Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure
David H Epstein et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006 Nov.
Abstract
Background and rationale: The reinstatement model is widely used to study relapse to drug addiction. However, the model's validity is open to question.
Objective: We assess the reinstatement model in terms of criterion and construct validity.
Research highlights and conclusions: We find that the reinstatement model has adequate criterion validity in the broad sense of the term, as evidenced by the fact that reinstatement in laboratory animals is induced by conditions reported to provoke relapse in humans. The model's criterion validity in the narrower sense, as a medication screen, seems promising for relapse to heroin, nicotine, and alcohol. For relapse to cocaine, criterion validity has not yet been established primarily because clinical studies have examined medication's effects on reductions in cocaine intake rather than relapse during abstinence. The model's construct validity faces more substantial challenges and is yet to be established, but we argue that some of the criticisms of the model in this regard may have been overstated.
Figures
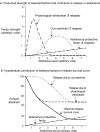
Figure 1. Hypothetical depiction of the contribution of relapse and abstinence factors to an observed relapse survival curve
(A) Time course of strength of three factors hypothesized to influence relapse: physiological withdrawal (dashed line; early onset and offset), cue reactivity (dotted line; gradual onset and offset), and an abstinence protective factor (dotted-dashed line; gradual increase over time). (B) Relapse survival curve (percent abstinent): relapse due to each of two factors (physiological withdrawal, dashed line; cue reactivity, dotted line) was calculated for each time point by subtracting a constant proportion of the factor’s strength (shown above in A) from 100. The Observed Relapse Survival Curve (solid black line) was then calculated by adding relapse due to physiological withdrawal and cue reactivity, subtracting the abstinence protective factor (dotted-dashed line) and subtracting the result from 100.
Similar articles
- Magnesium in drug dependences.
Nechifor M. Nechifor M. Magnes Res. 2008 Mar;21(1):5-15. Magnes Res. 2008. PMID: 18557129 Review. - Aripiprazole blocks reinstatement of cocaine seeking in an animal model of relapse.
Feltenstein MW, Altar CA, See RE. Feltenstein MW, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Mar 1;61(5):582-90. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.04.010. Epub 2006 Jun 27. Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 16806092 - A memory retrieval-extinction procedure to prevent drug craving and relapse.
Xue YX, Luo YX, Wu P, Shi HS, Xue LF, Chen C, Zhu WL, Ding ZB, Bao YP, Shi J, Epstein DH, Shaham Y, Lu L. Xue YX, et al. Science. 2012 Apr 13;336(6078):241-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1215070. Science. 2012. PMID: 22499948 Free PMC article. - The reinstatement model and relapse prevention: a clinical perspective.
Epstein DH, Preston KL. Epstein DH, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003 Jul;168(1-2):31-41. doi: 10.1007/s00213-003-1470-6. Epub 2003 Apr 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003. PMID: 12721778 Free PMC article. Review. - Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: an update and clinical implications.
Bossert JM, Ghitza UE, Lu L, Epstein DH, Shaham Y. Bossert JM, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Dec 5;526(1-3):36-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.09.030. Epub 2005 Nov 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16289451 Review.
Cited by
- Emerging role for corticotropin releasing factor signaling in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis at the intersection of stress and reward.
Silberman Y, Winder DG. Silberman Y, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2013 May 29;4:42. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00042. eCollection 2013. Front Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23755023 Free PMC article. - A dysphoric-like state during early withdrawal from extended access to methamphetamine self-administration in rats.
Jang CG, Whitfield T, Schulteis G, Koob GF, Wee S. Jang CG, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Feb;225(3):753-63. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2864-0. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23007601 Free PMC article. - Electroacupuncture suppresses discrete cue-evoked heroin-seeking and fos protein expression in the nucleus accumbens core in rats.
Liu S, Zhu F, Lai M, Sun L, Liu Y, Zhou W. Liu S, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:286404. doi: 10.1155/2012/286404. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22454660 Free PMC article. - Intrathecal cocaine delivery enables long-access self-administration with binge-like behavior in mice.
Nakamura M, Gao S, Okamura H, Nakahara D. Nakamura M, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Jan;213(1):119-29. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-2021-6. Epub 2010 Sep 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 20862455 - A lack of association between severity of nicotine withdrawal and individual differences in compensatory nicotine self-administration in rats.
Harris AC, Pentel PR, Burroughs D, Staley MD, Lesage MG. Harris AC, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Sep;217(2):153-66. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2273-9. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21494791 Free PMC article.
References
- Antelman SM, Levine J, Gershon S. Time-dependent sensitization: the odyssey of a scientific heresy from the laboratory to the door of the clinic. Mol Psychiatry. 2000;5:350–356. - PubMed
- Bachteler D, Economidou D, Danysz W, Ciccocioppo R, Spanagel R. The effects of acamprosate and neramexane on cue-induced reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior in rat. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:1104–1110. - PubMed
- Baker DA, McFarland K, Lake RW, Shen H, Tang XC, Toda S, Kalivas PW. Neuroadaptations in cystine-glutamate exchange underlie cocaine relapse. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:743–749. - PubMed
- Bindra D, Cameron L. Changes in experimentallly poroduced anxiety with the passage of time: incubation effect. J Exp Psychol. 1953;45:197–203. - PubMed
- Bossert JM, Ghitza UE, Lu L, Epstein DH, Shaham Y. Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: An update and clinical implications. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005;526:36–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical