly enhance the statistical power of clinical trial subgroup analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multivariable risk prediction can greatly enhance the statistical power of clinical trial subgroup analysis
Rodney A Hayward et al. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006.
Abstract
Background: When subgroup analyses of a positive clinical trial are unrevealing, such findings are commonly used to argue that the treatment's benefits apply to the entire study population; however, such analyses are often limited by poor statistical power. Multivariable risk-stratified analysis has been proposed as an important advance in investigating heterogeneity in treatment benefits, yet no one has conducted a systematic statistical examination of circumstances influencing the relative merits of this approach vs. conventional subgroup analysis.
Methods: Using simulated clinical trials in which the probability of outcomes in individual patients was stochastically determined by the presence of risk factors and the effects of treatment, we examined the relative merits of a conventional vs. a "risk-stratified" subgroup analysis under a variety of circumstances in which there is a small amount of uniformly distributed treatment-related harm. The statistical power to detect treatment-effect heterogeneity was calculated for risk-stratified and conventional subgroup analysis while varying: 1) the number, prevalence and odds ratios of individual risk factors for risk in the absence of treatment, 2) the predictiveness of the multivariable risk model (including the accuracy of its weights), 3) the degree of treatment-related harm, and 5) the average untreated risk of the study population.
Results: Conventional subgroup analysis (in which single patient attributes are evaluated "one-at-a-time") had at best moderate statistical power (30% to 45%) to detect variation in a treatment's net relative risk reduction resulting from treatment-related harm, even under optimal circumstances (overall statistical power of the study was good and treatment-effect heterogeneity was evaluated across a major risk factor [OR = 3]). In some instances a multi-variable risk-stratified approach also had low to moderate statistical power (especially when the multivariable risk prediction tool had low discrimination). However, a multivariable risk-stratified approach can have excellent statistical power to detect heterogeneity in net treatment benefit under a wide variety of circumstances, instances under which conventional subgroup analysis has poor statistical power.
Conclusion: These results suggest that under many likely scenarios, a multivariable risk-stratified approach will have substantially greater statistical power than conventional subgroup analysis for detecting heterogeneity in treatment benefits and safety related to previously unidentified treatment-related harm. Subgroup analyses must always be well-justified and interpreted with care, and conventional subgroup analyses can be useful under some circumstances; however, clinical trial reporting should include a multivariable risk-stratified analysis when an adequate externally-developed risk prediction tool is available.
Figures
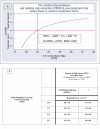
Figure 1
Panel A shows how overall treatment benefit (net RRR is a function of [treatment benefit] – [treatment harm]) varies as a function of pretreatment risk (as estimated by the control event rate [CER] of an RCT) when a treatment decreases pre-treatment risk by 50% but at a cost of 0.003 treatment-related adverse events per treatment-year. As a result, lower risk patients are harmed by treatment and higher risk patients benefit from treatment. Panel B demonstrates two statistical phenomena: (1) that statistical power can be greatly enhanced by combining risk factors (RF's) into a risk index, and (2) statistical power is greatest when the study population includes more low risk patients
Similar articles
- Subgroup analyses in randomised controlled trials: quantifying the risks of false-positives and false-negatives.
Brookes ST, Whitley E, Peters TJ, Mulheran PA, Egger M, Davey Smith G. Brookes ST, et al. Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(33):1-56. doi: 10.3310/hta5330. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701102 Review. - Assessing and reporting heterogeneity in treatment effects in clinical trials: a proposal.
Kent DM, Rothwell PM, Ioannidis JP, Altman DG, Hayward RA. Kent DM, et al. Trials. 2010 Aug 12;11:85. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-11-85. Trials. 2010. PMID: 20704705 Free PMC article. - Low-Dose Aspirin for the Prevention of Morbidity and Mortality From Preeclampsia: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].
Henderson JT, Whitlock EP, O'Conner E, Senger CA, Thompson JH, Rowland MG. Henderson JT, et al. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2014 Apr. Report No.: 14-05207-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2014 Apr. Report No.: 14-05207-EF-1. PMID: 24783270 Free Books & Documents. Review. - The future of Cochrane Neonatal.
Soll RF, Ovelman C, McGuire W. Soll RF, et al. Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834 - Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: An Evidence Update for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].
Patnode CD, Perdue LA, Rossom RC, Rushkin MC, Redmond N, Thomas RG, Lin JS. Patnode CD, et al. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2020 Feb. Report No.: 19-05257-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2020 Feb. Report No.: 19-05257-EF-1. PMID: 32129963 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
- A clustering method to identify who benefits most from the treatment group in clinical trials.
Lee BS, Sen PK, Park NS, Boothroyd RA, Peters RH, Chiriboga DA. Lee BS, et al. Health Psychol Behav Med. 2014 Jan 1;2(1):723-734. doi: 10.1080/21642850.2014.924857. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Health Psychol Behav Med. 2014. PMID: 25750814 Free PMC article. - Economic inequalities in the effectiveness of a primary care intervention for depression and suicidal ideation.
Gilman SE, Fitzmaurice GM, Bruce ML, Ten Have T, Glymour MM, Carliner H, Alexopoulos GS, Mulsant BH, Reynolds CF 3rd, Cohen A. Gilman SE, et al. Epidemiology. 2013 Jan;24(1):14-22. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3182762403. Epidemiology. 2013. PMID: 23232609 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Lessons learned from the first wave of aging with HIV.
Justice AC, Braithwaite RS. Justice AC, et al. AIDS. 2012 Jul 31;26 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S11-8. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283558500. AIDS. 2012. PMID: 22781174 Free PMC article. - Subgroup analyses in randomized controlled trials: the need for risk stratification in kidney transplantation.
Wagner M, Balk EM, Kent DM, Kasiske BL, Ekberg H. Wagner M, et al. Am J Transplant. 2009 Oct;9(10):2217-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02802.x. Am J Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19764948 Free PMC article. - Postoperative enoxaparin prevents symptomatic venous thromboembolism in high-risk plastic surgery patients.
Pannucci CJ, Dreszer G, Wachtman CF, Bailey SH, Portschy PR, Hamill JB, Hume KM, Hoxworth RE, Rubin JP, Kalliainen LK, Pusic AL, Wilkins EG. Pannucci CJ, et al. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011 Nov;128(5):1093-1103. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31822b6817. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011. PMID: 22030491 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K23 NS044929/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK-20572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS44929/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical