Cutting edge: inherent and acquired resistance to radiation-induced apoptosis in B cells: a pivotal role for STAT3 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cutting edge: inherent and acquired resistance to radiation-induced apoptosis in B cells: a pivotal role for STAT3
Dennis C Otero et al. J Immunol. 2006.
Abstract
Radiation-induced apoptosis (RiA) is used therapeutically for tumor cell ablation as well as a tool to characterize hemopoietic cell lineages. We report that the peritoneal B-1 B cell subset is selectively resistant to RiA. Inherent radioresistance is not shared by splenic B-2 or B-1 cells. However, it is conferred upon B-2 cells by BCR crosslinking in the presence of IL-6 or IL-10. In vivo experiments with gene-targeted mice confirm that IL-6 and, to a lesser extent, IL-10 are the relevant stimuli that combine with BCR ligands to promote B-1 cell radioresistance. STAT3 promotes cell survival in response to selected growth factors, and is activated by combined BCR crosslinking and IL-6 (IL-10). Importantly, STAT3(-/-) B-1 cells become susceptible to irradiation, indicating that STAT3 activation by the BCR in the presence of IL costimuli account for the inherent radioresistance of peritoneal B-1 B cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
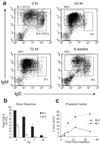
FIGURE 1
Murine B-1 cells are radioresistant. a, Flow cytometry profiles of peritoneal B-1 (IgMhighIgDlow) and B-2 (IgMlowIgDhigh) cells at indicated time points postirradiation (5 Gy) (n = 6 mice). b, B cell recovery from PeC 48 h after indicated exposure (n = 3 per group). c, Kinetics of in vitro cell death determined by PI staining after 2 Gy exposure; representative of more than three experiments.
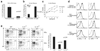
FIGURE 2
Cytokines and cell activation contribute to B cell radioresistance. a, Recovery of splenic B-1 cells from VH12 transgenic mice 48 h postirradiation (5 Gy, n = 3 mice). b, Rescue of B-2 cells from RiA. Purified CFSE-labeled splenic B-2 cells were left untreated or stimulated with anti-IgM (10 µg/ml) and immediately injected i.p. or i.v. Recipient mice were irradiated (5 Gy) and transferred B cells from PeC or spleen were enumerated 24 h postirradiation. Graph represents percent cell recovery from irradiated mice compared with non-irradiated mice (n = 3 mice per group). c, In vitro rescue of B cells from RiA. Purified splenic B cells were irradiated (2 Gy) following an 18-h incubation with anti-IgM and/or IL-6. Apoptosis was measured by PI (sub-G0-G1) staining 24 h postirradiation; representative of four experiments. d, Expression levels of IL-6 and IL-10 receptor on ex vivo and stimulated (24 h) B cells; LPS (1 µg/ml), anti-CD40 (10 µg/ml), and anti-IgM (1 µg/ml). e, B cell recovery from the PeC of IL-6−/− and IL-10−/− mice. Relative numbers of B-1 (CD23negIgMhigh) and B-2 (CD23posIgMlow) cells were analyzed before and after (48 h) irradiation (5 Gy). Graph represents percent cell recovery from the PeC of irradiated mice compared with non-irradiated mice (average ± SEM of at least three mice per group).
FIGURE 3
B-1 cell radioresistance requires STAT3. a, B cell recovery from the PeC of STAT3−/−, STAT1−/−, and STAT5a/b−/− mice. Relative numbers of B-1 and B-2 cells were determined before and after (48 h) irradiation (5 Gy). Graph represents percent cell recovery from the PeC of irradiated mice compared with non-irradiated mice (average ± SEM of at ≥3 mice per group). b, Impaired in vitro rescue of STAT3−/− B cells from RiA. Purified splenic B cells from WT and STAT-3−/− mice were cultured (18 h) in the presence of anti-IgM and/or IL-6 (top) or anti-IgM/IL-10 (bottom), irradiated (2 Gy), and apoptosis measured by PI (sub-G0-G1) staining 24 h postirradiation; representative of three experiments (mean ± SEM).
Similar articles
- Myeloid STAT3 inhibits T cell-mediated hepatitis by regulating T helper 1 cytokine and interleukin-17 production.
Lafdil F, Wang H, Park O, Zhang W, Moritoki Y, Yin S, Fu XY, Gershwin ME, Lian ZX, Gao B. Lafdil F, et al. Gastroenterology. 2009 Dec;137(6):2125-35.e1-2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.004. Epub 2009 Aug 15. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19686746 Free PMC article. - CD5-mediated negative regulation of antigen receptor-induced growth signals in B-1 B cells.
Bikah G, Carey J, Ciallella JR, Tarakhovsky A, Bondada S. Bikah G, et al. Science. 1996 Dec 13;274(5294):1906-9. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5294.1906. Science. 1996. PMID: 8943203 - Inhibition of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway blocks a subset of B cell responses to antigen.
Richards JD, Davé SH, Chou CH, Mamchak AA, DeFranco AL. Richards JD, et al. J Immunol. 2001 Mar 15;166(6):3855-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.6.3855. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11238629 - FcγRIIb and BAFF differentially regulate peritoneal B1 cell survival.
Amezcua Vesely MC, Schwartz M, Bermejo DA, Montes CL, Cautivo KM, Kalergis AM, Rawlings DJ, Acosta-Rodríguez EV, Gruppi A. Amezcua Vesely MC, et al. J Immunol. 2012 May 15;188(10):4792-800. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102070. Epub 2012 Apr 18. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22516957 Free PMC article. - Essential role for Cmtm7 in cell-surface phenotype, BCR signaling, survival and Igμ repertoire of splenic B-1a cells.
Liu Z, Liu Y, Li T, Wang P, Mo X, Lv P, Ma D, Han W. Liu Z, et al. Cell Immunol. 2020 Jun;352:104100. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2020.104100. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Cell Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32305130
Cited by
- Suppression by Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol of the primary immunoglobulin M response by human peripheral blood B cells is associated with impaired STAT3 activation.
Ngaotepprutaram T, Kaplan BL, Carney S, Crawford R, Kaminski NE. Ngaotepprutaram T, et al. Toxicology. 2013 Aug 9;310:84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 May 29. Toxicology. 2013. PMID: 23727458 Free PMC article. - Quercetin shortened survival of radio-resistant B-1 cells in vitro and in vivo by restoring miR15a/16 expression.
Ramos YAL, Souza OF, Novo MCT, Guimarães CFC, Popi AF. Ramos YAL, et al. Oncotarget. 2021 Feb 16;12(4):355-365. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27883. eCollection 2021 Feb 16. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 33659046 Free PMC article. - Candidate gene association study in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia evaluated by Bayesian network based Bayesian multilevel analysis of relevance.
Lautner-Csorba O, Gézsi A, Semsei AF, Antal P, Erdélyi DJ, Schermann G, Kutszegi N, Csordás K, Hegyi M, Kovács G, Falus A, Szalai C. Lautner-Csorba O, et al. BMC Med Genomics. 2012 Sep 28;5:42. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-5-42. BMC Med Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23021489 Free PMC article. - STAT3 inhibitor in combination with irradiation significantly inhibits cell viability, cell migration, invasion and tumorsphere growth of human medulloblastoma cells.
Pan L, Zhang R, Ma L, Pierson CR, Finlay JL, Li C, Lin J. Pan L, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2021 Sep 2;22(7-9):430-439. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2021.1951573. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Cancer Biol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34254873 Free PMC article. - Liver-expressed Igkappa superantigen induces tolerance of polyclonal B cells by clonal deletion not kappa to lambda receptor editing.
Ota T, Ota M, Duong BH, Gavin AL, Nemazee D. Ota T, et al. J Exp Med. 2011 Mar 14;208(3):617-29. doi: 10.1084/jem.20102265. Epub 2011 Feb 28. J Exp Med. 2011. PMID: 21357741 Free PMC article.
References
- Berland R, Wortis HH. Origins and functions of B-1 cells with notes on the role of CD5. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:253–300. - PubMed
- Montecino-Rodriguez E, Leathers H, Dorshkind K. Identification of a B-1 B cell-specified progenitor. Nat. Immunol. 2006;7:293–301. - PubMed
- Hayakawa K, Asano M, Shinton SA, Gui M, Allman D, Stewart CL, Silver J, Hardy RR. Positive selection of natural autoreactive B cells. Science. 1999;285:113–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous