The case of the misleading funnel plot - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The case of the misleading funnel plot
Joseph Lau et al. BMJ. 2006.
Abstract
Evidence based medicine insists on rigorous standards to appraise clinical interventions. Failure to apply the same rules to its own tools could be equally damaging
Figures
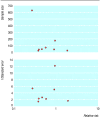
Fig 1
Effect of measure of precision (plotted on y axis) on appearance of funnel plots. Redrawn from Tang and Liu
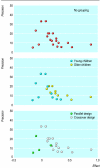
Fig 2
Effect of grouping of data on impression of funnel plot for meta-analysis of inhaled disodium cromoglicate that found significant heterogeneity
Similar articles
- Misleading funnel plot for detection of bias in meta-analysis.
Tang JL, Liu JL. Tang JL, et al. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000 May;53(5):477-84. doi: 10.1016/s0895-4356(99)00204-8. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000. PMID: 10812319 - Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials.
Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, Carpenter J, Rücker G, Harbord RM, Schmid CH, Tetzlaff J, Deeks JJ, Peters J, Macaskill P, Schwarzer G, Duval S, Altman DG, Moher D, Higgins JP. Sterne JA, et al. BMJ. 2011 Jul 22;343:d4002. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d4002. BMJ. 2011. PMID: 21784880 No abstract available. - In an empirical evaluation of the funnel plot, researchers could not visually identify publication bias.
Terrin N, Schmid CH, Lau J. Terrin N, et al. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005 Sep;58(9):894-901. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.01.006. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005. PMID: 16085192 - Advancing evidence-based practice through meta-analysis.
Cowan PA. Cowan PA. Nephrol Nurs J. 2004 May-Jun;31(3):343-4, 347. Nephrol Nurs J. 2004. PMID: 15303433 Review. No abstract available. - Development of the Veritas plot and its application in cardiac surgery: an evidence-synthesis graphic tool for the clinician to assess multiple meta-analyses reporting on a common outcome.
Panesar SS, Rao C, Vecht JA, Mirza SB, Netuveli G, Morris R, Rosenthal J, Darzi A, Athanasiou T. Panesar SS, et al. Can J Surg. 2009 Oct;52(5):E137-45. Can J Surg. 2009. PMID: 19865543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Prophylactic subcutaneous drainage reduces post-operative incisional infections in colorectal surgeries: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Pang K, Sun P, Li J, Zeng N, Yang X, Jin L, Yang Y, Jin L, Yao H, Zhang Z. Pang K, et al. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Aug;36(8):1633-1642. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03908-8. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021. PMID: 33723634 - A comparison of electronically-delivered and face to face cognitive behavioural therapies in depressive disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Luo C, Sanger N, Singhal N, Pattrick K, Shams I, Shahid H, Hoang P, Schmidt J, Lee J, Haber S, Puckering M, Buchanan N, Lee P, Ng K, Sun S, Kheyson S, Chung DC, Sanger S, Thabane L, Samaan Z. Luo C, et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Jun 27;24:100442. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100442. eCollection 2020 Jul. EClinicalMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32775969 Free PMC article. - EGFR gene copy number as a predictive biomarker for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer with anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies: a meta-analysis.
Yang ZY, Shen WX, Hu XF, Zheng DY, Wu XY, Huang YF, Chen JZ, Mao C, Tang JL. Yang ZY, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2012 Aug 16;5:52. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-5-52. J Hematol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22897982 Free PMC article. Review. - Birth weight in relation to health and disease in later life: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
Belbasis L, Savvidou MD, Kanu C, Evangelou E, Tzoulaki I. Belbasis L, et al. BMC Med. 2016 Sep 28;14(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12916-016-0692-5. BMC Med. 2016. PMID: 27677312 Free PMC article. - p53 codon 72 polymorphism and hematological cancer risk: an update meta-analysis.
Weng Y, Lu L, Yuan G, Guo J, Zhang Z, Xie X, Chen G, Zhang J. Weng Y, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045820. Epub 2012 Sep 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029260 Free PMC article.
References
- Light RJ, Pillemer DB. Summing up. The science of reviewing research. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1984.
- Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JPT, eds. Cochrane reviewers' handbook 4.2.2 [updated March 2004]. In: Cochrane Library, Issue 1. Chichester: Wiley, 2004.
- Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses. Lancet 1999;354: 1896-900. - PubMed
- Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000;283: 2008-12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical