Distinct expression profiles of TGF-beta1 signaling mediators in pathogenic SIVmac and non-pathogenic SIVagm infections - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Distinct expression profiles of TGF-beta1 signaling mediators in pathogenic SIVmac and non-pathogenic SIVagm infections
Mickaël J-Y Ploquin et al. Retrovirology. 2006.
Abstract
Background: The generalized T-cell activation characterizing HIV-1 and SIVmac infections in humans and macaques (MACs) is not found in the non-pathogenic SIVagm infection in African green monkeys (AGMs). We have previously shown that TGF-beta1, Foxp3 and IL-10 are induced very early after SIVagm infection. In SIVmac-infected MACs, plasma TGF-beta1 induction persists during primary infection 1. We raised the hypothesis that MACs are unable to respond to TGF-beta1 and thus cannot resorb virus-driven inflammation. We therefore compared the very early expression dynamics of pro- and anti-inflammatory markers as well as of factors involved in the TGF-beta1 signaling pathway in SIV-infected AGMs and MACs.
Methods: Levels of transcripts encoding for pro- and anti-inflammatory markers (tnf-alpha, ifn-gamma, il-10, t-bet, gata-3) as well as for TGF-beta1 signaling mediators (smad3, smad4, smad7) were followed by real time PCR in a prospective study enrolling 6 AGMs and 6 MACs.
Results: During primary SIVmac infection, up-regulations of tnf-alpha, ifn-gamma and t-bet responses (days 1-16 p.i.) were stronger whereas il-10 response was delayed (4th week p.i.) compared to SIVagm infection. Up-regulation of smad7 (days 3-8 p.i.), a cellular mediator inhibiting the TGF-beta1 signaling cascade, characterized SIV-infected MACs. In AGMs, we found increases of gata-3 but not t-bet, a longer lasting up-regulation of smad4 (days 1-21 p.i), a mediator enhancing TGF-beta1 signaling, and no smad7 up-regulations.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that the inability to resorb virus-driven inflammation and activation during the pathogenic HIV-1/SIVmac infections is associated with an unresponsiveness to TGF-beta1.
Figures
Figure 1
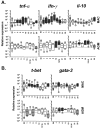
Dynamics of pro- and anti-inflammatory markers in PBMC during pathogenic and non-pathogenic SIV infections. A. Tnf-α, ifn-γ and il-10 expressions. B. T-bet and gata-3 expressions. Upper and lower panels represent data from 6 SIVmac-infected rhesus MACs and from 6 SIVagm-infected AGMs, respectively. Relative transcript levels are represented by box plots in a log scale. BI indicates the baseline before infection (n = 42 corresponding to 7 time points for each of the 6 animals) and the following boxes present the gene expression after infection (n = 6 per box). The top and the bottom of the boxes represent the 75th and 25th percentiles, respectively, whereas the horizontal line between the box limits represent the median. Open circles indicate individual values which are not included between the 90th and 10th percentiles. Dark and light grey boxes indicate significant (p < 0.05) increases and decreases, respectively, relative to the baseline. Stars indicate a trend towards significant up-regulation (p < 0.08). The data on AGMs (tnf-α, ifn-γ and il-10) were previously published [1]. The latter are displayed here in a log scale to allow easy and direct comparisons with the data obtained for the pathogenic SIVmac infection.
Figure 2
Dynamics of smad3, smad4 and smad7 expressions in PBMC during pathogenic and non-pathogenic SIV infections. See legend in Figure 1.
Similar articles
- Antiinflammatory profiles during primary SIV infection in African green monkeys are associated with protection against AIDS.
Kornfeld C, Ploquin MJ, Pandrea I, Faye A, Onanga R, Apetrei C, Poaty-Mavoungou V, Rouquet P, Estaquier J, Mortara L, Desoutter JF, Butor C, Le Grand R, Roques P, Simon F, Barré-Sinoussi F, Diop OM, Müller-Trutwin MC. Kornfeld C, et al. J Clin Invest. 2005 Apr;115(4):1082-91. doi: 10.1172/JCI23006. Epub 2005 Mar 10. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15761496 Free PMC article. - Modulation of type I interferon-associated viral sensing during acute simian immunodeficiency virus infection in African green monkeys.
Jochems SP, Petitjean G, Kunkel D, Liovat AS, Ploquin MJ, Barré-Sinoussi F, Lebon P, Jacquelin B, Müller-Trutwin MC. Jochems SP, et al. J Virol. 2015 Jan;89(1):751-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02430-14. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25355871 Free PMC article. - Innate immune responses and rapid control of inflammation in African green monkeys treated or not with interferon-alpha during primary SIVagm infection.
Jacquelin B, Petitjean G, Kunkel D, Liovat AS, Jochems SP, Rogers KA, Ploquin MJ, Madec Y, Barré-Sinoussi F, Dereuddre-Bosquet N, Lebon P, Le Grand R, Villinger F, Müller-Trutwin M. Jacquelin B, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jul 3;10(7):e1004241. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004241. eCollection 2014 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24991927 Free PMC article. - SIVagm: genetic and biological features associated with replication.
Müller MC, Barré-Sinoussi F. Müller MC, et al. Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:d1170-85. doi: 10.2741/1130. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12957815 Review. - SIVagm infection of its natural African green monkey host.
Norley SG. Norley SG. Immunol Lett. 1996 Jun;51(1-2):53-8. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(96)02555-2. Immunol Lett. 1996. PMID: 8811345 Review.
Cited by
- Regulation of the Immune Response by TGF-β: From Conception to Autoimmunity and Infection.
Sanjabi S, Oh SA, Li MO. Sanjabi S, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 Jun 1;9(6):a022236. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022236. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017. PMID: 28108486 Free PMC article. Review. - T regulatory cells: aid or hindrance in the clearance of disease?
Coleman CA, Muller-Trutwin MC, Apetrei C, Pandrea I. Coleman CA, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2007 Nov-Dec;11(6):1291-325. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00087.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 18205702 Free PMC article. Review. - Functional genomics analyses of differential macaque peripheral blood mononuclear cell infections by human immunodeficiency virus-1 and simian immunodeficiency virus.
Li Y, Chan EY, Katze MG. Li Y, et al. Virology. 2007 Sep 15;366(1):137-49. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.04.020. Epub 2007 May 15. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17507074 Free PMC article. - Nonpathogenic SIV infection of African green monkeys induces a strong but rapidly controlled type I IFN response.
Jacquelin B, Mayau V, Targat B, Liovat AS, Kunkel D, Petitjean G, Dillies MA, Roques P, Butor C, Silvestri G, Giavedoni LD, Lebon P, Barré-Sinoussi F, Benecke A, Müller-Trutwin MC. Jacquelin B, et al. J Clin Invest. 2009 Dec;119(12):3544-55. doi: 10.1172/JCI40093. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19959873 Free PMC article. - Plasmacytoid dendritic cell dynamics and alpha interferon production during Simian immunodeficiency virus infection with a nonpathogenic outcome.
Diop OM, Ploquin MJ, Mortara L, Faye A, Jacquelin B, Kunkel D, Lebon P, Butor C, Hosmalin A, Barré-Sinoussi F, Müller-Trutwin MC. Diop OM, et al. J Virol. 2008 Jun;82(11):5145-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02433-07. Epub 2008 Apr 2. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18385227 Free PMC article.
References
- Kornfeld C, Ploquin MJ, Pandrea I, Faye A, Onanga R, Apetrei C, Poaty-Mavoungou V, Rouquet P, Estaquier J, Mortara L, Desoutter JF, Butor C, Le Grand R, Roques P, Simon F, Barre-Sinoussi F, Diop OM, Muller-Trutwin MC. Antiinflammatory profiles during primary SIV infection in African green monkeys are associated with protection against AIDS. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1082–1091. doi: 10.1172/JCI200523006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Sousa AE, Carneiro J, Meier-Schellersheim M, Grossman Z, Victorino RM. CD4 T cell depletion is linked directly to immune activation in the pathogenesis of HIV-1 and HIV-2 but only indirectly to the viral load. J Immunol. 2002;169:3400–3406. - PubMed
- Deeks SG, Kitchen CM, Liu L, Guo H, Gascon R, Narvaez AB, Hunt P, Martin JN, Kahn JO, Levy J, McGrath MS, Hecht FM. Immune activation set point during early HIV infection predicts subsequent CD4+ T-cell changes independent of viral load. Blood. 2004;104:942–7. Epub 2004 Apr 29.. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-09-3333. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous