BindingDB: a web-accessible database of experimentally determined protein-ligand binding affinities - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D198-201.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl999. Epub 2006 Dec 1.
Affiliations
- PMID: 17145705
- PMCID: PMC1751547
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl999
BindingDB: a web-accessible database of experimentally determined protein-ligand binding affinities
Tiqing Liu et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan.
Abstract
BindingDB (http://www.bindingdb.org) is a publicly accessible database currently containing approximately 20,000 experimentally determined binding affinities of protein-ligand complexes, for 110 protein targets including isoforms and mutational variants, and approximately 11,000 small molecule ligands. The data are extracted from the scientific literature, data collection focusing on proteins that are drug-targets or candidate drug-targets and for which structural data are present in the Protein Data Bank. The BindingDB website supports a range of query types, including searches by chemical structure, substructure and similarity; protein sequence; ligand and protein names; affinity ranges and molecular weight. Data sets generated by BindingDB queries can be downloaded in the form of annotated SDfiles for further analysis, or used as the basis for virtual screening of a compound database uploaded by the user. The data in BindingDB are linked both to structural data in the PDB via PDB IDs and chemical and sequence searches, and to the literature in PubMed via PubMed IDs.
Figures
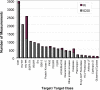
Figure 1
Number of measurements in BindingDB for various targets and target classes.
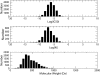
Figure 2
Histograms of binding affinities (1 M standard concentration), and molecular weights of ligands in BindingDB.
Similar articles
- BindingDB in 2015: A public database for medicinal chemistry, computational chemistry and systems pharmacology.
Gilson MK, Liu T, Baitaluk M, Nicola G, Hwang L, Chong J. Gilson MK, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D1045-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1072. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26481362 Free PMC article. - BindingDB: a web-accessible molecular recognition database.
Chen X, Liu M, Gilson MK. Chen X, et al. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2001 Dec;4(8):719-25. doi: 10.2174/1386207013330670. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2001. PMID: 11812264 - AffinDB: a freely accessible database of affinities for protein-ligand complexes from the PDB.
Block P, Sotriffer CA, Dramburg I, Klebe G. Block P, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D522-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj039. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16381925 Free PMC article. - The use of protein-ligand interaction fingerprints in docking.
Brewerton SC. Brewerton SC. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008 May;11(3):356-64. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008. PMID: 18428089 Review. - MINT: a Molecular INTeraction database.
Zanzoni A, Montecchi-Palazzi L, Quondam M, Ausiello G, Helmer-Citterich M, Cesareni G. Zanzoni A, et al. FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 20;513(1):135-40. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03293-8. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11911893 Review.
Cited by
- Comparability of mixed IC₅₀ data - a statistical analysis.
Kalliokoski T, Kramer C, Vulpetti A, Gedeck P. Kalliokoski T, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 16;8(4):e61007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061007. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23613770 Free PMC article. - A high quality, industrial data set for binding affinity prediction: performance comparison in different early drug discovery scenarios.
Tosstorff A, Rudolph MG, Cole JC, Reutlinger M, Kramer C, Schaffhauser H, Nilly A, Flohr A, Kuhn B. Tosstorff A, et al. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2022 Oct;36(10):753-765. doi: 10.1007/s10822-022-00478-x. Epub 2022 Sep 25. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2022. PMID: 36153472 - New Frontiers in Druggability.
Kozakov D, Hall DR, Napoleon RL, Yueh C, Whitty A, Vajda S. Kozakov D, et al. J Med Chem. 2015 Dec 10;58(23):9063-88. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00586. Epub 2015 Aug 11. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26230724 Free PMC article. - Multi-task bioassay pre-training for protein-ligand binding affinity prediction.
Yan J, Ye Z, Yang Z, Lu C, Zhang S, Liu Q, Qiu J. Yan J, et al. Brief Bioinform. 2023 Nov 22;25(1):bbad451. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad451. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 38084920 Free PMC article. - TOPAS, a network-based approach to detect disease modules in a top-down fashion.
Buzzao D, Castresana-Aguirre M, Guala D, Sonnhammer ELL. Buzzao D, et al. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2022 Nov 29;4(4):lqac093. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqac093. eCollection 2022 Dec. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36458021 Free PMC article.
References
- Chen X., Liu M., Gilson M.K. BindingDB: A Web-accessible molecular recognition database. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2002;4:719–725. - PubMed
- Chen X., Lin Y., Liu M., Gilson M.K. The binding database: Data management and interface design. Bioinformatics. 2002;18:130–139. - PubMed
- Chen X., Liu M., Gilson M.K. The binding database: Overview and user's guide. Biopolymers/Nucleic Acid Sci. 2002;61:127–141. - PubMed
- Bernstein F.C., Koetzle T.F., Williams T.F., Meyer G.J.B., Jr, Brice M.D., Rodgers J.R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: A computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Biol. 1977;112:535–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases