4SALE--a tool for synchronous RNA sequence and secondary structure alignment and editing - PubMed (original) (raw)
4SALE--a tool for synchronous RNA sequence and secondary structure alignment and editing
Philipp N Seibel et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006.
Abstract
Background: In sequence analysis the multiple alignment builds the fundament of all proceeding analyses. Errors in an alignment could strongly influence all succeeding analyses and therefore could lead to wrong predictions. Hand-crafted and hand-improved alignments are necessary and meanwhile good common practice. For RNA sequences often the primary sequence as well as a secondary structure consensus is well known, e.g., the cloverleaf structure of the t-RNA. Recently, some alignment editors are proposed that are able to include and model both kinds of information. However, with the advent of a large amount of reliable RNA sequences together with their solved secondary structures (available from e.g. the ITS2 Database), we are faced with the problem to handle sequences and their associated secondary structures synchronously.
Results: 4SALE fills this gap. The application allows a fast sequence and synchronous secondary structure alignment for large data sets and for the first time synchronous manual editing of aligned sequences and their secondary structures. This study describes an algorithm for the synchronous alignment of sequences and their associated secondary structures as well as the main features of 4SALE used for further analyses and editing. 4SALE builds an optimal and unique starting point for every RNA sequence and structure analysis.
Conclusion: 4SALE, which provides an user-friendly and intuitive interface, is a comprehensive toolbox for RNA analysis based on sequence and secondary structure information. The program connects sequence and structure databases like the ITS2 Database to phylogeny programs as for example the CBCAnalyzer. 4SALE is written in JAVA and therefore platform independent. The software is freely available and distributed from the website at http://4sale.bioapps.biozentrum.uni-wuerzburg.de.
Figures
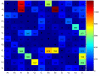
Figure 1
ITS2 sequence and secondary structure ratematrix. This figure shows the estimated sequence/secondary structure substitution rates (*105). Diagonal entries are by definition the negative sum of all row entries. Note, high rates depict frequent substitutions, and vice versa small rates depict rare substitutions, e.g., within a secondary structure Cs an Us are often replaced by each other.
Figure 2
Overview. This figure shows a complete overview of the main features in 4SALE. All parts and their use are described in the boxes within the figure.
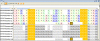
Figure 3
Synchronous editing. This figure illustrates the synchronous sequence and secondary structure handling in 4SALE. When selecting a helical region in the secondary structure alignment, as shown in this example, 4SALE synchronously selects its structural counterpart and its corresponding parts in the sequence alignment. The figure also shows very well, how easily an error in the alignment could be detected and corrected by using the selection and edit features in 4SALE.
Similar articles
- CBCAnalyzer: inferring phylogenies based on compensatory base changes in RNA secondary structures.
Wolf M, Friedrich J, Dandekar T, Müller T. Wolf M, et al. In Silico Biol. 2005;5(3):291-4. Epub 2005 Mar 16. In Silico Biol. 2005. PMID: 15996120 - ITS2, 18S, 16S or any other RNA - simply aligning sequences and their individual secondary structures simultaneously by an automatic approach.
Wolf M, Koetschan C, Müller T. Wolf M, et al. Gene. 2014 Aug 10;546(2):145-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.05.065. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24881812 Review. - The internal transcribed spacer 2 database--a web server for (not only) low level phylogenetic analyses.
Schultz J, Müller T, Achtziger M, Seibel PN, Dandekar T, Wolf M. Schultz J, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W704-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl129. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845103 Free PMC article. - A method for aligning RNA secondary structures and its application to RNA motif detection.
Liu J, Wang JT, Hu J, Tian B. Liu J, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr 7;6:89. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-89. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15817128 Free PMC article. - From consensus structure prediction to RNA gene finding.
Bernhart SH, Hofacker IL. Bernhart SH, et al. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2009 Nov;8(6):461-71. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elp043. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2009. PMID: 19833701 Review.
Cited by
- GC heterogeneity reveals sequence-structures evolution of angiosperm ITS2.
Liu Y, Liang N, Xian Q, Zhang W. Liu Y, et al. BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Dec 1;23(1):608. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04634-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 38036992 Free PMC article. - Including RNA secondary structures improves accuracy and robustness in reconstruction of phylogenetic trees.
Keller A, Förster F, Müller T, Dandekar T, Schultz J, Wolf M. Keller A, et al. Biol Direct. 2010 Jan 15;5:4. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-5-4. Biol Direct. 2010. PMID: 20078867 Free PMC article. - Nuclear and Mitochondrial SSU rRNA Genes Reveal Hidden Diversity of Haptophrya Endosymbionts in Freshwater Planarians and Challenge Their Traditional Classification in Astomatia.
Rataj M, Zhang T, Vd'ačný P. Rataj M, et al. Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 14;13:830951. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.830951. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35495648 Free PMC article. - Structural diversity of eukaryotic 18S rRNA and its impact on alignment and phylogenetic reconstruction.
Xie Q, Lin J, Qin Y, Zhou J, Bu W. Xie Q, et al. Protein Cell. 2011 Feb;2(2):161-70. doi: 10.1007/s13238-011-1017-2. Epub 2011 Mar 12. Protein Cell. 2011. PMID: 21400046 Free PMC article. - Diversity and Eco-Evolutionary Associations of Endosymbiotic Astome Ciliates With Their Lumbricid Earthworm Hosts.
Obert T, Rurik I, Vd'ačný P. Obert T, et al. Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 18;12:689987. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.689987. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34220782 Free PMC article.
References
- Stoye J, Moulton V, Dress AW. DCA: an efficient implementation of the divide-and-conquer approach to simultaneous multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1997;13:625–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous