Pooled association genome scanning for alcohol dependence using 104,268 SNPs: validation and use to identify alcoholism vulnerability loci in unrelated individuals from the collaborative study on the genetics of alcoholism - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Pooled association genome scanning for alcohol dependence using 104,268 SNPs: validation and use to identify alcoholism vulnerability loci in unrelated individuals from the collaborative study on the genetics of alcoholism
Catherine Johnson et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2006.
Abstract
Association genome scanning can identify markers for the allelic variants that contribute to vulnerability to complex disorders, including alcohol dependence. To improve the power and feasibility of this approach, we report validation of "100k" microarray-based allelic frequency assessments in pooled DNA samples. We then use this approach with unrelated alcohol-dependent versus control individuals sampled from pedigrees collected by the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA). Allele frequency differences between alcohol-dependent and control individuals are assessed in quadruplicate at 104,268 autosomal SNPs in pooled samples. One hundred eighty-eight SNPs provide (1) the largest allele frequency differences between dependent versus control individuals; (2) t values >or= 3 for these differences; and (3) clustering, so that 51 relatively small chromosomal regions contain at least three SNPs that satisfy criteria 1 and 2 above (Monte Carlo P = 0.00034). These positive SNP clusters nominate interesting genes whose products are implicated in cellular signaling, gene regulation, development, "cell adhesion," and Mendelian disorders. The results converge with linkage and association results for alcohol and other addictive phenotypes. The data support polygenic contributions to vulnerability to alcohol dependence. These SNPs provide new tools to aid the understanding, prevention, and treatment of alcohol abuse and dependence.
(c) 2006 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
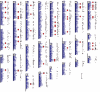
Figure 1
Main axes: Abuser/control ratios to the chromosomal position of each SNP for COGA alcohol dependent and control individuals. The positions of the SNPs whose data yield outlier abuser/control values are indicated by larger symbols. Supplementary axis (right of main axis): SNPs for which abuser/control differences display t values ≥ 3. Red dots designate clustered positive SNPs that display outlier abuser/control and t values. Scale: chromosomal positions based on NCBI Map Viewer coordinates and supplemental data from NETAFFYX. The vertical bar represents 25 MB.
Similar articles
- Genomic regions identified by overlapping clusters of nominally-positive SNPs from genome-wide studies of alcohol and illegal substance dependence.
Johnson C, Drgon T, Walther D, Uhl GR. Johnson C, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e19210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019210. Epub 2011 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21818250 Free PMC article. - Pooled association genome scanning: validation and use to identify addiction vulnerability loci in two samples.
Liu QR, Drgon T, Walther D, Johnson C, Poleskaya O, Hess J, Uhl GR. Liu QR, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 16;102(33):11864-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500329102. Epub 2005 Aug 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16091475 Free PMC article. - Genome scan linkage analysis comparing microsatellites and single-nucleotide polymorphisms markers for two measures of alcoholism in chromosomes 1, 4, and 7.
Chen G, Adeyemo A, Zhou J, Yuan A, Chen Y, Rotimi C. Chen G, et al. BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S4. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451650 Free PMC article. - Molecular genetics of substance abuse vulnerability: remarkable recent convergence of genome scan results.
Uhl GR. Uhl GR. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Oct;1025:1-13. doi: 10.1196/annals.1316.001. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15542694 Review. - 5. Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism: Functional genomics.
Gameiro-Ros I, Popova D, Prytkova I, Pang ZP, Liu Y, Dick D, Bucholz KK, Agrawal A, Porjesz B, Goate AM, Xuei X, Kamarajan C; COGA Collaborators; Tischfield JA, Edenberg HJ, Slesinger PA, Hart RP. Gameiro-Ros I, et al. Genes Brain Behav. 2023 Oct;22(5):e12855. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12855. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Genes Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37533187 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Genome-wide association study of d-amphetamine response in healthy volunteers identifies putative associations, including cadherin 13 (CDH13).
Hart AB, Engelhardt BE, Wardle MC, Sokoloff G, Stephens M, de Wit H, Palmer AA. Hart AB, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42646. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042646. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952603 Free PMC article. - Utility of the pooling approach as applied to whole genome association scans with high-density Affymetrix microarrays.
Schosser A, Pirlo K, Gaysina D, Cohen-Woods S, Schalkwyk LC, Elkin A, Korszun A, Gunasinghe C, Gray J, Jones L, Meaburn E, Farmer AE, Craig IW, McGuffin P. Schosser A, et al. BMC Res Notes. 2010 Nov 1;3:274. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-3-274. BMC Res Notes. 2010. PMID: 21040578 Free PMC article. - XRCC5 as a risk gene for alcohol dependence: evidence from a genome-wide gene-set-based analysis and follow-up studies in Drosophila and humans.
Juraeva D, Treutlein J, Scholz H, Frank J, Degenhardt F, Cichon S, Ridinger M, Mattheisen M, Witt SH, Lang M, Sommer WH, Hoffmann P, Herms S, Wodarz N, Soyka M, Zill P, Maier W, Jünger E, Gaebel W, Dahmen N, Scherbaum N, Schmäl C, Steffens M, Lucae S, Ising M, Smolka MN, Zimmermann US, Müller-Myhsok B, Nöthen MM, Mann K, Kiefer F, Spanagel R, Brors B, Rietschel M. Juraeva D, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Jan;40(2):361-71. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.178. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25035082 Free PMC article. - Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Alcohol Consumption Across Youth and Early Adulthood.
Adkins DE, Clark SL, Copeland WE, Kennedy M, Conway K, Angold A, Maes H, Liu Y, Kumar G, Erkanli A, Patkar AA, Silberg J, Brown TH, Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ, Eaves L, van den Oord EJ, Sullivan PF, Costello EJ. Adkins DE, et al. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2015 Aug;18(4):335-47. doi: 10.1017/thg.2015.36. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 26081443 Free PMC article. - Molecular genetics of addiction vulnerability.
Uhl GR. Uhl GR. NeuroRx. 2006 Jul;3(3):295-301. doi: 10.1016/j.nurx.2006.05.006. NeuroRx. 2006. PMID: 16815213 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bansal A. Trends in reporting of SNP associations. Lancet. 2001;358(9298):2016. - PubMed
- Butcher LM, Meaburn E, Liu L, Fernandes C, Hill L, Al-Chalabi A, Plomin R, Schalkwyk L, Craig IW. Genotyping pooled DNA on microarrays: a systematic genome screen of thousands of SNPs in large samples to detect QTLs for complex traits. Behav Genet. 2004;34(5):549–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U10AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DA000401/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401-19/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DA000401-10/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases