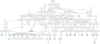Online system for faster multipoint linkage analysis via parallel execution on thousands of personal computers - PubMed (original) (raw)
Online system for faster multipoint linkage analysis via parallel execution on thousands of personal computers
M Silberstein et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Jun.
Abstract
Computation of LOD scores is a valuable tool for mapping disease-susceptibility genes in the study of Mendelian and complex diseases. However, computation of exact multipoint likelihoods of large inbred pedigrees with extensive missing data is often beyond the capabilities of a single computer. We present a distributed system called "SUPERLINK-ONLINE," for the computation of multipoint LOD scores of large inbred pedigrees. It achieves high performance via the efficient parallelization of the algorithms in SUPERLINK, a state-of-the-art serial program for these tasks, and through the use of the idle cycles of thousands of personal computers. The main algorithmic challenge has been to efficiently split a large task for distributed execution in a highly dynamic, nondedicated running environment. Notably, the system is available online, which allows computationally intensive analyses to be performed with no need for either the installation of software or the maintenance of a complicated distributed environment. As the system was being developed, it was extensively tested by collaborating medical centers worldwide on a variety of real data sets, some of which are presented in this article.
Figures
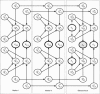
Figure 1
A Bayesian network for three-point analysis
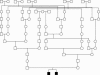
Figure 2
Pedigree reprinted from Knappskog et al.
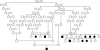
Figure 3
Pedigree reprinted from Seboun et al.
Figure 4
Pedigree with 266 individuals (produced by OPediT)
Similar articles
- A system for exact and approximate genetic linkage analysis of SNP data in large pedigrees.
Silberstein M, Weissbrod O, Otten L, Tzemach A, Anisenia A, Shtark O, Tuberg D, Galfrin E, Gannon I, Shalata A, Borochowitz ZU, Dechter R, Thompson E, Geiger D. Silberstein M, et al. Bioinformatics. 2013 Jan 15;29(2):197-205. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts658. Epub 2012 Nov 18. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23162081 Free PMC article. - Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach.
Kruglyak L, Daly MJ, Reeve-Daly MP, Lander ES. Kruglyak L, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1347-63. Am J Hum Genet. 1996. PMID: 8651312 Free PMC article. - Multipoint linkage analysis with many multiallelic or dense diallelic markers: Markov chain-Monte Carlo provides practical approaches for genome scans on general pedigrees.
Wijsman EM, Rothstein JH, Thompson EA. Wijsman EM, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Nov;79(5):846-58. doi: 10.1086/508472. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Am J Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 17033961 Free PMC article. - A survey of current software for linkage analysis.
Dudbridge F. Dudbridge F. Hum Genomics. 2003 Nov;1(1):63-5. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-1-1-63. Hum Genomics. 2003. PMID: 15601534 Free PMC article. Review. - Developments in gene mapping with linkage methods.
Risch N. Risch N. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Jun;1(1):93-8. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(91)80048-q. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991. PMID: 1840884 Review.
Cited by
- Wolfram-like syndrome with bicuspid aortic valve due to a homozygous missense variant in CDK13.
Acharya A, Raza SI, Anwar MZ, Bharadwaj T, Liaqat K, Khokhar MAS, Everard JL, Nasir A; University of Washington Center for Mendelian Genomics; Nickerson DA, Bamshad MJ, Ansar M, Schrauwen I, Ahmad W, Leal SM. Acharya A, et al. J Hum Genet. 2021 Oct;66(10):1009-1018. doi: 10.1038/s10038-021-00922-0. Epub 2021 Apr 21. J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33879837 Free PMC article. - Recurrent gain-of-function mutation in PRKG1 causes thoracic aortic aneurysms and acute aortic dissections.
Guo DC, Regalado E, Casteel DE, Santos-Cortez RL, Gong L, Kim JJ, Dyack S, Horne SG, Chang G, Jondeau G, Boileau C, Coselli JS, Li Z, Leal SM, Shendure J, Rieder MJ, Bamshad MJ, Nickerson DA; GenTAC Registry Consortium; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Grand Opportunity Exome Sequencing Project; Kim C, Milewicz DM. Guo DC, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2013 Aug 8;93(2):398-404. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.06.019. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Am J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23910461 Free PMC article. - FOXE3 mutations predispose to thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections.
Kuang SQ, Medina-Martinez O, Guo DC, Gong L, Regalado ES, Reynolds CL, Boileau C, Jondeau G, Prakash SK, Kwartler CS, Zhu LY, Peters AM, Duan XY, Bamshad MJ, Shendure J, Nickerson DA, Santos-Cortez RL, Dong X, Leal SM, Majesky MW, Swindell EC, Jamrich M, Milewicz DM. Kuang SQ, et al. J Clin Invest. 2016 Mar 1;126(3):948-61. doi: 10.1172/JCI83778. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 26854927 Free PMC article. - ADAMTS1, MPDZ, MVD, and SEZ6: candidate genes for autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment.
Bharadwaj T, Schrauwen I, Rehman S, Liaqat K, Acharya A, Giese APJ, Nouel-Saied LM, Nasir A, Everard JL, Pollock LM, Zhu S, Bamshad MJ, Nickerson DA, Ali RH, Ullah A, Wali A, Ali G, Santos-Cortez RLP, Ahmed ZM, McDermott BM Jr, Ansar M, Riazuddin S, Ahmad W, Leal SM. Bharadwaj T, et al. Eur J Hum Genet. 2022 Jan;30(1):22-33. doi: 10.1038/s41431-021-00913-x. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Eur J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 34135477 Free PMC article. - Biallelic mutations in the autophagy regulator DRAM2 cause retinal dystrophy with early macular involvement.
El-Asrag ME, Sergouniotis PI, McKibbin M, Plagnol V, Sheridan E, Waseem N, Abdelhamed Z, McKeefry D, Van Schil K, Poulter JA; UK Inherited Retinal Disease Consortium; Johnson CA, Carr IM, Leroy BP, De Baere E, Inglehearn CF, Webster AR, Toomes C, Ali M. El-Asrag ME, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2015 Jun 4;96(6):948-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.04.006. Epub 2015 May 14. Am J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25983245 Free PMC article.
References
Web Resources
- OPediT, http://www.circusoft.com/content/product/5 (for drawings of the pedigree in experiment D)
- SUPERLINK-ONLINE, http://bioinfo.cs.technion.ac.il/superlink-online (for download, http://bioinfo.cs.technion.ac.il/superlink-online/download)
References
- Elston R, Stewart J (1971) A general model for the analysis of pedigree data. Hum Hered 21:523–542 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials