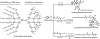A single dose of doxorubicin-functionalized bow-tie dendrimer cures mice bearing C-26 colon carcinomas - PubMed (original) (raw)
A single dose of doxorubicin-functionalized bow-tie dendrimer cures mice bearing C-26 colon carcinomas
Cameron C Lee et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006.
Abstract
The antitumor effect of doxorubicin (DOX) conjugated to a biodegradable dendrimer was evaluated in mice bearing C-26 colon carcinomas. An asymmetric biodegradable polyester dendrimer containing 8-10 wt % DOX was prepared. The design of the dendrimer carrier optimized blood circulation time through size and molecular architecture, drug loading through multiple attachment sites, solubility through PEGylation, and drug release through the use of pH-sensitive hydrazone linkages. In culture, dendrimer-DOX was >10 times less toxic than free DOX toward C-26 colon carcinoma cells after exposure for 72 h. Upon i.v. administration to BALB/c mice with s.c. C-26 tumors, dendrimer-DOX was eliminated from the serum with a half-life of 16 +/- 1 h, and its tumor uptake was ninefold higher than i.v. administered free DOX at 48 h. In efficacy studies performed with BALB/c mice bearing s.c. C-26 tumors, a single i.v. injection of dendrimer-DOX at 20 mg/kg DOX equivalents 8 days after tumor implantation caused complete tumor regression and 100% survival of the mice over the 60-day experiment. No cures were achieved in tumor-implanted mice treated with free DOX at its maximum tolerated dose (6 mg/kg), drug-free dendrimer, or dendrimer-DOX in which the DOX was attached by means of a stable carbamate bond. The antitumor effect of dendrimer-DOX was similar to that of an equimolar dose of liposomal DOX (Doxil). The remarkable antitumor activity of dendrimer-DOX results from the ability of the dendrimer to favorably modulate the pharmacokinetics of attached DOX.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
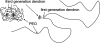
Fig. 1.
Cartoon representation of two bow-tie dendrimers with the same mass of PEO attached (40,000 Da). The more compact [G-3]-(PEO5k)8-[G-3]-(OH)8 dendrimer on the left is composed of eight 5,000-Da PEO chains attached to one side of the dendrimer; the less branched [G-1]-(PEO20k)2-[G-3]-(OH)8 dendrimer on the right is composed of two 20,000-Da PEO chains attached to one side of the dendrimer. The other half of each dendrimer is used for drug attachment and is presumably wrapped and shielded by the PEO chains to some extent.
Fig. 2.
Functionalization of the [G-3]-(PEO5k)8-[G-4]-(OH)16 bow-tie dendrimers for therapeutic studies. DOX is linked to the bow tie by means of a carbamate (top) or acyl hydrazone (middle) linkage. In the bottom route, hydrazide groups of the bow tie are blocked upon reaction with acetone. The top and bottom bow ties represent control treatments.
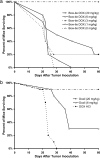
Fig. 3.
Survival versus time for BALB/c mice bearing s.c. C-26 tumors. In a, treatment consisted of a single i.v. dose of hydrazone-linked bow-tie DOX given 8 days after tumor implantation. In b, treatment consisted of a single i.v. injection of either free DOX or Doxil given 8 days after tumor implantation. Doses (in DOX equivalents) are specified in the key. (n = 10 for each group.)
Similar articles
- Pharmacokinetics and therapeutics of sterically stabilized liposomes in mice bearing C-26 colon carcinoma.
Huang SK, Mayhew E, Gilani S, Lasic DD, Martin FJ, Papahadjopoulos D. Huang SK, et al. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6774-81. Cancer Res. 1992. PMID: 1458465 - Investigation of Hexadecylphosphocholine (miltefosine) usage in Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin as a synergistic ingredient: In vitro and in vivo evaluation in mice bearing C26 colon carcinoma and B16F0 melanoma.
Teymouri M, Farzaneh H, Badiee A, Golmohammadzadeh S, Sadri K, Jaafari MR. Teymouri M, et al. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015 Dec 1;80:66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 26299343 - Liposomes and hyperthermia in mice: increased tumor uptake and therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin in sterically stabilized liposomes.
Huang SK, Stauffer PR, Hong K, Guo JW, Phillips TL, Huang A, Papahadjopoulos D. Huang SK, et al. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 15;54(8):2186-91. Cancer Res. 1994. PMID: 8174126 - Peptide dendrimer-Doxorubicin conjugate-based nanoparticles as an enzyme-responsive drug delivery system for cancer therapy.
Zhang C, Pan D, Luo K, She W, Guo C, Yang Y, Gu Z. Zhang C, et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014 Aug;3(8):1299-308. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201300601. Epub 2014 Apr 6. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014. PMID: 24706635 - Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a robust, biodegradable dendrimer.
van der Poll DG, Kieler-Ferguson HM, Floyd WC, Guillaudeu SJ, Jerger K, Szoka FC, Fréchet JM. van der Poll DG, et al. Bioconjug Chem. 2010 Apr 21;21(4):764-73. doi: 10.1021/bc900553n. Bioconjug Chem. 2010. PMID: 20353169 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Well-defined single polymer nanoparticles for the antibody-targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic agents.
Lane DD, Chiu DY, Su FY, Srinivasan S, Kern HB, Press OW, Stayton PS, Convertine AJ. Lane DD, et al. Polym Chem. 2015 Feb 28;6(8):1286-1299. doi: 10.1039/C4PY01250J. Polym Chem. 2015. PMID: 26097514 Free PMC article. - Analysis of Lanthanide Complex Dendrimer Conjugates for Bimodal NIR and MRI Imaging.
Andolina CM, Klemm PJ, Floyd WC 3rd, Fréchet JM, Raymond KN. Andolina CM, et al. Macromolecules. 2012 Nov 27;45(22):8982-8990. doi: 10.1021/ma302206g. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Macromolecules. 2012. PMID: 23226878 Free PMC article. - Dendritic Guanidines as Efficient Analogues of Cell Penetrating Peptides.
Bonduelle CV, Gillies ER. Bonduelle CV, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2010 Mar 12;3(3):636-666. doi: 10.3390/ph3030636. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2010. PMID: 27713272 Free PMC article. Review. - Nanocarriers for effective delivery: modulation of innate immunity for the management of infections and the associated complications.
Ko CN, Zang S, Zhou Y, Zhong Z, Yang C. Ko CN, et al. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Aug 19;20(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01582-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35986268 Free PMC article. Review. - Enhanced antitumor efficacy of doxorubicin-encapsulated halloysite nanotubes.
Li K, Zhang Y, Chen M, Hu Y, Jiang W, Zhou L, Li S, Xu M, Zhao Q, Wan R. Li K, et al. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Dec 19;13:19-30. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S143928. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 29296083 Free PMC article.
References
- Duncan R. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:347–360. - PubMed
- Drobník J, Rypácek F. Adv Polym Sci. 1984;57:1–50.
- Allen TM, Cullis PR. Science. 2004;303:1818–1822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous