Recent history of artificial outcrossing facilitates whole-genome association mapping in elite inbred crop varieties - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2006 Dec 5;103(49):18656-61.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606133103. Epub 2006 Nov 3.
Luke Ramsay, Katrin MacKenzie, Linda Cardle, Prasanna R Bhat, Mikeal L Roose, Jan T Svensson, Nils Stein, Rajeev K Varshney, David F Marshall, Andreas Graner, Timothy J Close, Robbie Waugh
Affiliations
- PMID: 17085595
- PMCID: PMC1693718
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0606133103
Recent history of artificial outcrossing facilitates whole-genome association mapping in elite inbred crop varieties
Nils Rostoks et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006.
Abstract
Genomewide association studies depend on the extent of linkage disequilibrium (LD), the number and distribution of markers, and the underlying structure in populations under study. Outbreeding species generally exhibit limited LD, and consequently, a very large number of markers are required for effective whole-genome association genetic scans. In contrast, several of the world's major food crops are self-fertilizing inbreeding species with narrow genetic bases and theoretically extensive LD. Together these are predicted to result in a combination of low resolution and a high frequency of spurious associations in LD-based studies. However, inbred elite plant varieties represent a unique human-induced pseudo-outbreeding population that has been subjected to strong selection for advantageous alleles. By assaying 1,524 genomewide SNPs we demonstrate that, after accounting for population substructure, the level of LD exhibited in elite northwest European barley, a typical inbred cereal crop, can be effectively exploited to map traits by using whole-genome association scans with several hundred to thousands of biallelic SNPs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Fig. 1.
PCOs of the SNP genotype data of 102 barley varieties. The full genotype data set is partitioned into foreign material (triangles), European two-row spring (squares), and winter (diamonds) varieties. The complete list of varieties is available in Table 1.
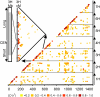
Fig. 2.
Diversity and LD in barley genome. (a) Distribution of PIC along the linkage map. PIC was averaged across a window of 25 adjacent loci with a step of one and plotted against the linkage map. Data points are colored by group of germplasm. (b) Decay of LD (_r_2) as a function of genetic distance (cM) between pairs of loci on individual chromosomes in European two-row spring barley. Loci with MAF < 0.1 were excluded from analysis. Only LD values with P < 0.001 are shown.
Fig. 3.
LD matrix of European two-row spring barley. Data points are colored by magnitude of LD (_r_2). LD is plotted along the cumulative linkage map of the barley genome with chromosome starting at multiples of 200 cM. (Inset) Variation in LD along the barley chromosome 3H, which correlates with the recombination (genetic distance) and physical map of centromeric region of 3H (23). BIN 6 of the linkage map encompasses ≈600 Mb of chromosome 3H including the centromere (CEN) (23, 24), and _r_2 exhibits strong LD across the whole region.
Comment in
- Disequilibrium and association in barley: thinking outside the glass.
Hayes P, Szucs P. Hayes P, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Dec 5;103(49):18385-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609405103. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17130443 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Extreme population-dependent linkage disequilibrium detected in an inbreeding plant species, Hordeum vulgare.
Caldwell KS, Russell J, Langridge P, Powell W. Caldwell KS, et al. Genetics. 2006 Jan;172(1):557-67. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.038489. Epub 2005 Oct 11. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16219791 Free PMC article. - Whole-genome association mapping in elite inbred crop varieties.
Waugh R, Marshall D, Thomas B, Comadran J, Russell J, Close T, Stein N, Hayes P, Muehlbauer G, Cockram J, O'Sullivan D, Mackay I, Flavell A; AGOUEB; BarleyCAP; Ramsay L. Waugh R, et al. Genome. 2010 Nov;53(11):967-72. doi: 10.1139/G10-078. Genome. 2010. PMID: 21076512 - Analysis of molecular diversity, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in a worldwide survey of cultivated barley germplasm (Hordeum vulgare L.).
Malysheva-Otto LV, Ganal MW, Röder MS. Malysheva-Otto LV, et al. BMC Genet. 2006 Jan 24;7:6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-7-6. BMC Genet. 2006. PMID: 16433922 Free PMC article. - Applications of single nucleotide polymorphisms in crop genetics.
Rafalski A. Rafalski A. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002 Apr;5(2):94-100. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(02)00240-6. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002. PMID: 11856602 Review. - The emergence of whole genome association scans in barley.
Waugh R, Jannink JL, Muehlbauer GJ, Ramsay L. Waugh R, et al. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2009 Apr;12(2):218-22. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2008.12.007. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2009. PMID: 19185530 Review.
Cited by
- High-density SNP-based genetic map development and linkage disequilibrium assessment in Brassica napus L.
Delourme R, Falentin C, Fomeju BF, Boillot M, Lassalle G, André I, Duarte J, Gauthier V, Lucante N, Marty A, Pauchon M, Pichon JP, Ribière N, Trotoux G, Blanchard P, Rivière N, Martinant JP, Pauquet J. Delourme R, et al. BMC Genomics. 2013 Feb 22;14:120. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-120. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23432809 Free PMC article. - Functional Markers for Precision Plant Breeding.
Salgotra RK, Stewart CN Jr. Salgotra RK, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 6;21(13):4792. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134792. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32640763 Free PMC article. Review. - Statistical genetic issues for genome-wide association studies.
Weir BS. Weir BS. Genome. 2010 Nov;53(11):869-75. doi: 10.1139/G10-062. Genome. 2010. PMID: 21076502 Free PMC article. - Farmers without borders-genetic structuring in century old barley (Hordeum vulgare).
Forsberg NE, Russell J, Macaulay M, Leino MW, Hagenblad J. Forsberg NE, et al. Heredity (Edinb). 2015 Feb;114(2):195-206. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2014.83. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Heredity (Edinb). 2015. PMID: 25227257 Free PMC article. - The genetic diversity and evolution of field pea (Pisum) studied by high throughput retrotransposon based insertion polymorphism (RBIP) marker analysis.
Jing R, Vershinin A, Grzebyta J, Shaw P, Smýkal P, Marshall D, Ambrose MJ, Ellis TH, Flavell AJ. Jing R, et al. BMC Evol Biol. 2010 Feb 15;10:44. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-44. BMC Evol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20156342 Free PMC article.
References
- Lander ES, Schork NJ. Science. 1994;265:2037–2048. - PubMed
- Ardlie KG, Kruglyak L, Seielstad M. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:299–309. - PubMed
- Hirschhorn JN, Daly MJ. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:95–108. - PubMed
- Tishkoff SA, Verrelli BC. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2003;4:293–340. - PubMed
- Nordborg M, Tavare S. Trends Genet. 2002;18:83–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials