Swiss residents' speciality choices--impact of gender, personality traits, career motivation and life goals - PubMed (original) (raw)
Swiss residents' speciality choices--impact of gender, personality traits, career motivation and life goals
Barbara Buddeberg-Fischer et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2006.
Abstract
Background: The medical specialties chosen by doctors for their careers play an important part in the development of health-care services. This study aimed to investigate the influence of gender, personality traits, career motivation and life goal aspirations on the choice of medical specialty.
Methods: As part of a prospective cohort study of Swiss medical school graduates on career development, 522 fourth-year residents were asked in what specialty they wanted to qualify. They also assessed their career motivation and life goal aspirations. Data concerning personality traits such as sense of coherence, self-esteem, and gender role orientation were collected at the first assessment, four years earlier, in their final year of medical school. Data analyses were conducted by univariate and multivariate analyses of variance and covariance.
Results: In their fourth year of residency 439 (84.1%) participants had made their specialty choice. Of these, 45 (8.6%) subjects aspired to primary care, 126 (24.1%) to internal medicine, 68 (13.0%) to surgical specialties, 31 (5.9%) to gynaecology & obstetrics (G&O), 40 (7.7%) to anaesthesiology/intensive care, 44 (8.4%) to paediatrics, 25 (4.8%) to psychiatry and 60 (11.5%) to other specialties. Female residents tended to choose G&O, paediatrics, and anaesthesiology, males more often surgical specialties; the other specialties did not show gender-relevant differences of frequency distribution. Gender had the strongest significant influence on specialty choice, followed by career motivation, personality traits, and life goals. Multivariate analyses of covariance indicated that career motivation and life goals mediated the influence of personality on career choice. Personality traits were no longer significant after controlling for career motivation and life goals as covariates. The effect of gender remained significant after controlling for personality traits, career motivation and life goals.
Conclusion: Gender had the greatest impact on specialty and career choice, but there were also two other relevant influencing factors, namely career motivation and life goals. Senior physicians mentoring junior physicians should pay special attention to these aspects. Motivational guidance throughout medical training should not only focus on the professional career but also consider the personal life goals of those being mentored.
Figures
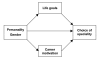
Figure 1
Conceptual framework of the study.
Figure 2
Study residents' speciality choices over time (T1 – T3) and speciality distribution of working doctors (2005).
Similar articles
- Residents' reasons for specialty choice: influence of gender, time, patient and career.
van der Horst K, Siegrist M, Orlow P, Giger M. van der Horst K, et al. Med Educ. 2010 Jun;44(6):595-602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.2010.03631.x. Med Educ. 2010. PMID: 20604856 - A decade of Australian Rural Clinical School graduates--where are they and why?
Eley DS, Synnott R, Baker PG, Chater AB. Eley DS, et al. Rural Remote Health. 2012;12:1937. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Rural Remote Health. 2012. PMID: 22394086 - Swiss residents' arguments for and against a career in medicine.
Buddeberg-Fischer B, Dietz C, Klaghofer R, Buddeberg C. Buddeberg-Fischer B, et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2006 Aug 14;6:98. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-6-98. BMC Health Serv Res. 2006. PMID: 16907981 Free PMC article. - Eroding students' rural motivation: first do no harm?
Hurst S. Hurst S. Swiss Med Wkly. 2014 Nov 15;144:w14020. doi: 10.4414/smw.2014.14020. eCollection 2014. Swiss Med Wkly. 2014. PMID: 25399015 Review. - House officers' specialist career choices and motivators for their choice- a sequential mixed-methods study from Malaysia.
Nadarajah A, Shankar PR, Jayaraman S, Sreeramareddy CT. Nadarajah A, et al. BMC Med Educ. 2022 Nov 16;22(1):796. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03845-2. BMC Med Educ. 2022. PMID: 36384571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Shortage in general practice despite the feminisation of the medical workforce: a seeming paradox? A cohort study.
Maiorova T, Stevens F, van der Zee J, Boode B, Scherpbier A. Maiorova T, et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2008 Dec 17;8:262. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-8-262. BMC Health Serv Res. 2008. PMID: 19091105 Free PMC article. - The sense of coherence and styles of success in the medical career: a longitudinal study.
Tartas M, Walkiewicz M, Budzinski W, Majkowicz M, Wojcikiewicz K. Tartas M, et al. BMC Med Educ. 2014 Nov 28;14:254. doi: 10.1186/s12909-014-0254-5. BMC Med Educ. 2014. PMID: 25429899 Free PMC article. - Private or salaried practice: how do young general practitioners make their career choice? A qualitative study.
Kinouani S, Boukhors G, Luaces B, Durieux W, Cadwallader JS, Aubin-Auger I, Gay B. Kinouani S, et al. BMC Med Educ. 2016 Sep 1;16(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12909-016-0754-6. BMC Med Educ. 2016. PMID: 27585603 Free PMC article. - Does medical students' personality have an impact on their intention to show empathic behavior?
Seitz T, Längle AS, Seidman C, Löffler-Stastka H. Seitz T, et al. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2018 Dec;21(6):611-618. doi: 10.1007/s00737-018-0837-y. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2018. PMID: 29623465 Free PMC article. - Gender differences in specialty preference and mismatch with real needs in Japanese medical students.
Fukuda Y, Harada T. Fukuda Y, et al. BMC Med Educ. 2010 Feb 11;10:15. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-10-15. BMC Med Educ. 2010. PMID: 20149219 Free PMC article.
References
- Bundesamt für Statistik . Das Medizinstudium in der Schweiz im Profil. Neuchatel, Bundesamt für Statistik; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials