Rho kinase inhibition improves endothelial function in human subjects with coronary artery disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Rho kinase inhibition improves endothelial function in human subjects with coronary artery disease
Anju Nohria et al. Circ Res. 2006.
Abstract
Investigations from basic biology suggest that activation of the Rho/Rho kinase pathway reduces the bioavailability of nitric oxide (NO) and thereby promotes atherosclerosis and its clinical complications. Yet, little information is available about the relationship of the Rho/Rho kinase pathway to NO bioavailability in humans with atherosclerosis. Accordingly, we determined whether inhibition of Rho kinase augments NO bioavailability and improves endothelial function in human subjects with coronary artery disease (CAD). Thirteen CAD subjects and 16 age- and sex-matched healthy controls were randomly assigned to receive the Rho kinase inhibitor, fasudil, or placebo for 1 month each in a double-blind crossover trial. Flow-mediated, endothelium-dependent and nitroglycerin-induced, endothelium-independent vasodilation were assessed by brachial artery ultrasonography. Rho kinase activity was measured in peripheral leukocytes. Fasudil increased endothelium-dependent vasodilation in CAD subjects from 9.4+/-1.9% to 13.4+/-1.9% (P=0.001) but not in healthy controls (from 11.3+/-1.4% to 7.7+/-1.1%; P=0.07). Endothelium-independent vasodilation was not affected by fasudil in either CAD or healthy subjects. Fasudil reduced Rho kinase activity by 59+/-18% in CAD subjects (P=0.001) but not in healthy subjects (by 3+/-6%; P=0.60). The change in endothelium-dependent vasodilation achieved with fasudil relative to placebo was inversely proportional to Rho kinase inhibition (ie, greater Rho kinase inhibition was associated with larger improvement in endothelium-dependent vasodilation) (r=-0.48; P=0.01). These findings suggest that Rho/Rho kinase activation promotes endothelial dysfunction in humans with atherosclerosis. Inhibition of the Rho/Rho kinase pathway should provide a useful strategy to restore NO bioavailability in humans with atherosclerosis.
Figures
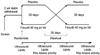
Figure 1
Study protocol.
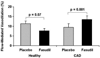
Figure 2
Effect of fasudil on flow-mediated vasodilation. Results are expressed as mean±SE. The percentage increase in brachial artery diameter 1 minute after cuff release compared with the baseline is illustrated. Fasudil increased flow-mediated, endothelium-dependent vasodilation significantly in the CAD subjects (_P_=0.001) but not in healthy controls (_P_=0.07).
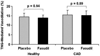
Figure 3
Effect of fasudil on nitroglycerin-mediated vasodilation. Results are expressed as mean±SE. The percentage increase in brachial artery diameter 3 minutes after sublingual nitroglycerin administration compared with baseline is illustrated. Fasudil did not significantly alter nitroglycerin-mediated, endothelium-independent vasodilation in either CAD or healthy subjects
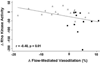
Figure 4
Correlation of Rho kinase inhibition with fasudil and change in endothelium-dependent vasodilation. For the entire cohort of 28 patients, the change in flow-mediated, endothelium-dependent vasodilation after fasudil relative to placebo was inversely proportional to the extent of Rho kinase inhibition with fasudil (_r_=−0.48, _P_=0.01). Squares represent CAD and triangles represent healthy subjects, respectively.
Similar articles
- Rho-kinase inhibition improves vasodilator responsiveness during hyperinsulinemia in the metabolic syndrome.
Schinzari F, Tesauro M, Rovella V, Di Daniele N, Gentileschi P, Mores N, Campia U, Cardillo C. Schinzari F, et al. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Sep 15;303(6):E806-11. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00206.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22829585 Free PMC article. - Long term Rho-kinase inhibition ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in LDL-Receptor deficient mice.
Steioff K, Rütten H, Busch AE, Plettenburg O, Ivashchenko Y, Löhn M. Steioff K, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Apr 11;512(2-3):247-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.03.001. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15840411 - Acute vasodilator effects of a Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, in patients with severe pulmonary hypertension.
Fukumoto Y, Matoba T, Ito A, Tanaka H, Kishi T, Hayashidani S, Abe K, Takeshita A, Shimokawa H. Fukumoto Y, et al. Heart. 2005 Mar;91(3):391-2. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2003.029470. Heart. 2005. PMID: 15710736 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Recent progress in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: expectation for rho-kinase inhibitors.
Fukumoto Y, Tawara S, Shimokawa H. Fukumoto Y, et al. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2007 Apr;211(4):309-20. doi: 10.1620/tjem.211.309. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17409670 Review. - Rho-kinase as a novel therapeutic target in treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Shimokawa H. Shimokawa H. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2002 Mar;39(3):319-27. doi: 10.1097/00005344-200203000-00001. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11862109 Review.
Cited by
- Molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of statins on bone metabolism: an evolving paradigm of statins delivery modalities for bone regeneration.
Zaki RM, Ali MAM, Said M, Chaudhary AA, Boufahja F, Afzal O, Abu-Elsaoud AM, Abdel Halim AS. Zaki RM, et al. Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Jun;77(3):624-644. doi: 10.1007/s43440-025-00716-7. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40167878 Review. - Involvement of RhoA/ROCK Signaling Pathway in Methamphetamine-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption.
Hwang JS, Vo TTL, Kim M, Cha EH, Mun KC, Ha E, Seo JH. Hwang JS, et al. Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 27;15(3):340. doi: 10.3390/biom15030340. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149876 Free PMC article. - Evidence for statin pleiotropy in humans: differential effects of statins and ezetimibe on rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase activity, endothelial function, and inflammation.
Liu PY, Liu YW, Lin LJ, Chen JH, Liao JK. Liu PY, et al. Circulation. 2009 Jan 6;119(1):131-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.813311. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Circulation. 2009. PMID: 19075102 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Endothelial Barrier Function and Leukocyte Transmigration in Atherosclerosis.
Sluiter TJ, van Buul JD, Huveneers S, Quax PHA, de Vries MR. Sluiter TJ, et al. Biomedicines. 2021 Mar 24;9(4):328. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040328. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33804952 Free PMC article. Review. - Pericyte Rho GTPase mediates both pericyte contractile phenotype and capillary endothelial growth state.
Kutcher ME, Kolyada AY, Surks HK, Herman IM. Kutcher ME, et al. Am J Pathol. 2007 Aug;171(2):693-701. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070102. Epub 2007 Jun 7. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17556591 Free PMC article.
References
- Vane JR, Anggard EE, Botting RM. Regulatory functions of the vascular endothelium. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:27–36. - PubMed
- Ganz P, Vita JA. Testing endothelial vasomotor function: nitric oxide, a multipotent molecule. Circulation. 2003;108:2049–2053. - PubMed
- Lerman A, Zeiher AM. Endothelial function: cardiac events. Circulation. 2005;111:363–368. - PubMed
- Shimokawa H, Hiramori K, Iinuma H, Hosoda S, Kishida H, Osada H, Katagiri T, Yamauchi K, Yui Y, Minamino T, Nakashima M, Kato K. Anti-anginal effect of fasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, in patients with stable effort angina: a multicenter study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2002;40:751–761. - PubMed
- Loirand G, Guerin P, Pacaud P. Rho kinases in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. Circ Res. 2006;98:322–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL048743/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL-48743/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL52233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070274/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062729/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous