Mutations in the gene encoding the synaptic scaffolding protein SHANK3 are associated with autism spectrum disorders - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1038/ng1933. Epub 2006 Dec 17.
Catalina Betancur, Tobias M Boeckers, Juergen Bockmann, Pauline Chaste, Fabien Fauchereau, Gudrun Nygren, Maria Rastam, I Carina Gillberg, Henrik Anckarsäter, Eili Sponheim, Hany Goubran-Botros, Richard Delorme, Nadia Chabane, Marie-Christine Mouren-Simeoni, Philippe de Mas, Eric Bieth, Bernadette Rogé, Delphine Héron, Lydie Burglen, Christopher Gillberg, Marion Leboyer, Thomas Bourgeron
Affiliations
- PMID: 17173049
- PMCID: PMC2082049
- DOI: 10.1038/ng1933
Mutations in the gene encoding the synaptic scaffolding protein SHANK3 are associated with autism spectrum disorders
Christelle M Durand et al. Nat Genet. 2007 Jan.
Abstract
SHANK3 (also known as ProSAP2) regulates the structural organization of dendritic spines and is a binding partner of neuroligins; genes encoding neuroligins are mutated in autism and Asperger syndrome. Here, we report that a mutation of a single copy of SHANK3 on chromosome 22q13 can result in language and/or social communication disorders. These mutations concern only a small number of individuals, but they shed light on one gene dosage-sensitive synaptic pathway that is involved in autism spectrum disorders.
Figures
Figure 1
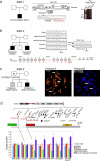
Genetic analyses of three families with ASD and SHANK3 mutations, (a) In family ASD 1, the proband carries a de novo terminal deletion of the paternal chromosome 22q13. The deletion breakpoint is located in intron 8 of SHANK3. The breakpoint was sequenced after amplification of the proband DNA using primer 1 in SHANK3 and primer 2 in the telomeric repeats. The heterogenous smear in the proband is likely due to the difference in telomere length from chromosome to chromosome and/or priming at different locations by the telomeric primer, (b) In family ASD 2, the two probands carry the same de novo SHANK3 frame-shift mutation on the maternal chromosome 22q13. The mutation is absent from the mother blood and buccal cells, suggesting a germinal mosaicism. The guanine insertion is located in exon 21 of SHANK3, leading to a premature truncated protein, (c) In family ASD 3, the father carries a balanced translocation t(14,22)(p11.2;q13.33), proband A (Asperger syndrome) presents a partial 22qter trisomy and proband B (autism) has a 22qter deletion, (d) Using quantitative fluorescent PCR, we mapped the breakpoint between the genes ALG12 and MLC1. The dosage quotient has a theoretical value of 0.5 for a deletion and 1.5 for a duplication.
Figure 2
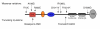
Localization of rare nonsynonymous variations or truncating SHANK3 mutations identified in families with ASD. ANK: ankyrin repeats; SH3: Src homology 3 domain; PDZ: postsynaptic density 95/Discs large/zona occludens-1 homology domain; SAM: sterile alpha motif domain.
Similar articles
- Mutations of the X-linked genes encoding neuroligins NLGN3 and NLGN4 are associated with autism.
Jamain S, Quach H, Betancur C, Råstam M, Colineaux C, Gillberg IC, Soderstrom H, Giros B, Leboyer M, Gillberg C, Bourgeron T; Paris Autism Research International Sibpair Study. Jamain S, et al. Nat Genet. 2003 May;34(1):27-9. doi: 10.1038/ng1136. Nat Genet. 2003. PMID: 12669065 Free PMC article. - [Autism: more evidence of a genetic cause].
Bourgeron T, Leboyer M, Delorme R. Bourgeron T, et al. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2009 Feb;193(2):299-304; discussion 304-5. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2009. PMID: 19718887 French. - Association between deletion size and important phenotypes expands the genomic region of interest in Phelan-McDermid syndrome (22q13 deletion syndrome).
Sarasua SM, Dwivedi A, Boccuto L, Rollins JD, Chen CF, Rogers RC, Phelan K, DuPont BR, Collins JS. Sarasua SM, et al. J Med Genet. 2011 Nov;48(11):761-6. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100225. Epub 2011 Oct 7. J Med Genet. 2011. PMID: 21984749 - The possible interplay of synaptic and clock genes in autism spectrum disorders.
Bourgeron T. Bourgeron T. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:645-54. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2007.72.020. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007. PMID: 18419324 Review. - Analysis of a purported SHANK3 mutation in a boy with autism: clinical impact of rare variant research in neurodevelopmental disabilities.
Kolevzon A, Cai G, Soorya L, Takahashi N, Grodberg D, Kajiwara Y, Willner JP, Tryfon A, Buxbaum JD. Kolevzon A, et al. Brain Res. 2011 Mar 22;1380:98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.11.005. Epub 2010 Nov 6. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21062623 Review.
Cited by
- Common mechanisms of excitatory and inhibitory imbalance in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorders.
Gao R, Penzes P. Gao R, et al. Curr Mol Med. 2015;15(2):146-67. doi: 10.2174/1566524015666150303003028. Curr Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25732149 Free PMC article. Review. - Meta-analysis of epigenome-wide association studies of major depressive disorder.
Li QS, Morrison RL, Turecki G, Drevets WC. Li QS, et al. Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 1;12(1):18361. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22744-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36319817 Free PMC article. - A Novel Stratification Method in Linkage Studies to Address Inter- and Intra-Family Heterogeneity in Autism.
Talebizadeh Z, Arking DE, Hu VW. Talebizadeh Z, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Jun 26;8(6):e67569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067569. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840741 Free PMC article. - Prospective diagnostic analysis of copy number variants using SNP microarrays in individuals with autism spectrum disorders.
Nava C, Keren B, Mignot C, Rastetter A, Chantot-Bastaraud S, Faudet A, Fonteneau E, Amiet C, Laurent C, Jacquette A, Whalen S, Afenjar A, Périsse D, Doummar D, Dorison N, Leboyer M, Siffroi JP, Cohen D, Brice A, Héron D, Depienne C. Nava C, et al. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014 Jan;22(1):71-8. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.88. Epub 2013 May 1. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 23632794 Free PMC article. - Autism genetics: searching for specificity and convergence.
Berg JM, Geschwind DH. Berg JM, et al. Genome Biol. 2012 Jul 31;13(7):247. doi: 10.1186/gb4034. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 22849751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Folstein SE, Rosen-Sheidley B. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:943–955. - PubMed
- Persico AM, Bourgeron T. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:349–358. - PubMed
- Vorstman JA, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11(1):18–28. - PubMed
- Manning MA, et al. Pediatrics. 2004;114:451–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases