Identification of endophilins 1 and 3 as selective binding partners for VGLUT1 and their co-localization in neocortical glutamatergic synapses: implications for vesicular glutamate transporter trafficking and excitatory vesicle formation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Identification of endophilins 1 and 3 as selective binding partners for VGLUT1 and their co-localization in neocortical glutamatergic synapses: implications for vesicular glutamate transporter trafficking and excitatory vesicle formation
Stephanie De Gois et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006 Jul-Aug.
Abstract
1. Selective protein-protein interactions between neurotransmitter transporters and their synaptic targets play important roles in regulating chemical neurotransmission. We screened a yeast two-hybrid library with bait containing the C-terminal amino acids of VGLUT1 and obtained clones that encode endophilin 1 and endophilin 3, proteins considered to play an integral role in glutamatergic vesicle formation. 2. Using a modified yeast plasmid vector to enable more cost-effective screens, we analyzed the selectivity and specificity of this interaction. Endophilins 1 and 3 selectively recognize only VGLUT1 as the C-terminus of VGLUT2 and VGLUT3 do not interact with either endophilin isoform. We mutagenized four conserved stretches of primary sequence in VGLUT1 that includes two polyproline motifs (Pro1, PPAPPP, and Pro2, PPRPPPP), found only in VGLUT1, and two conserved stretches (SEEK, SYGAT), found also in VGLUT2 and VGLUT3. The absence of the VGLUT conserved regions does not affect VGLUT1-endophilin association. Of the two polyproline stretches, only one (Pro2) is required for binding specificity to both endophilin 1 and endophilin 3. 3. We also show that endophilin 1 and endophilin 3 co-localize with VGLUT1 in synaptic terminals of differentiated rat neocortical neurons in primary culture. These results indicate that VGLUT1 and both endophilins are enriched in a class of excitatory synaptic terminals in cortical neurons and there, may interact to play an important role affecting the vesicular sequestration and synaptic release of glutamate.
Figures
Fig. 1.
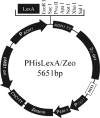
Modified yeast bait vector. The HIS3 gene was introduced in the _Bam_HI site of the pHybLex/Zeo vector and renamed pHisLexA/Zeo.
Fig. 2.
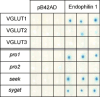
Pro2 domain of VGLUT1 interacts with endophilin 1. Yeast carrying the reporter plasmid p80pLacZ and pB42AD (EGY48[LacZ]/pB42AD) or endophilin1/pB42AD (EGY48[LacZ]/endo1) were transformed with either VGLUT1-, VGLUT2-, VGLUT3-pHisLexA or VGLUT1mutants-pHisLexA and grown at 30°C for 2 days on SD/-UHT plates. Three individual colonies were then spotted on SD/Xgal/GalRaf/-4aa selective plates and grown for 2 days at 30°C. Interaction between endophilin 1 and the bait is reflected by the blue coloration of colonies. Note that VGLUT2 or VGLUT3 do not show any interaction with endophilin 1. Also note that the blue coloration with VGLUT is lost only when one of the two proline-rich domains (Pro2) is mutated to alanine residues. Loss of VGLUT conserved regions (SEEK and SYGAT) do not affect VGLUT1 association with endophilin 1.
Fig. 3.
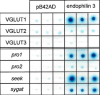
Endophilin 3 also interacts with VGLUT1-Pro2 domain. As before, EGY48[LacZ]/pB42AD or EGY48[LacZ]/endo3 yeasts were transformed with either VGLUT1-, VGLUT2-, VGLUT3-pHisLexA or VGLUT1 mutants-pHisLexA and grown at 30°C for 2 days on SD/-UHT plates. Three individual colonies were spotted on SD/Xgal/GalRaf/-4aa plates and grown for 2 days at 30°C. As for endopilin 1, neither the cytoplasmic tails of VGLUT2 or VGLUT3 interact with endophilin 3. Note that endophilin 3–VGLUT1 interaction is also mediated by the Pro2 domain of VGLUT1, as mutation of proline residues in this domain to alanine result in the loss of the blue coloration. Loss of the Pro1 domain or the VGLUT conserved regions (SEEK or SYGAT) do not affect VGLUT1 association with endophilin 3.
Fig. 4.
VGLUT1 colocalizes with both endophilin 1 and endophilin 3 in differentiated neocortical neurons in culture. Single Z planes of deconvolved (constrain iterative) images are shown (magnification 100×). Upper panel: all VGLUT1 terminals (red) also express endophilin 1 (green). Lower panel: VGLUT1 (red) is colocalized with endophilin 3 (green) in all VGLUT1 positive synapses. Scale bar: 10 μm
Similar articles
- Interaction between the vesicular glutamate transporter type 1 and endophilin A1, a protein essential for endocytosis.
Vinatier J, Herzog E, Plamont MA, Wojcik SM, Schmidt A, Brose N, Daviet L, El Mestikawy S, Giros B. Vinatier J, et al. J Neurochem. 2006 May;97(4):1111-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03821.x. Epub 2006 Apr 5. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16606361 - Heterogeneity of glutamatergic and GABAergic release machinery in cerebral cortex: analysis of synaptogyrin, vesicle-associated membrane protein, and syntaxin.
Bragina L, Giovedì S, Barbaresi P, Benfenati F, Conti F. Bragina L, et al. Neuroscience. 2010 Feb 3;165(3):934-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.11.009. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 19909789 - Homeostatic scaling of vesicular glutamate and GABA transporter expression in rat neocortical circuits.
De Gois S, Schäfer MK, Defamie N, Chen C, Ricci A, Weihe E, Varoqui H, Erickson JD. De Gois S, et al. J Neurosci. 2005 Aug 3;25(31):7121-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5221-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16079394 Free PMC article. - Activity-dependent regulation of vesicular glutamate and GABA transporters: a means to scale quantal size.
Erickson JD, De Gois S, Varoqui H, Schafer MK, Weihe E. Erickson JD, et al. Neurochem Int. 2006 May-Jun;48(6-7):643-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2005.12.029. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Neurochem Int. 2006. PMID: 16546297 Review. - Complementary distribution of vesicular glutamate transporters in the central nervous system.
Kaneko T, Fujiyama F. Kaneko T, et al. Neurosci Res. 2002 Apr;42(4):243-50. doi: 10.1016/s0168-0102(02)00009-3. Neurosci Res. 2002. PMID: 11985876 Review.
Cited by
- Stoned B mediates sorting of integral synaptic vesicle proteins.
Mohrmann R, Matthies HJ, Woodruff E 3rd, Broadie K. Mohrmann R, et al. Neuroscience. 2008 Jun 2;153(4):1048-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.02.060. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18436388 Free PMC article. - Functional roles of short sequence motifs in the endocytosis of membrane receptors.
Pandey KN. Pandey KN. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jun 1;14(14):5339-60. doi: 10.2741/3599. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19482617 Free PMC article. Review. - Neurotransmitter corelease: mechanism and physiological role.
Hnasko TS, Edwards RH. Hnasko TS, et al. Annu Rev Physiol. 2012;74:225-43. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-020911-153315. Epub 2011 Oct 31. Annu Rev Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22054239 Free PMC article. Review. - Deep molecular diversity of mammalian synapses: why it matters and how to measure it.
O'Rourke NA, Weiler NC, Micheva KD, Smith SJ. O'Rourke NA, et al. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 May 10;13(6):365-79. doi: 10.1038/nrn3170. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22573027 Free PMC article. Review. - Molecular, Structural, Functional, and Pharmacological Sites for Vesicular Glutamate Transporter Regulation.
Pietrancosta N, Djibo M, Daumas S, El Mestikawy S, Erickson JD. Pietrancosta N, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Jul;57(7):3118-3142. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-01912-7. Epub 2020 May 30. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32474835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Barbosa, J., Jr., Ferreira, L. T., Martins-Silva, C., Santos, M. S., Torres, G. E., Caron, M. G., Gomez, M. V., Ferguson, S. S., Prado, M. A., and Prado, V. F. (2002). Trafficking of the vesicular acetylcholine transporter in SN56 cells: A dynamin-sensitive step and interaction with the AP-2 adaptor complex. J. Neurochem.82:1221–1228. - PubMed
- Brewer, G. J., Torricelli, J. B., Evege, E. K., and Price, P. J. (1993). Optimized survival of hippocampal neurons in B7-supplemted Neurobasal, a new serum-free medium combination. J. Neurosci. Res.35:567–576. - PubMed
- Cesareni, G., Panni, S., Nardelli, G., and Castagnoli, L. (2002). Can we infer peptide recognition specificity mediated by SH3 domains? FEBS Lett. 513:38–44. - PubMed
- Cestra, G., Castagnoli, L., Dente, L., Minenkova, O., Petrelli, A., Migone, N., Hoffmuller, U., Schneider-Mergener, J., and Cesareni, G. (1999). The SH3 domains of endophilin and amphiphysin bind to the proline-rich region of synaptojanin 1 at distinct sites that display an unconventional binding specificity. J. Biol. Chem.274:32001–32007. - PubMed
- Chen, Y., Deng, L., Maeno-Hikichi, Y., Lai, M., Chang, S., Chen, G., and Zhang, J. F. (2003). Formation of an endophilin-Ca2+ channel complex is critical for clathrin-mediated synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Cell115:37–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous