DeepSAGE--digital transcriptomics with high sensitivity, simple experimental protocol and multiplexing of samples - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
DeepSAGE--digital transcriptomics with high sensitivity, simple experimental protocol and multiplexing of samples
Kåre L Nielsen et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006.
Abstract
Digital transcriptomics with pyrophosphatase based ultra-high throughput DNA sequencing of di-tags provides high sensitivity and cost-effective gene expression profiling. Sample preparation and handling are greatly simplified compared to Serial Analysis of Gene Expression (SAGE). We compare DeepSAGE and LongSAGE data and demonstrate greater power of detection and multiplexing of samples derived from potato. The transcript analysis revealed a great abundance of up-regulated potato transcripts associated with stress in dormant potatoes compared to harvest. Importantly, many transcripts were detected that cannot be matched to known genes, but is likely to be part of the abiotic stress-response in potato.
Figures
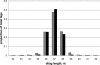
Figure 1
Distribution of ditags length in LongSAGE (solid) and DeepSAGE (hatched).
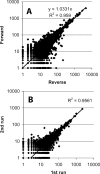
Figure 2
Correlation of tag counts extracted from (A) forward and reverse sequences, respectively. Data sets consisted of 167 159 forward sequences and 199 413 reverse sequences. Using tags observed at least once in both directions only (12 025 tags) the _R_2 = 0.9611. (B) Counts extracted from two different sequencing runs. Data sets consisted of 96 427 tags from the first run and 26 673 tags from the second run. Using tags observed at least once in both runs only (6631 tags) the _R_2 = 0.9609.
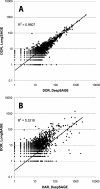
Figure 3
Correlation of LongSAGE and DeepSAGE DOR tags (A) and DeepSAGE HAR (B). Data sets consisted of 51 918 LongSAGE tags, 122 100 DeepSAGE DOR tags and 91 580 DeepSAGE HAR tags. The most abundant DOR tag was encountered 1397 in LongSAGE and 3145 in DeepSAGE. The least abundant tags were seen once in all data sets. Using tags observed at least once in both libraries only (8567 tags) the _R_2 for the comparison of DOR Deep- and LongSAGE increase to 0.9694.
Similar articles
- Transcriptome annotation using tandem SAGE tags.
Rivals E, Boureux A, Lejeune M, Ottones F, Pérez OP, Tarhio J, Pierrat F, Ruffle F, Commes T, Marti J. Rivals E, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(17):e108. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm495. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17709346 Free PMC article. - A large quantity of novel human antisense transcripts detected by LongSAGE.
Ge X, Wu Q, Jung YC, Chen J, Wang SM. Ge X, et al. Bioinformatics. 2006 Oct 15;22(20):2475-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl429. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16895931 - Abundant transcripts of malting barley identified by serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE).
White J, Pacey-Miller T, Crawford A, Cordeiro G, Barbary D, Bundock P, Henry R. White J, et al. Plant Biotechnol J. 2006 May;4(3):289-301. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2006.00181.x. Plant Biotechnol J. 2006. PMID: 17147635 - Exploring plant transcriptomes using ultra high-throughput sequencing.
Wang L, Li P, Brutnell TP. Wang L, et al. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010 Mar;9(2):118-28. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elp057. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20130067 Review. - Serial analysis of gene expression: probing transcriptomes for molecular targets.
Lal A, Sui IM, Riggins GJ. Lal A, et al. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 1999 Dec;1(6):720-6. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 1999. PMID: 19629869 Review.
Cited by
- Huntington's disease biomarker progression profile identified by transcriptome sequencing in peripheral blood.
Mastrokolias A, Ariyurek Y, Goeman JJ, van Duijn E, Roos RA, van der Mast RC, van Ommen GB, den Dunnen JT, 't Hoen PA, van Roon-Mom WM. Mastrokolias A, et al. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015 Oct;23(10):1349-56. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.281. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25626709 Free PMC article. - Transcriptome annotation using tandem SAGE tags.
Rivals E, Boureux A, Lejeune M, Ottones F, Pérez OP, Tarhio J, Pierrat F, Ruffle F, Commes T, Marti J. Rivals E, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(17):e108. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm495. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17709346 Free PMC article. - Digital gene expression analysis of the zebra finch genome.
Ekblom R, Balakrishnan CN, Burke T, Slate J. Ekblom R, et al. BMC Genomics. 2010 Apr 1;11:219. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-219. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20359325 Free PMC article. - Gene expression profiling by massively parallel sequencing.
Torres TT, Metta M, Ottenwälder B, Schlötterer C. Torres TT, et al. Genome Res. 2008 Jan;18(1):172-7. doi: 10.1101/gr.6984908. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 18032722 Free PMC article. - Genomics approaches for crop improvement against abiotic stress.
Akpınar BA, Lucas SJ, Budak H. Akpınar BA, et al. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Jun 6;2013:361921. doi: 10.1155/2013/361921. Print 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 23844392 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Lockhart D.J., Dong H.L., Byrne M.C., Follettie M.T., Gallo M.V., Chee M.S., Mittmann M., Wang C.W., Kobayashi M., Horton H., et al. Expression monitoring by hybridization to high-density oligonucleotide arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996;14:1675–1680. - PubMed
- Velculescu V.E., Zhang L., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K.W. Serial analysis of gene expression. Science. 1995;270:484–487. - PubMed
- Brenner S., Johnson M., Bridgham J., Golda G., Lloyd D.H., Johnson D., Luo S., McCurdy S., Foy M., Ewan M., et al. Gene expression analysis by massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) on microbead arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000;18:630–634. - PubMed
- Saha S., Sparks A.B., Rago C., Akmaev V., Wang C.J., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K.W., Velculescu V.E. Using the transcriptome to annotate the genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002;20:508–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources