Geographic variation in the prescription of schedule II opioid analgesics among outpatients in the United States - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Geographic variation in the prescription of schedule II opioid analgesics among outpatients in the United States
Lesley H Curtis et al. Health Serv Res. 2006 Jun.
Erratum in
- Health Serv Res. 2006 Jun;41(3 Pt 1):856-9
Abstract
Objective: To measure geographic variation in opioid use in a large, commercially insured, outpatient population in the United States.
Data sources: Outpatient prescription drug claims database of a national pharmaceutical benefit manager for 7,873,337 subjects with at least one prescription drug claim in 2000.
Study design: We measured the period prevalence of claims for opioid analgesics and controlled-release oxycodone at the state level. We measured geographic variation using the weighted coefficient of variation and systematic component of variation. In county-level multivariable regression, we explored associations between potential explanatory variables and claims for opioid analgesics and controlled-release oxycodone.
Principal findings: A total of 567,778 (64.2 per 1,000 total claims) were for oral opioid analgesics. Claim rates by state ranged from <20 to >100 claims per 1,000 total claims. States with long-standing prescription monitoring programs had among the lowest rates. In the county-level data, presence of a statewide prescription monitoring program and proportions of the population aged 15-24 and 65 years and older were independently and negatively associated with claim rates for all opioid analgesics. Surgeons per 1,000, proportion of the population reporting illicit drug use, and proportion who were female were independently and positively associated with claim rates for all opioid analgesics. Only the proportion of the population aged 25-34 and number of surgeons per 1,000 were independently and positively associated with claim rates for oxycodone.
Conclusions: Claim rates for opioid analgesics vary significantly by state. Presence of a statewide prescription monitoring program is associated with lower claim rates at the county level. Future research should use individual-level data to assess whether these findings reflect a reduction in abuse and diversion or suboptimal treatment of pain.
Figures
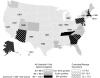
Figure 1
Claim Rates by State for All Opioid Analgesics and Controlled-Release Oxycodone The figure also displays the year in which state-based Schedule II prescription monitoring programs were first enacted in the states that have such a program.
Similar articles
- Controlled Substance Prescribing Patterns--Prescription Behavior Surveillance System, Eight States, 2013.
Paulozzi LJ, Strickler GK, Kreiner PW, Koris CM; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Paulozzi LJ, et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2015 Oct 16;64(9):1-14. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6409a1. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2015. PMID: 26469747 - Costs of gastrointestinal events after outpatient opioid treatment for non-cancer pain.
Kwong WJ, Diels J, Kavanagh S. Kwong WJ, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 2010 Apr;44(4):630-40. doi: 10.1345/aph.1M520. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Ann Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20197473 - Medical cost savings associated with an extended-release opioid with abuse-deterrent technology in the US.
Rossiter LF, Kirson NY, Shei A, White AG, Birnbaum HG, Ben-Joseph R, Michna E. Rossiter LF, et al. J Med Econ. 2014 Apr;17(4):279-87. doi: 10.3111/13696998.2014.897628. Epub 2014 Mar 7. J Med Econ. 2014. PMID: 24559196 - Routes of abuse of prescription opioid analgesics: a review and assessment of the potential impact of abuse-deterrent formulations.
Gasior M, Bond M, Malamut R. Gasior M, et al. Postgrad Med. 2016 Jan;128(1):85-96. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2016.1120642. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Postgrad Med. 2016. PMID: 26566680 Review.
Cited by
- Chronic Opioid Use Following Lumbar Discectomy: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Current Trends in the United States.
Harris AB, Zhang B, Marrache M, Puvanesarajah V, Raad M, Hassanzadeh H, Bicket M, Jain A. Harris AB, et al. Neurospine. 2020 Dec;17(4):879-887. doi: 10.14245/ns.2040122.061. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Neurospine. 2020. PMID: 33401866 Free PMC article. - Buprenorphine Prescribing: To Expand or Not to Expand.
Li X, Shorter D, Kosten TR. Li X, et al. J Psychiatr Pract. 2016 May;22(3):183-92. doi: 10.1097/PRA.0000000000000154. J Psychiatr Pract. 2016. PMID: 27123798 Free PMC article. Review. - Estimating the prevalence of opioid diversion by "doctor shoppers" in the United States.
McDonald DC, Carlson KE. McDonald DC, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Jul 17;8(7):e69241. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069241. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874923 Free PMC article. - Geographic variation in opioid prescribing in the U.S.
McDonald DC, Carlson K, Izrael D. McDonald DC, et al. J Pain. 2012 Oct;13(10):988-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2012.07.007. J Pain. 2012. PMID: 23031398 Free PMC article. - Opioid distribution trends (2006-2017) in the US Territories.
Cabrera FF, Gamarra ER, Garcia TE, Littlejohn AD, Chinga PA, Pinentel-Morillo LD, Tirado JR, Chung DY, Pande LJ, McCall KL, Nichols SD, Piper BJ. Cabrera FF, et al. PeerJ. 2019 Jan 15;7:e6272. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6272. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30671308 Free PMC article.
References
- American Pain Society. Principles of Analgesic Use in the Treatment of Acute Pain and Cancer Pain. 4. Glenview, IL: American Pain Society; 1999.
- American Pain Society. Guideline for the Management of Pain in Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Juvenile Chronic Arthritis. Clinical Practice Guideline Number 2. Glenview, IL: American Pain Society; 2002.
- American Pain Society. Guideline for the Management of Cancer Pain in Adults and Children. Glenview, IL: American Pain Society; 2004.
- Clancy MA. “Down East High; Washington County Pill Addicts Have Health Officials Worried.”. Bangor Daily News. 2000 May 13.
- Clark DO, Von Korff M, Saunders K, Baluch WM, Simon GE. “A Chronic Disease Score with Empirically Derived Weights.”. Medical Care. 1995;33(8):783–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources