Human cerebrospinal fluid contains CD4+ memory T cells expressing gut- or skin-specific trafficking determinants: relevance for immunotherapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Human cerebrospinal fluid contains CD4+ memory T cells expressing gut- or skin-specific trafficking determinants: relevance for immunotherapy
Pia Kivisäkk et al. BMC Immunol. 2006.
Abstract
Background: Circulating memory T cells can be divided into tissue-specific subsets, which traffic through distinct tissue compartments during physiologic immune surveillance, based on their expression of adhesion molecules and chemokine receptors. We reasoned that a bias (either enrichment or depletion) of CSF T cell expression of known organ-specific trafficking determinants might suggest that homing of T cells to the subarachnoid space could be governed by a CNS-specific adhesion molecule or chemokine receptor.
Results: The expression of cutaneous leukocyte antigen (CLA) and CC-chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4; associated with skin-homing) as well as the expression of integrin alpha4beta7 and CCR9 (associated with gut-homing) was analyzed on CD4+ memory T cells in CSF from individuals with non-inflammatory neurological diseases using flow cytometry. CSF contained similar proportions of CD4+ memory T cells expressing CLA, CCR4, integrin alpha4beta7 and CCR9 as paired blood samples.
Conclusion: The results extend our previous findings that antigen-experienced CD4+ memory T cells traffic through the CSF in proportion to their abundance in the peripheral circulation. Furthermore, the ready access of skin- and gut-homing CD4+ memory T cells to the CNS compartment via CSF has implications for the mechanisms of action of immunotherapeutic strategies, such as oral tolerance or therapeutic immunization, where immunogens are administered using an oral or subcutaneous route.
Figures
Figure 1
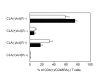
The majority of CD4+/CD45RA- memory T cells in the CSF (black bars) were CLA-/α4β7-, but discrete populations of CLA+ (associated with skin-homing) and integrin α4β7+ (associated with gut-homing) cells were observed. The expression pattern of CLA and integrin α4β7 was comparable on CD4+/CD45RA- memory T cells in peripheral blood (white bars) and CSF (black bars). Data are from four patients with non-inflammatory neurological diseases and figure shows mean+SEM.
Figure 2
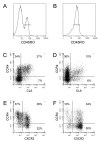
Multi-color flow cytometry was used to analyze the co-expression of CCR4 with CLA or CXCR3 on memory T cells in paired blood and CSF samples from an individual patient with a non-inflammatory neurological disease (A-D) or MS (E-F). The expression of trafficking determinants was analyzed on CD4+/CD45RO+ memory T cells to account for the different percentages of naïve and memory CD4+ cells in blood (A) and CSF (B). As expected, there was an association between the expression of CCR4 and CLA on CD4+/CD45RO+ T cells in peripheral blood (C). A majority of CLA+ memory T cells co-expressed CCR4 also in the CSF, but some CCR4 staining could be detected on CLA- memory T cells (D). While a large population of CCR4+/CXCR3- cells, which have been demonstrated to be enriched for Th2 cells [27], were present in peripheral blood (E), such cells were rare in the CSF (F).
Figure 3
Flow cytometry was used to determine the expression of CCR9 and integrin β7, associated with homing to the gut, on CD4+/CD45RA- memory T cells in paired blood and CSF samples from patients with non-inflammatory neurological diseases. Memory T cells expressing CCR9 and integrin β7 were detected at comparable numbers in blood (A) and CSF (B), indicating that gut-homing memory T cells readily access the CNS.
Similar articles
- Skin-versus gut-skewed homing receptor expression and intrinsic CCR4 expression on human peripheral blood CD4+CD25+ suppressor T cells.
Iellem A, Colantonio L, D'Ambrosio D. Iellem A, et al. Eur J Immunol. 2003 Jun;33(6):1488-96. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323658. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12778466 - Human cerebrospinal fluid central memory CD4+ T cells: evidence for trafficking through choroid plexus and meninges via P-selectin.
Kivisäkk P, Mahad DJ, Callahan MK, Trebst C, Tucky B, Wei T, Wu L, Baekkevold ES, Lassmann H, Staugaitis SM, Campbell JJ, Ransohoff RM. Kivisäkk P, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 8;100(14):8389-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1433000100. Epub 2003 Jun 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12829791 Free PMC article. - Circulating clonal CLA(+) and CD4(+) T cells in Sezary syndrome express the skin-homing chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR10 as well as the lymph node-homing chemokine receptor CCR7.
Sokolowska-Wojdylo M, Wenzel J, Gaffal E, Lenz J, Speuser P, Erdmann S, Abuzahra F, Bowman E, Roszkiewicz J, Bieber T, Tüting T. Sokolowska-Wojdylo M, et al. Br J Dermatol. 2005 Feb;152(2):258-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06325.x. Br J Dermatol. 2005. PMID: 15727636 - T lymphocytes in food allergy: overview of an intricate network of circulating and organ-resident cells.
Eigenmann PA. Eigenmann PA. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2002 Jun;13(3):162-71. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3038.2002.01015.x. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12144637 Review. - Human endothelial cell presentation of antigen and the homing of memory/effector T cells to skin.
Pober JS, Kluger MS, Schechner JS. Pober JS, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Sep;941:12-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03706.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11594565 Review.
Cited by
- Translational Mini-Review Series on Vaccines for HIV: T lymphocyte trafficking and vaccine-elicited mucosal immunity.
Kaufman DR, Barouch DH. Kaufman DR, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 Aug;157(2):165-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03927.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19604255 Free PMC article. Review. - Alzheimer's Disease: From Immune Homeostasis to Neuroinflammatory Condition.
Princiotta Cariddi L, Mauri M, Cosentino M, Versino M, Marino F. Princiotta Cariddi L, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13008. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113008. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361799 Free PMC article. Review. - Association of Brain Metastases With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Efficacy in Advanced Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Wang Y, Zhang Q, Chen C, Hu Y, Miao L, Zhou Y. Wang Y, et al. Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 8;11:721760. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.721760. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34956860 Free PMC article. - Nanowire array chips for molecular typing of rare trafficking leukocytes with application to neurodegenerative pathology.
Kwak M, Kim DJ, Lee MR, Wu Y, Han L, Lee SK, Fan R. Kwak M, et al. Nanoscale. 2014 Jun 21;6(12):6537-50. doi: 10.1039/c3nr06465d. Nanoscale. 2014. PMID: 24705924 Free PMC article. - An immunohistochemical study of lymphatic elements in the human brain.
Mezey É, Szalayova I, Hogden CT, Brady A, Dósa Á, Sótonyi P, Palkovits M. Mezey É, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 19;118(3):e2002574118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2002574118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33446503 Free PMC article.
References
- Butcher EC, Williams M, Youngman K, Rott L, Briskin M. Lymphocyte trafficking and regional immunity. Adv Immunol. 1999;72:209–253. - PubMed
- Rott LS, Briskin MJ, Andrew DP, Berg EL, Butcher EC. A fundamental subdivision of circulating lymphocytes defined by adhesion to mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1. Comparison with vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and correlation with beta 7 integrins and memory differentiation. J Immunol. 1996;156:3727–3736. - PubMed
- Tietz W, Allemand Y, Borges E, von Laer D, Hallmann R, Vestweber D, Hamann A. CD4+ T cells migrate into inflamed skin only if they express ligands for E- and P-selectin. J Immunol. 1998;161:963–970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials