Interleukin-6: discovery of a pleiotropic cytokine - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2006;8 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S2.
doi: 10.1186/ar1916. Epub 2006 Jul 28.
Affiliations
- PMID: 16899106
- PMCID: PMC3226075
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1916
Review
Interleukin-6: discovery of a pleiotropic cytokine
Tadamitsu Kishimoto. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006.
Abstract
In the late 1960s, the essential role played by T cells in antibody production was reported. This led to our hypothesis that certain molecules would have to be released from T cells to effect the stimulation of B cells. This hypothesis was shown to be true. There were certain factors present in the culture supernatant of T cells that induced proliferation and differentiation of B cells. The factor that induced B cells to produce immunoglobulins was initially named B cell stimulatory factor-2. The cDNA encoding the human B cell stimulatory factor-2 was cloned in 1986. At the same time, IFN-beta2 and a 26 kDa protein in the fibroblasts were independently cloned and found to be identical to B cell stimulatory factor-2. Later, a hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor and a hepatocyte stimulating factor were also proven to be the same molecule as B cell stimulatory factor-2. Various names were used for this single molecule because of its multiple biological activities, but these have all been unified and the molecule is now known as IL-6. Since the discovery of IL-6, rapid progress has been made in our understanding of IL-6 activities, the IL-6 receptor system and the IL-6 signal transduction mechanism. More importantly, it has been shown to be involved in a number of diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and Castleman's disease. When taking into account all the accumulated basic research on the various aspects of this molecule, it appeared that blocking the activity of IL-6 was a feasible, new therapeutic approach for chronic inflammatory diseases.
Figures
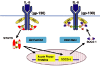
Figure 1
Feedback regulation in IL-6 signaling by SOCS. IL, interleukin; IL-6R, interleukin-6 receptor; JAK, Janus activated kinase; SOCS, suppressors of cytokine signaling; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.
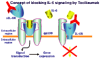
Figure 2
Blockade of IL-6 signals by anti-IL-6 receptor antibody (MRA, Tocilizumab). h, human; IL, interleukin; sIL-6R, soluble interleukin-6 receptor.
Similar articles
- IL-6: from its discovery to clinical applications.
Kishimoto T. Kishimoto T. Int Immunol. 2010 May;22(5):347-52. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxq030. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Int Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20410258 Review. - IL-6: from laboratory to bedside.
Kishimoto T. Kishimoto T. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2005 Jun;28(3):177-86. doi: 10.1385/CRIAI:28:3:177. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16129902 Review. - Inhibition of IL-6 for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T. Nishimoto N, et al. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004 Aug;4(4):386-91. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2004.03.005. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15251133 Review. - Interleukin 6: from bench to bedside.
Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T. Nishimoto N, et al. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006 Nov;2(11):619-26. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum0338. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 17075601 Review. - Immunotherapeutic implication of IL-6 blockade.
Tanaka T, Kishimoto T. Tanaka T, et al. Immunotherapy. 2012 Jan;4(1):87-105. doi: 10.2217/imt.11.147. Immunotherapy. 2012. PMID: 22150003 Review.
Cited by
- An interleukin 6-based genetic risk score strengthened with interleukin 10 polymorphisms associated with long-term kidney allograft outcomes.
Eskandari SK, Gaya da Costa M, Faria B, Petr V, Azzi JR, Berger SP, Seelen MAJ, Damman J, Poppelaars F. Eskandari SK, et al. Am J Transplant. 2022 Dec;22 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):45-57. doi: 10.1111/ajt.17212. Am J Transplant. 2022. PMID: 36453708 Free PMC article. - Plasma fetuin-A/α2-HS-glycoprotein correlates negatively with inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and activation biomarkers in individuals with type-2 diabetes.
Sindhu S, Akhter N, Shenouda S, Wilson A, Ahmad R. Sindhu S, et al. BMC Immunol. 2016 Sep 26;17(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12865-016-0171-y. BMC Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27671862 Free PMC article. - Effect of irradiation on the expression of E-cadherin and β-catenin in early and late radiation sequelae of the urinary bladder and its modulation by NF-κB inhibitor thalidomide.
Krischak A, Kowaliuk J, Sarsarshahi S, Dörr W, Kleiter M. Krischak A, et al. Strahlenther Onkol. 2021 Jun;197(6):537-546. doi: 10.1007/s00066-021-01751-y. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Strahlenther Onkol. 2021. PMID: 33688971 Free PMC article. - Combining TNFR2-Expressing Tregs and IL-6 as Superior Diagnostic Biomarkers for High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Masses.
Kampan NC, Kartikasari AER, Deceneux C, Madondo MT, McNally OM, Flanagan KL, Aziz NA, Stephens AN, Reynolds J, Quinn MA, Plebanski M. Kampan NC, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 21;15(3):667. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030667. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765633 Free PMC article. - Phospholipase D1 mediates TNFalpha-induced inflammation in a murine model of TNFalpha-induced peritonitis.
Sethu S, Pushparaj PN, Melendez AJ. Sethu S, et al. PLoS One. 2010 May 5;5(5):e10506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010506. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20463923 Free PMC article.
References
- Claman HN, Chaperon EA, Selner JC. Thymusmarrow immunocompetence. 3. The requirement for living thymus cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968;127:462–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical