Derivatization with Girard reagent T combined with LC-MS/MS for the sensitive detection of 5-formyl-2'-deoxyuridine in cellular DNA - PubMed (original) (raw)
Derivatization with Girard reagent T combined with LC-MS/MS for the sensitive detection of 5-formyl-2'-deoxyuridine in cellular DNA
Haizheng Hong et al. Anal Chem. 2007.
Abstract
Nucleoside 5-formyl-2'-deoxyuridine (FodU) is a major thymidine lesion generated by reactive oxygen species. In vitro and in vivo replication studies revealed that FodU can be mutagenic. A reliable and sensitive quantification method is, therefore, important for assessing the biological implications of this lesion. However, the detection limit of FodU by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was relatively poor compared with those of other oxidative DNA base damages. In this paper we described a new approach for the highly sensitive detection of FodU. We derivatized FodU with Girard reagent T to form a hydrazone conjugate harboring a precharged quaternary ammonium moiety, which enabled the facile detection of the resulting conjugate by positive-ion electrospray ionization MS. We also showed that the combination of derivatization with LC-MS/MS on a linear-ion-trap mass spectrometer could allow for the quantification of FodU at a detection limit of 3-4 fmol, which is approximately 20-fold better than that for the direct analysis of the underivatized compound. By using isotope-labeled FodU as the internal standard and this derivatization method, we further quantified, by using LC-MS/MS, the yield of FodU formed in cellular DNA.
Figures
Figure 1
The reaction of FodU with GirT.
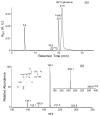
Figure 2
(a) The HPLC trace for the separation of the reaction mixture where FodU was treated with GirT at a molar ratio of 1:2 at room temperature for 12 h. (b) ESI-MS of the ion of m/z 254 observed in MS/MS; shown in the inset are the MS/MS of the [M + H]+ ion of the hydrazone conjugate and the cleavage reactions for the formation of major fragment ions found in MS.
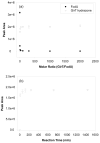
Figure 3
(a) Optimization of the molar ratios of GirT over FodU for the derivatization. GirT was mixed with FodU at molar ratios of 2:1, 10:1, 30:1, 100:1, 300:1, 1000:1 and 2000:1 in the presence of 10% acetic acid, and the reactions were continued at room temperature for 12 h. Plotted are the HPLC peak areas for FodU and the hydrazone conjugate. (b) Optimization of the derivatization time. GirT was mixed with FodU at a molar ratio of 10:1 in the presence of 10% acetic acid, and the reactions were carried out at room temperature for time periods of 10 min and 1, 2, 4, 12 and 24 h, respectively. Plotted are the HPLC peak areas for the hydrazone conjugate (the fractions were monitored by UV detection at 281 nm). The values represent the means ± SD from three independent measurements.
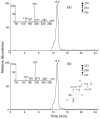
Figure 4
SICs for the monitoring of the m/z 370→254→195 [a, for unlabeled FodU-GirT hydrazone] and m/z 373→256→197 [b, for isotopically labeled FodU-GirT hydrazone] transitions of the digestion mixtures of the cellular DNA samples, which were extracted from Hela-S3 cells treated with 110 Gy of γ-rays. Shown in the insets are the MS of the ions of m/z 254 and 256 for the unlabeled and labeled hydrazones, respectively. The “*” in the structure shown in the inset of panel b designates that the nitrogen atoms are replaced with an “15N”.
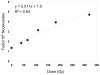
Figure 5
Dose-dependent formation of FodU in Hela-S3 cells upon exposure to γ-rays. The values represent the means ± SD from three independent measurements.
Similar articles
- Development of a rapid and sensitive LC-ESI/MS/MS assay for the quantification of propofol using a simple off-line dansyl chloride derivatization reaction to enhance signal intensity.
Beaudry F, Guénette SA, Winterborn A, Marier JF, Vachon P. Beaudry F, et al. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005 Sep 15;39(3-4):411-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2005.04.041. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005. PMID: 15963676 - Sensitive Detection of 8-Nitroguanine in DNA by Chemical Derivatization Coupled with Online Solid-Phase Extraction LC-MS/MS.
Hu CW, Chang YJ, Chen JL, Hsu YW, Chao MR. Hu CW, et al. Molecules. 2018 Mar 8;23(3):605. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030605. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29517997 Free PMC article. - Girard derivatization for LC-MS/MS profiling of endogenous ecdysteroids in Drosophila.
Lavrynenko O, Nedielkov R, Möller HM, Shevchenko A. Lavrynenko O, et al. J Lipid Res. 2013 Aug;54(8):2265-2272. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D035949. Epub 2013 Feb 19. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23843360 Free PMC article. - LC-MS determination of bioactive molecules based upon stable isotope-coded derivatization method.
Toyo'oka T. Toyo'oka T. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012 Oct;69:174-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2012.04.018. Epub 2012 Apr 25. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012. PMID: 22575224 Review. - Androgen glucuronides analysis by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry: could it raise new perspectives in the diagnostic field of hormone-dependent malignancies?
Kalogera E, Pistos C, Provatopoulou X, Athanaselis S, Spiliopoulou C, Gounaris A. Kalogera E, et al. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 Dec 1;940:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.09.022. Epub 2013 Sep 27. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24140653 Review.
Cited by
- Gene specific-loci quantitative and single-base resolution analysis of 5-formylcytosine by compound-mediated polymerase chain reaction.
Wang Y, Liu C, Zhang X, Yang W, Wu F, Zou G, Weng X, Zhou X. Wang Y, et al. Chem Sci. 2018 Mar 19;9(15):3723-3728. doi: 10.1039/c8sc00493e. eCollection 2018 Apr 21. Chem Sci. 2018. PMID: 29780504 Free PMC article. - Synergistic effects on mutagenicity of tandem lesions containing 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine or Fapy•dG flanked by a 3' 5-formyl-2'-deoxyuridine in human cells.
Bacurio JHT, Gao S, Yang H, Basu AK, Greenberg MM. Bacurio JHT, et al. DNA Repair (Amst). 2023 Sep;129:103527. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2023.103527. Epub 2023 Jun 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2023. PMID: 37467631 Free PMC article. - High-throughput quantification of bioactive lipids by MALDI mass spectrometry: application to prostaglandins.
Manna JD, Reyzer ML, Latham JC, Weaver CD, Marnett LJ, Caprioli RM. Manna JD, et al. Anal Chem. 2011 Sep 1;83(17):6683-8. doi: 10.1021/ac201224n. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Anal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21770391 Free PMC article. - A Carbonyl Capture Approach for Profiling Oxidized Metabolites in Cell Extracts.
Mattingly SJ, Xu T, Nantz MH, Higashi RM, Fan TW. Mattingly SJ, et al. Metabolomics. 2012;8(6):989-996. doi: 10.1007/s11306-011-0395-z. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Metabolomics. 2012. PMID: 23175637 Free PMC article. - Ultrasensitive Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Rare Modified Nucleosides as Promising Biomarkers in Low-Put Breast Cancer DNA Samples for Clinical Multi-Dimensional Diagnosis.
Yu Y, Pan HY, Zheng X, Yuan F, Zhou YL, Zhang XX. Yu Y, et al. Molecules. 2022 Oct 19;27(20):7041. doi: 10.3390/molecules27207041. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296634 Free PMC article.
References
- Lindahl T. NATO ASI Ser., Ser. A. 1999;302:251–257.
- Finkel T, Holbrook NJ. Nature. 2000;408:239–247. - PubMed
- Marnett LJ. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:361–370. - PubMed
- Masaoka A, Terato H, Kobayashi M, Ohyama Y, Ide H. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:16501–16510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources