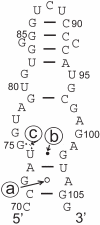CorreLogo: an online server for 3D sequence logos of RNA and DNA alignments - PubMed (original) (raw)
CorreLogo: an online server for 3D sequence logos of RNA and DNA alignments
Eckart Bindewald et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006.
Abstract
We present an online server that generates a 3D representation of properties of user-submitted RNA or DNA alignments. The visualized properties are information of single alignment columns, mutual information of two alignment positions as well as the position-specific fraction of gaps. The nucleotide composition of both single columns and column pairs is visualized with the help of color-coded 3D bars labeled with letters. The server generates both VRML and JVX output that can be viewed with a VRML viewer or the JavaView applet, respectively. We show that combining these different features of an alignment into one 3D representation is helpful in identifying correlations between bases and potential RNA and DNA base pairs. Significant known correlations between the tRNA 3' anticodon cardinal nucleotide and the extended anticodon were observed, as were correlations within the amino acid acceptor stem and between the cardinal nucleotide and the acceptor stem. The online server can be accessed using the URL http://correlogo.abcc.ncifcrf.gov.
Figures
Figure 1
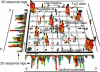
An annotated screenshot of the graphics output corresponding to an alignment of 1114 tRNA sequences showing 2D and 3D sequence logos. The 3D arrows point from the 5′ end to the 3′ end of the alignment. The labels ‘a’ to ‘e’ correspond to the base pairs G15:C48, G19:C56, C13:G46, G22:G46 and G18:G19, respectively. The black cubes correspond to base pairs in a reference consensus secondary structure. Only stacks corresponding to mutual information values Mij ≥ 0.01 bits and Mij ≥ 2 SDs are shown. The sequences correspond to the ‘seed’ alignment of RFAM entry RF00005, RFAM database version 7 (20,21). The consensus secondary structure provided by RFAM originated from (36).
Figure 2
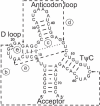
tRNA consensus secondary structure according to RFAM entry RF00005 (20,21,36) mapped onto the sequence of yeast (S.cerevisiae) Phe-tRNA (GenBank accession no. K01553.1). The correlations a, b, c, d and e (compare Figures 1 and 2) are indicated by dashed lines.
Figure 3
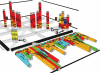
A 3D sequence logo of the loop E region of 5S ribosomal RNA [from RFAM entry RF00001 (20,21,35)]. Individual bars corresponding to base pairs are labeled in this view. The gray bars depict with their height the standard deviation of the estimated information in the 2D logos and the mutual information in the 3D logos. Stacks corresponding to mutual information values of <0.5 bits are not shown. The labels a–c correspond to pairs of positions that are not Watson–Crick base pairs and have a mutual information >0.5 bits.
Figure 4
A consensus secondary structure of the loop E region of 5S ribosomal RNA derived from the 3D sequence logo is shown in Figure 3. The consensus structure is mapped onto the loop E region of E.coli 5S rRNA sequence (AB03926.1/6056-6092). The labels a–c correspond to pairs of positions that are not Watson–Crick base pairs and have a mutual information >0.5 bits.
Similar articles
- The FOLDALIGN web server for pairwise structural RNA alignment and mutual motif search.
Havgaard JH, Lyngsø RB, Gorodkin J. Havgaard JH, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 1;33(Web Server issue):W650-3. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki473. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15980555 Free PMC article. - DIAL: a web server for the pairwise alignment of two RNA three-dimensional structures using nucleotide, dihedral angle and base-pairing similarities.
Ferrè F, Ponty Y, Lorenz WA, Clote P. Ferrè F, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W659-68. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm334. Epub 2007 Jun 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17567620 Free PMC article. - R3D-2-MSA: the RNA 3D structure-to-multiple sequence alignment server.
Cannone JJ, Sweeney BA, Petrov AI, Gutell RR, Zirbel CL, Leontis N. Cannone JJ, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 1;43(W1):W15-23. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv543. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26048960 Free PMC article. - MultiPipMaker: comparative alignment server for multiple DNA sequences.
Elnitski L, Riemer C, Burhans R, Hardison R, Miller W. Elnitski L, et al. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr;Chapter 10:Unit10.4. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1004s9. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 18428743 - The art of editing RNA structural alignments.
Andersen ES. Andersen ES. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1097:379-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-709-9_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24639168 Review.
Cited by
- ProfileGrids: a sequence alignment visualization paradigm that avoids the limitations of Sequence Logos.
Roca AI. Roca AI. BMC Proc. 2014 Aug 28;8(Suppl 2 Proceedings of the 3rd Annual Symposium on Biologica):S6. doi: 10.1186/1753-6561-8-S2-S6. eCollection 2014. BMC Proc. 2014. PMID: 25237393 Free PMC article. - CircularLogo: A lightweight web application to visualize intra-motif dependencies.
Ye Z, Ma T, Kalmbach MT, Dasari S, Kocher JA, Wang L. Ye Z, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 May 22;18(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1680-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28532394 Free PMC article. - CodonLogo: a sequence logo-based viewer for codon patterns.
Sharma V, Murphy DP, Provan G, Baranov PV. Sharma V, et al. Bioinformatics. 2012 Jul 15;28(14):1935-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts295. Epub 2012 May 17. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22595210 Free PMC article. - Computational detection of abundant long-range nucleotide covariation in Drosophila genomes.
Bindewald E, Shapiro BA. Bindewald E, et al. RNA. 2013 Sep;19(9):1171-82. doi: 10.1261/rna.037630.112. Epub 2013 Jul 25. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23887147 Free PMC article. - A brief review of molecular information theory.
Schneider TD. Schneider TD. Nano Commun Netw. 2010 Sep;1(3):173-180. doi: 10.1016/j.nancom.2010.09.002. Nano Commun Netw. 2010. PMID: 22110566 Free PMC article.
References
- Robison K., McGuire A.M., Church G.M. A comprehensive library of DNA-binding site matrices for 55 proteins applied to the complete Escherichia coli K-12 genome. J. Mol. Biol. 1998;284:241–254. - PubMed
- Stephens R.M., Schneider T.D. Features of spliceosome evolution and function inferred from an analysis of the information at human splice sites. J. Mol. Biol. 1992;228:1124–1136. - PubMed
- Rogan P.K., Svojanovsky S., Leeder J.S. Information theory-based analysis of CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A5 splicing mutations. Pharmacogenetics. 2003;13:207–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources