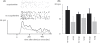A novel electrode-pipette design for simultaneous recording of extracellular spikes and iontophoretic drug application in awake behaving monkeys - PubMed (original) (raw)
A novel electrode-pipette design for simultaneous recording of extracellular spikes and iontophoretic drug application in awake behaving monkeys
A Thiele et al. J Neurosci Methods. 2006.
Abstract
We developed a novel design of an electrode-pipette combination (EPC) which allows access to brain structures in awake behaving primates without the need for guide tubes or to mechanically open the dura prior to electrode insertion. The EPC consists of an etched tungsten in glass electrode flanked by two pipettes which allow for local and highly controlled iontophoretic administration of neuroactive substances. These EPCs have excellent single cell isolation properties and are sturdy enough to penetrate the primate dura for up to 8 weeks following either a craniotomy or a dura scrape (i.e. even after substantial built up of fibrous scar tissue). We show that the EPCs can be used to selectively manipulate the cholinergic system in primate V1 during passive fixation and while animals perform an attentionally demanding task.
Figures
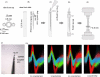
Fig. 1
Manufacture and photograph of standard electrode–pipette combination, and spike isolation. (A) Shape of glass barrels. (B)–(D) Sketches of electrode–pipette manufacture. (E) Electrode–pipette combination following placement in the Narishige PE-21 puller, prior to pulling. (F) Photograph of electrode–pipette combination after pulling and grinding. The central sharpened tungsten in glass wire is flanked by two pipettes. Following the pulling process the tungsten wire and the pipettes are ground to form a conical shape, thereby opening the pipettes and sharpening the tip to allow for passage of the dura during chronic recordings in awake behaving monkeys. (G) Waveforms of isolated spikes from a recording session during which scopolamine was applied. During this session two single units (red and green) and one multi unit (blue) were distinguishable.
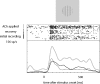
Fig. 2
Neuronal activity of a V1 neuron in the passively viewing monkey while ACh was not applied (black curves) and while ACH was applied (grey curves). A stimulus of optimal size and orientation was presented for 500 ms. Back solid line: activity during the initial recording, grey solid line: activity during ACh application, black dashed line: activity following recovery from ACh application.
Fig. 3
(A) Reduction of activity in a V1 neuron upon scopolamine application. (B) Three repetitions of the pattern: neuronal activity recorded without scopolamine application (−10 nA hold current, black curves), followed by scopolamine application (20 nA application current, grey curves) were performed, resulting in three interleaved sets of scopolamine not applied and scopolamine applied recordings. Black bars show mean and standard deviation of the activity during stimulus presentation (500 ms) in the absence of scopolamine application, gray bars the activity in the presence of scopolamine application. Each repetition contained 10 trials.
Similar articles
- A technique for microiontophoretic study of single neurones in the behaving monkey.
Perrett DI, Rolls ET. Perrett DI, et al. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Feb;12(4):289-95. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90013-5. J Neurosci Methods. 1985. PMID: 3921775 - Multibarreled glass-coated tungsten microelectrode for both neuronal activity recording and iontophoresis in monkeys.
Li BM, Mei ZT, Kubota K. Li BM, et al. Neurosci Res. 1990 Jul;8(3):214-9. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(90)90023-8. Neurosci Res. 1990. PMID: 2170880 - Simultaneous multi-site recordings and iontophoretic drug and dye applications along the trigeminal system of anesthetized rats.
Haidarliu S, Sosnik R, Ahissar E. Haidarliu S, et al. J Neurosci Methods. 1999 Dec 15;94(1):27-40. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0270(99)00123-5. J Neurosci Methods. 1999. PMID: 10638813 - A review of patent literature for iontophoretic delivery and devices.
Kasha PC, Banga AK. Kasha PC, et al. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2008;2(1):41-50. doi: 10.2174/187221108783331438. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2008. PMID: 19075896 Review. - Multiple single unit recording in the cortex of monkeys using independently moveable microelectrodes.
Baker SN, Philbin N, Spinks R, Pinches EM, Wolpert DM, MacManus DG, Pauluis Q, Lemon RN. Baker SN, et al. J Neurosci Methods. 1999 Dec 15;94(1):5-17. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0270(99)00121-1. J Neurosci Methods. 1999. PMID: 10638811 Review.
Cited by
- Segregated cholinergic transmission modulates dopamine neurons integrated in distinct functional circuits.
Dautan D, Souza AS, Huerta-Ocampo I, Valencia M, Assous M, Witten IB, Deisseroth K, Tepper JM, Bolam JP, Gerdjikov TV, Mena-Segovia J. Dautan D, et al. Nat Neurosci. 2016 Aug;19(8):1025-33. doi: 10.1038/nn.4335. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27348215 Free PMC article. - Attention and normalization circuits in macaque V1.
Sanayei M, Herrero JL, Distler C, Thiele A. Sanayei M, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2015 Apr;41(7):949-64. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12857. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Eur J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25757941 Free PMC article. - Stimulus-induced dissociation of neuronal firing rates and local field potential gamma power and its relationship to the resonance blood oxygen level-dependent signal in macaque primary visual cortex.
Bartolo MJ, Gieselmann MA, Vuksanovic V, Hunter D, Sun L, Chen X, Delicato LS, Thiele A. Bartolo MJ, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Dec;34(11):1857-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07877.x. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22081989 Free PMC article. - Merging functional and structural properties of the monkey auditory cortex.
Joly O, Baumann S, Balezeau F, Thiele A, Griffiths TD. Joly O, et al. Front Neurosci. 2014 Jul 21;8:198. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00198. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25100930 Free PMC article. - Distinct feedforward and feedback pathways for cell-type specific attention effects.
Spyropoulos G, Schneider M, van Kempen J, Gieselmann MA, Thiele A, Vinck M. Spyropoulos G, et al. Neuron. 2024 Jul 17;112(14):2423-2434.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.04.020. Epub 2024 May 16. Neuron. 2024. PMID: 38759641 Free PMC article.
References
- Davidson M.C., Marrocco R.T. Local infusion of scopolamine into intraparietal cortex slows covert orienting in rhesus monkeys. J Neurophysiol. 2000;83:1536–1549. - PubMed
- Everitt B.J., Robbins T.W. Central cholinergic systems and cognition. Annu Rev Psychol. 1997;48:649–684. - PubMed
- Haidarliu S., Shulz D., Ahissar E. A multi-electrode array for combined microiontophoresis and multiple single-unit recordings. J Neurosci Meth. 1995;56:125–131. - PubMed
- Hasselmo M.E., Linster C., Patil M., Ma D., Cekic M. Noradrenergic suppression of synaptic transmission may influence cortical signal-to-noise ratio. J Neurophysiol. 1997;77:3326–3339. - PubMed
- Patil M.M., Linster C., Lubenov E., Hasselmo M.E. Cholinergic agonist carbachol enables associative long-term potentiation in piriform cortex slices. J Neurophysiol. 1998;80:2467–2474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 070380/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BBS/B/09325/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 070380/Z/03/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical