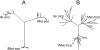Differential annotation of tRNA genes with anticodon CAT in bacterial genomes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Differential annotation of tRNA genes with anticodon CAT in bacterial genomes
Francisco J Silva et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006.
Abstract
We have developed three strategies to discriminate among the three types of tRNA genes with anticodon CAT (tRNA(Ile), elongator tRNA(Met) and initiator tRNA(fMet)) in bacterial genomes. With these strategies, we have classified the tRNA genes from 234 bacterial and several organellar genomes. These sequences, in an aligned or unaligned format, may be used for the identification and annotation of tRNA (CAT) genes in other genomes. The first strategy is based on the position of the problem sequences in a phenogram (a tree-like network), the second on the minimum average number of differences against the tRNA sequences of the three types and the third on the search for the highest score value against the profiles of the three types of tRNA genes. The species with the maximum number of tRNA(fMet) and tRNA(Met) was Photobacterium profundum, whereas the genome of one Escherichia coli strain presented the maximum number of tRNA(Ile) (CAT) genes. This last tRNA gene and tilS, encoding an RNA-modifying enzyme, are not essential in bacteria. The acquisition of a tRNA(Ile) (TAT) gene by Mycoplasma mobile has led to the loss of both the tRNA(Ile) (CAT) and the tilS genes. The new tRNA has appropriated the function of decoding AUA codons.
Figures
Figure 1
Phenograms of tRNA gene sequences with anticodon CAT. (A) Enterobacteriaceae. (B) Clostridia and Mollicutes. Filled circles show the location of the tRNA genes of a known type from E.coli (eco) and M.capricolum (mcp).
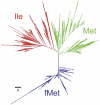
Figure 2
Phenogram of the complete set of tRNA genes with anticodon CAT. Red (tRNAIle), green (tRNAMet) and blue (tRNAfMet). The bar shows the branch length for 2 nt differences. The largest branch at the fMet group corresponds to the mitochondrial tRNA genes.
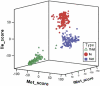
Figure 3
Three-dimensional plot of TFAM scores for tRNA gene sequences. Positive values show proximity to the profile of a specific tRNA type.
Figure 4
Comparative maps of the region including tilS gene.
Similar articles
- The various strategies of codon decoding in organisms of the three domains of life: evolutionary implications.
Grosjean H, Marck C, de Crécy-Lagard V. Grosjean H, et al. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2007;(51):15-6. doi: 10.1093/nass/nrm008. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2007. PMID: 18029563 - An operational RNA code for faithful assignment of AUG triplets to methionine.
Jones TE, Brown CL, Geslain R, Alexander RW, Ribas de Pouplana L. Jones TE, et al. Mol Cell. 2008 Feb 15;29(3):401-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.021. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18280245 - Life without the essential bacterial tRNA Ile2-lysidine synthetase TilS: a case of tRNA gene recruitment in Bacillus subtilis.
Fabret C, Dervyn E, Dalmais B, Guillot A, Marck C, Grosjean H, Noirot P. Fabret C, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2011 May;80(4):1062-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07630.x. Epub 2011 Apr 5. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21435031 - tRNA's wobble decoding of the genome: 40 years of modification.
Agris PF, Vendeix FA, Graham WD. Agris PF, et al. J Mol Biol. 2007 Feb 9;366(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.046. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17187822 Review. - Mechanisms of the tRNA wobble cytidine modification essential for AUA codon decoding in prokaryotes.
Numata T. Numata T. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015;79(3):347-53. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2014.975185. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25348586 Review.
Cited by
- Decoding in Candidatus Riesia pediculicola, close to a minimal tRNA modification set?
de Crécy-Lagard V, Marck C, Grosjean H. de Crécy-Lagard V, et al. Trends Cell Mol Biol. 2012;7:11-34. Trends Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23308034 Free PMC article. - Genome reduction and potential metabolic complementation of the dual endosymbionts in the whitefly Bemisia tabaci.
Rao Q, Rollat-Farnier PA, Zhu DT, Santos-Garcia D, Silva FJ, Moya A, Latorre A, Klein CC, Vavre F, Sagot MF, Liu SS, Mouton L, Wang XW. Rao Q, et al. BMC Genomics. 2015 Mar 21;16(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1379-6. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25887812 Free PMC article. - Data on true tRNA diversity among uncultured and bacterial strains.
Rekadwad BN, Khobragade CN. Rekadwad BN, et al. Data Brief. 2016 Apr 26;7:1538-40. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.04.049. eCollection 2016 Jun. Data Brief. 2016. PMID: 27222849 Free PMC article. - Whole-genome sequence of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia D457, a clinical isolate and a model strain.
Lira F, Hernández A, Belda E, Sánchez MB, Moya A, Silva FJ, Martínez JL. Lira F, et al. J Bacteriol. 2012 Jul;194(13):3563-4. doi: 10.1128/JB.00602-12. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22689246 Free PMC article. - The frontier between cell and organelle: genome analysis of Candidatus Carsonella ruddii.
Tamames J, Gil R, Latorre A, Peretó J, Silva FJ, Moya A. Tamames J, et al. BMC Evol Biol. 2007 Oct 1;7:181. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-181. BMC Evol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17908294 Free PMC article.
References
- Grosjean H., Bjork G.R. Enzymatic conversion of cytidine to lysidine in anticodon of bacterial tRNA(lle)—an alternative way of RNA editing. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004;29:165–168. - PubMed
- Soma A., Ikeuchi Y., Kanemasa S., Kobayashi K., Ogasawara N., Ote T., Kato J., Watanabe K., Sekine Y., Suzuki T. An RNA-modifying enzyme that governs both the codon and amino acid specificities of isoleucine tRNA. Mol. Cell. 2003;12:689–698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous