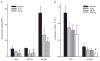Protectin D1 is generated in asthma and dampens airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness - PubMed (original) (raw)
Protectin D1 is generated in asthma and dampens airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness
Bruce D Levy et al. J Immunol. 2007.
Abstract
Protectins are newly identified natural chemical mediators that counter leukocyte activation to promote resolution of inflammation. In this study, we provide the first evidence for protectin D1 (PD1, 10R,17S-dihydroxy-docosa-4Z,7Z,11E,13E,15Z,19Z-hexaenoic acid) formation from docosahexaenoic acid in human asthma in vivo and PD1 counterregulatory actions in allergic airway inflammation. PD1 and 17S-hydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid were present in exhaled breath condensates from healthy subjects. Of interest, levels of PD1 were significantly lower in exhaled breath condensates from subjects with asthma exacerbations. PD1 was also present in extracts of murine lungs from both control animals and those sensitized and aerosol challenged with allergen. When PD1 was administered before aeroallergen challenge, airway eosinophil and T lymphocyte recruitment were decreased, as were airway mucus, levels of specific proinflammatory mediators, including IL-13, cysteinyl leukotrienes, and PGD(2), and airway hyperresponsiveness to inhaled methacholine. Of interest, PD1 treatment after aeroallergen challenge markedly accelerated the resolution of airway inflammation. Together, these findings provide evidence for endogenous PD1 as a pivotal counterregulatory signal in allergic airway inflammation and point to new therapeutic strategies for modulating inflammation in asthmatic lung.
Figures
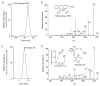
FIGURE 1
Generation of PD1 in asthma. EBC were obtained from volunteer subjects in the emergency department during a clinical exacerbation of asthma. Lipids were extracted and subjected to analysis by LC-PDA-MS-MS. a, LC chromatogram plotted for ms/ms at m/z 343 and corresponding MS profile were diagnostic for 17_S_-hydroxy-DHA (i.e., 17_S_-hydroxy-docosa-4Z, 7Z,11E,13E,15Z,19Z-hexaenoic acid) (b). Material was also present in the lipid extracts with LC chromatogram for m/z 217 of MS-MS at m/z 359 (c), UV absorbance spectrum (d, inset, left), and mass spectrum diagnostic for authentic PD1 (i.e., 10_R_,17_S_-dihydroxy-docosa-4Z,7Z,11E,13E,15Z, 19Z-hexaenoic acid). _Inset_s, the fragmentation ions are denoted for 17_S_-hydroxy-DHA (b) and PD1 (d). Results are representative of n = 3.
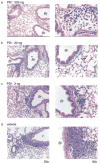
FIGURE 2
Lung histopathology from mice given PD1. Mice were sensitized and aerosol challenged with OVA in the presence of PD1 (200 ng (a), 20 ng (b), 2 ng (c)) or vehicle (d). Representative (n ≥ 3) lung tissue sections (original magnifications, ×20 (left column) and ×40 (right column)) were obtained from fixed, paraffin-embedded lung tissue, prepared, and stained with H&E. Arrows denote representative EOS; Br, bronchus; v, vessel.
FIGURE 3
PD1 decreases airway mucus. Representative lung tissue sections from mice given PD1 (200 ng (a), 20 ng (b)) or vehicle (c) were stained with periodic acid Schiff (original magnifications, ×20 (left column) and ×40 (right column). Arrows indicate representative mucus (magenta) containing goblet cells.
FIGURE 4
PD1 sharply reduces leukocyte infiltration. a, Tissue morphometric analyses were performed to determine the impact of PD1 on EOS accumulation in pulmonary vessels (V-EOS), large airways (Aw-EOS), and alveoli (Alv-EOS). b, BALFs were obtained from OVA-sensitized and challenged mice. Leukocytes in BALF were enumerated and identified after Wright-Giemsa stain. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3).*, p < 0.05 by Student’s t test compared with control animals.
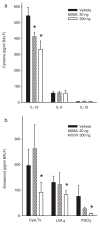
FIGURE 5
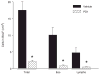
PD1 selectively decreases airway inflammatory mediators. In the presence or absence of PD1, the mediator profile in BALF was determined in materials from OVA-sensitized and challenged mice for specific cytokines (IL-13, IL-5, IL-12) (a ), and lipid mediators (CysLTs, LXA4, and PGD2) (b). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 5, determinations = 2).*, p < 0.05 by Student’s t test compared with control animals.
FIGURE 6
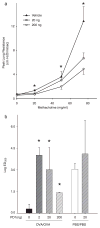
PD1 reduces airway hyperresponsiveness. a, OVA-sensitized mice were treated with PD1 20 ng (□), 200 ng (○), or vehicle (▲) before OVA aerosol challenge. Airway reactivity was determined by methacholine-dependent change in peak lung resistance. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 5).*, p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA compared with control animals. b, ED200 was determined for methacholine-dependent changes in mean lung resistance for OVA-sensitized animals receiving PD1 (0, 2, 20, or 200 ng) before OVA aerosol challenge and for control animals receiving buffer (PBS) instead of OVA during sensitization and challenge phases of the model.*, p < 0.05 by Student’s t test compared with control animals.
FIGURE 7
PD1 treatment promotes resolution of allergen-driven leukocytes in mouse lung. BALFs were obtained from OVA-sensitized and challenged mice that received either PD1 (20 ng, ▨) or vehicle (0.9% saline, ■) for three consecutive days before study. Leukocytes in BALF were enumerated and identified after Wright-Giemsa stain. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3).*, p < 0.05 by Student’s t test compared with control animals.
Similar articles
- Anti-inflammatory actions of neuroprotectin D1/protectin D1 and its natural stereoisomers: assignments of dihydroxy-containing docosatrienes.
Serhan CN, Gotlinger K, Hong S, Lu Y, Siegelman J, Baer T, Yang R, Colgan SP, Petasis NA. Serhan CN, et al. J Immunol. 2006 Feb 1;176(3):1848-59. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.3.1848. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16424216 - Resolvins D1, D2, and other mediators of self-limited resolution of inflammation in human blood following n-3 fatty acid supplementation.
Mas E, Croft KD, Zahra P, Barden A, Mori TA. Mas E, et al. Clin Chem. 2012 Oct;58(10):1476-84. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2012.190199. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Clin Chem. 2012. PMID: 22912397 - Resolvin E1 dampens airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma.
Aoki H, Hisada T, Ishizuka T, Utsugi M, Kawata T, Shimizu Y, Okajima F, Dobashi K, Mori M. Aoki H, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Mar 7;367(2):509-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.012. Epub 2008 Jan 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18190790 - Airway hyperresponsiveness: first eosinophils and then neuropeptides.
Kraneveld AD, Folkerts G, Van Oosterhout AJ, Nijkamp FP. Kraneveld AD, et al. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1997 Sep-Oct;19(9-10):517-27. doi: 10.1016/s0192-0561(97)00085-4. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9637348 Review. - Understanding asthma pathophysiology.
Fireman P. Fireman P. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2003 Mar-Apr;24(2):79-83. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2003. PMID: 12776439 Review.
Cited by
- Cutting edge: maresin-1 engages regulatory T cells to limit type 2 innate lymphoid cell activation and promote resolution of lung inflammation.
Krishnamoorthy N, Burkett PR, Dalli J, Abdulnour RE, Colas R, Ramon S, Phipps RP, Petasis NA, Kuchroo VK, Serhan CN, Levy BD. Krishnamoorthy N, et al. J Immunol. 2015 Feb 1;194(3):863-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402534. Epub 2014 Dec 24. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25539814 Free PMC article. - Chronic endotoxin exposure produces airflow obstruction and lung dendritic cell expansion.
Lai PS, Fresco JM, Pinilla MA, Macias AA, Brown RD, Englert JA, Hofmann O, Lederer JA, Hide W, Christiani DC, Cernadas M, Baron RM. Lai PS, et al. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Aug;47(2):209-17. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0447OC. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22517795 Free PMC article. - Specific lipid mediator signatures of human phagocytes: microparticles stimulate macrophage efferocytosis and pro-resolving mediators.
Dalli J, Serhan CN. Dalli J, et al. Blood. 2012 Oct 11;120(15):e60-72. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-423525. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22904297 Free PMC article. - Endogenous pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory lipid mediators: a new pharmacologic genus.
Serhan CN, Chiang N. Serhan CN, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;153 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S200-15. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707489. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17965751 Free PMC article. Review. - Fat-1 transgenic mice with elevated omega-3 fatty acids are protected from allergic airway responses.
Bilal S, Haworth O, Wu L, Weylandt KH, Levy BD, Kang JX. Bilal S, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Sep;1812(9):1164-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.05.002. Epub 2011 May 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21616147 Free PMC article.
References
- Busse WW, Lemanske RF., Jr Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:350–362. - PubMed
- Levy BD. Lipoxins and lipoxin analogs in asthma. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Essent Fatty Acids. 2005;73:231–237. - PubMed
- Hong S, Gronert K, Devchand PR, Moussignac RL, Serhan CN. Novel docosatrienes and 17S-resolvins generated from docosahexaenoic acid in murine brain, human blood, and glial cells: autacoids in anti-inflammation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:14677–14687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL068669/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DE016191/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- AI068084/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL068669/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI068084/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50-DE016191/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI068084/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous