Nucleoporin 88 expression in hepatitis B and C virus-related liver diseases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Nucleoporin 88 expression in hepatitis B and C virus-related liver diseases
Martina Knoess et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2006.
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the expression of nucleoporin 88 (Nup88) in hepatitis B virus (HBV) and C virus (HCV)-related liver diseases.
Methods: We generated a new monoclonal Nup88 antibody to investigate the Nup88 protein expression by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in 294 paraffin-embedded liver specimens comprising all stages of hepatocellular carcinogenesis. In addition, in cell culture experiments HBV-positive (HepG2.2.15 and HB611) and HBV-negative (HepG2) hepatoma cell lines were tested for the Nup88 expression by Western-immunoblotting to test data obtained by IHC.
Results: Specific Nup88 expression was found in chronic HCV hepatitis and unspecific chronic hepatitis, whereas no or very weak Nup88 expression was detected in normal liver. The Nup88 expression was markedly reduced or missing in mild chronic HBV infection and inversely correlated with HBcAg expression. Irrespective of the HBV- or HCV-status, increasing Nup88 expression was observed in cirrhosis and dysplastic nodules, and Nup88 was highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinomas. The intensity of Nup88 expression significantly increased during carcinogenesis (P<0.0001) and correlated with dedifferentiation (P<0.0001). Interestingly, Nup88 protein expression was significantly downregulated in HBV-positive HepG2.2.15 (P<0.002) and HB611 (P<0.001) cell lines as compared to HBV-negative HepG2 cells.
Conclusion: Based on our immunohistochemical data, HBV and HCV are unlikely to influence the expression of Nup88 in cirrhotic and neoplastic liver tissue, but point to an interaction of HBV with the nuclear pore in chronic hepatitis. The expression of Nup88 in nonneoplastic liver tissue might reflect enhanced metabolic activity of the liver tissue. Our data strongly indicate a dichotomous role for Nup88 in non-neoplastic and neoplastic conditions of the liver.
Figures
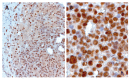
Figure 3
Nuclear Nup88-expression in a DN (A) and in dark brown nuclei of an undifferentiated HCC (B).
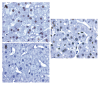
Figure 1
Nuclear Nup88 expression (brown nuclei) in non-neoplastic hepatocytes of a liver biopsy with mild unspecific chronic hepatitis (A), weak nuclear expression of Nup88 in chronic HBV-related hepatitis with mild inflammatory changes (B), and moderate nuclear expression of Nup88 in chronic HCV-related hepatitis with mild inflammatory changes (C).
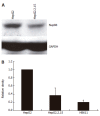
Figure 2
Western blot analysis showing reduced expression of Nup88 in HBV-positive HepG2.2.15 cells (A) and increased Nup88 expression in HBV-negative HepG2 and HBV-positive HepG2.2.15 (P < 0.002) and HB611 (P < 0.001) cells (B).
Similar articles
- Hepatic expression of the proliferative marker Ki-67 and p53 protein in HBV or HCV cirrhosis in relation to dysplastic liver cell changes and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Koskinas J, Petraki K, Kavantzas N, Rapti I, Kountouras D, Hadziyannis S. Koskinas J, et al. J Viral Hepat. 2005 Nov;12(6):635-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2005.00635.x. J Viral Hepat. 2005. PMID: 16255765 - Expression of B7-H4 and hepatitis B virus X in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hong B, Qian Y, Zhang H, Sang YW, Cheng LF, Wang Q, Gao S, Zheng M, Yao HP. Hong B, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2016 May 14;22(18):4538-46. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4538. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27182163 Free PMC article. - Hepatitis virus infection affects DNA methylation in mice with humanized livers.
Okamoto Y, Shinjo K, Shimizu Y, Sano T, Yamao K, Gao W, Fujii M, Osada H, Sekido Y, Murakami S, Tanaka Y, Joh T, Sato S, Takahashi S, Wakita T, Zhu J, Issa JP, Kondo Y. Okamoto Y, et al. Gastroenterology. 2014 Feb;146(2):562-72. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.10.056. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24184133 - Comparison of pathways associated with hepatitis B- and C-infected hepatocellular carcinoma using pathway-based class discrimination method.
Lee SY, Song KH, Koo I, Lee KH, Suh KS, Kim BY. Lee SY, et al. Genomics. 2012 Jun;99(6):347-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2012.04.004. Epub 2012 Apr 29. Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22564472 - [Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular biology aspects].
Blum HE. Blum HE. Zentralbl Chir. 1994;119(11):759-63. Zentralbl Chir. 1994. PMID: 7846955 Review. German.
Cited by
- Genome-wide association study among four horse breeds identifies a common haplotype associated with in vitro CD3+ T cell susceptibility/resistance to equine arteritis virus infection.
Go YY, Bailey E, Cook DG, Coleman SJ, Macleod JN, Chen KC, Timoney PJ, Balasuriya UB. Go YY, et al. J Virol. 2011 Dec;85(24):13174-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06068-11. Epub 2011 Oct 12. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21994447 Free PMC article. - Lamins and Lamin-Associated Proteins in Gastrointestinal Health and Disease.
Brady GF, Kwan R, Bragazzi Cunha J, Elenbaas JS, Omary MB. Brady GF, et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 May;154(6):1602-1619.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.026. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 29549040 Free PMC article. Review. - Esophageal cancer alters the expression of nuclear pore complex binding protein Hsc70 and eIF5A-1.
Moghanibashi M, Rastgar Jazii F, Soheili ZS, Zare M, Karkhane A, Parivar K, Mohamadynejad P. Moghanibashi M, et al. Funct Integr Genomics. 2013 Jun;13(2):253-60. doi: 10.1007/s10142-013-0320-9. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Funct Integr Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23539416 - Nuclear Morphological Abnormalities in Cancer: A Search for Unifying Mechanisms.
Singh I, Lele TP. Singh I, et al. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2022;70:443-467. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-06573-6_16. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2022. PMID: 36348118 Free PMC article. - The nuclear envelope environment and its cancer connections.
Chow KH, Factor RE, Ullman KS. Chow KH, et al. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Feb 16;12(3):196-209. doi: 10.1038/nrc3219. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22337151 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Block TM, Mehta AS, Fimmel CJ, Jordan R. Molecular viral oncology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2003;22:5093–5107. - PubMed
- Kau TR, Way JC, Silver PA. Nuclear transport and cancer: from mechanism to intervention. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:106–117. - PubMed
- Agudo D, Gómez-Esquer F, Martínez-Arribas F, Núñez-Villar MJ, Pollán M, Schneider J. Nup88 mRNA overexpression is associated with high aggressiveness of breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2004;109:717–720. - PubMed
- Vasu SK, Forbes DJ. Nuclear pores and nuclear assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:363–375. - PubMed
- Suntharalingam M, Wente SR. Peering through the pore: nuclear pore complex structure, assembly, and function. Dev Cell. 2003;4:775–789. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical