Combination chemoimmunotherapy with pentostatin, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab shows significant clinical activity with low accompanying toxicity in previously untreated B chronic lymphocytic leukemia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2007 Jan 15;109(2):405-11.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-033274. Epub 2006 Sep 28.
Susan M Geyer, Timothy G Call, Tait D Shanafelt, Clive S Zent, Diane F Jelinek, Renee Tschumper, Nancy D Bone, Gordon W Dewald, Thomas S Lin, Nyla A Heerema, Lisa Smith, Michael R Grever, John C Byrd
Affiliations
- PMID: 17008537
- PMCID: PMC1785105
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-033274
Clinical Trial
Combination chemoimmunotherapy with pentostatin, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab shows significant clinical activity with low accompanying toxicity in previously untreated B chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Neil E Kay et al. Blood. 2007.
Abstract
Building on the prior work of use of pentostatin in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), we initiated a trial of combined pentostatin (2 mg/m2), cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2), and rituximab (375 mg/m2) for 65 symptomatic, previously untreated patients. Of 64 evaluable patients, 34 (53%) were high Rai risk, 71% were nonmutated for the immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region gene, 34% were CD38+, and 34% were ZAP-70+. Thirty patients (52%) had one anomaly detected by fluorescence in situ (FISH) hybridization, and 21 (36%) had complex FISH defects. Thirty-eight patients (58%) had grade 3+ hematologic toxicity but minimal transfusion needs and no major infections. Responses occurred in 58 patients (91%), with 26 (41%) complete responses (CRs), 14 (22%) nodular partial responses (nodular PRs), and 18 (28%) partial responses (PRs). Many patients with a CR also lacked evidence of minimal residual disease by 2-color flow cytometry. Examination of prognostic factors demonstrated poor response in the 3 patients with del(17p). In contrast, we found this regimen was equally effective in young versus older (>70 years) patients and in del(11q22.3) versus other favorable prognostic factors. Thus, this novel regimen of pentostatin, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab for previously untreated patients with CLL demonstrated significant clinical activity despite poor risk-based prognoses, achievement of minimal residual disease in some, and modest toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
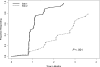
Figure 1
The time to NCI Working Group 96 response between patients enrolled at site 1 versus site 2.
Figure 2
Time to progression in relation to NCI Working Group 96 response criteria. CR indicates complete remission; NPR, nodular partial remission; PR, partial remission.
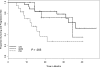
Figure 3
PFS by CD5+/CD19+ levels. Difference in the 2 curves was significant at P < .001.
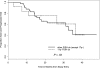
Figure 4
PFS by del(11q22.3) versus other FISH cohorts. There was no significant difference in PFS between the 2 CLL cohorts.
Figure 5
PFS by age cutoff of 70 years. There was no significant difference in PFS between the 2 age cohorts.
Similar articles
- Ofatumumab-based chemoimmunotherapy is effective and well tolerated in patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Shanafelt T, Lanasa MC, Call TG, Beaven AW, Leis JF, LaPlant B, Bowen D, Conte M, Jelinek DF, Hanson CA, Kay NE, Zent CS. Shanafelt T, et al. Cancer. 2013 Nov 1;119(21):3788-96. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28292. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23922059 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Pentostatin, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab is an active, well-tolerated regimen for patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Lamanna N, Kalaycio M, Maslak P, Jurcic JG, Heaney M, Brentjens R, Zelenetz AD, Horgan D, Gencarelli A, Panageas KS, Scheinberg DA, Weiss MA. Lamanna N, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2006 Apr 1;24(10):1575-81. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.3836. Epub 2006 Mar 6. J Clin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16520464 - Pentostatin and rituximab therapy for previously untreated patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Kay NE, Wu W, Kabat B, LaPlant B, Lin TS, Byrd JC, Jelinek DF, Grever MR, Zent CS, Call TG, Shanafelt TD. Kay NE, et al. Cancer. 2010 May 1;116(9):2180-7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25028. Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20187101 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
Plosker GL, Figgitt DP. Plosker GL, et al. Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review. - Rituximab plus fludarabine and cyclophosphamide or other agents in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Robak T, Lech-Maranda E, Robak P. Robak T, et al. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010 Oct;10(10):1529-43. doi: 10.1586/era.10.132. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20942624 Review.
Cited by
- Targeted Silencing of NRF2 by rituximab-conjugated nanoparticles increases the sensitivity of chronic lymphoblastic leukemia cells to Cyclophosphamide.
Khodakarami A, Kashani MA, Nazer A, Kheshti AM, Rashidi B, Karpisheh V, Masjedi A, Abolhasani S, Izadi S, Bagherifar R, Hejazian SS, Mohammadi H, Movassaghpour A, Feizi AAH, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Khodakarami A, et al. Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Aug 1;21(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01213-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37528446 Free PMC article. - [Simultaneous determination of pentostatin and 2'-amino-2'-deoxyadenosine in fermentation broth by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry].
Zhao M, Zhang H, Lou T, Zhao K, Wang S. Zhao M, et al. Se Pu. 2021 Jul 8;39(7):744-749. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.09018. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227372 Free PMC article. Chinese. - Measurable residual disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: expert review and consensus recommendations.
Wierda WG, Rawstron A, Cymbalista F, Badoux X, Rossi D, Brown JR, Egle A, Abello V, Cervera Ceballos E, Herishanu Y, Mulligan SP, Niemann CU, Diong CP, Soysal T, Suzuki R, Tran HTT, Wu SJ, Owen C, Stilgenbauer S, Ghia P, Hillmen P. Wierda WG, et al. Leukemia. 2021 Nov;35(11):3059-3072. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01241-1. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Leukemia. 2021. PMID: 34168283 Free PMC article. Review. - Pentostatin, Cyclophosphamide, and Rituximab Followed by Alemtuzumab for Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Phase 2 Trial of the ECOG-Acrin Cancer Research Group (E2903).
Kempin S, Sun Z, Kay NE, Paietta EM, Mazza JJ, Ketterling RP, Frankfurt O, Claxton DF, Saltzman JN, Srkalovic G, Callander NS, Gross G, Tallman MS. Kempin S, et al. Acta Haematol. 2019;142(4):224-232. doi: 10.1159/000500164. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Acta Haematol. 2019. PMID: 31336367 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Canadian evidence-based guideline for the first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Owen C, Gerrie AS, Banerji V, Assouline S, Chen C, Robinson KS, Lye E, Fraser G. Owen C, et al. Curr Oncol. 2018 Oct;25(5):e461-e474. doi: 10.3747/co.25.4092. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Curr Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30464698 Free PMC article.
References
- Han T, Ezdinli EZ, Shimaoka K, Desai DV. Chlorambucil vs. combined chlorambucil-corticosteroid therapy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer. 1973;31:502–508. - PubMed
- Hansen MM, Andersen E, Birgens H. CHOP versus chlorambucil + prednisolone in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 1991;5:97–100. - PubMed
- Raphael B, Andersen JW, Silber R, et al. Comparison of chlorambucil and prednisone versus cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone as initial treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: long-term follow-up of an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group randomized clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 1991;9:770–776. - PubMed
- Keller JW, Knospe WH, Raney M, et al. Treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia using chlorambucil and prednisone with or without cycle-active consolidation chemotherapy. A Southeastern Cancer Study Group Trial. Cancer. 1986;58:1185–1192. - PubMed
- Keating MJ. Fludarabine phosphate in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin Oncols. 1990;17:49–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA095241-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095241-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095241-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095241-02S1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095241-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 95241/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095241-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095241/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials