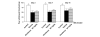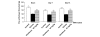Antinociceptive efficacy of lacosamide in the monosodium iodoacetate rat model for osteoarthritis pain - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Antinociceptive efficacy of lacosamide in the monosodium iodoacetate rat model for osteoarthritis pain
Bettina Beyreuther et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007.
Abstract
The etiology of osteoarthritis is multifactorial, with inflammatory, metabolic, and mechanical causes. Pain in osteoarthritis is initiated by mild intra-articular inflammation and degeneration of articular cartilage and subchondral bone. The principle of treatment with acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is to reduce pain and improve joint function. Recently, animal models for osteoarthritic pain behavior have been established. The most frequently used rat model for analyzing properties of drugs on the pathology of osteoarthritis is the injection of the metabolic inhibitor monosodium iodoacetate into the joint, which inhibits the activity of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in chondrocytes. Here, we characterize the effect on pain behavior of lacosamide, a member of a family of functionalized amino acids that are analogues of endogenous amino acids and D-serine, in the monosodium iodoacetate rat model for osteoarthritis in comparison to diclofenac and morphine. Lacosamide (3, 10, and 30 mg/kg) was able to reduce secondary mechanical allodynia and hyperalgesia similarly to morphine (3 mg/kg). In contrast, diclofenac (30 mg/kg) was only effective in reducing secondary mechanical hyperalgesia. During the first week, pain is induced mainly by inflammation in the iodoacetate model, but afterwards inflammation plays only a minor role in pain. Lacosamide was able to inhibit pain at days 3, 7 and 14 after induction of arthritis. This shows that lacosamide is able to reduce pain behavior induced by multiple mechanisms in animals.
Figures
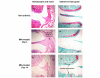
Figure 1
Histological analysis of synovial tissue and articular cartilage pre- and post-monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) injection. Time course of histological changes of the rat knee before and days 3 and 14 after MIA injection. Left sections of the medial aspect of rat knee joints were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, right sections with safranin-O fast green. In non-arthritic rats no abnormality is present. On day 3 after MIA treatment the hematoxylin and eosin stained sections show significant expansion of the synovial membrane with a large amount of cellular infiltrate. No inflammation can be seen on day 14 post-MIA injection. The sections stained with safranin-O fast green reflect major cartilage degeneration on day 14 post-MIA injection. SM, synovial membrane; FE, femur; TI, tibia.
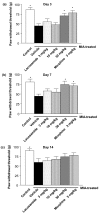
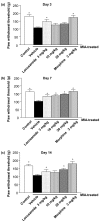
Figure 2
Effect of lacosamide and morphine on tactile allodynia after monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) injection. Effect of lacosamide and morphine on paw withdrawal threshold in the von Frey filament test in iodoacetate-treated animals on (a) day 3, (b) day 7 and (c) day 14 after arthritis induction. Rats were tested 45 to 60 minutes post-drug. Data from 12 animals/group are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 Dunnett's test versus MIA/vehicle treated animals.
Figure 3
Effect of diclofenac on tactile allodynia after monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) injection. Effect of diclofenac on paw withdrawal threshold in the von Frey filament test in iodoacetate-treated animals on days 3, 7 and 14 after arthritis induction. Rats were tested 45 to 60 minutes post drug. Data from12 animals/group are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 Dunnett's test versus MIA/vehicle treated animals.
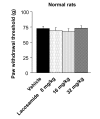
Figure 4
Tactile allodynia measurement in normal rats after lacosamide treatment. Effect of lacosamide on paw withdrawal threshold in the von Frey filament test in saline treated normal rats. Rats were tested 30 minutes post-drug. Data from eight animals/group are presented as mean ± SEM.
Figure 5
Effect of lacosamide and morphine on mechanical hyperalgesia after monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) injection. Effect of lacosamide and morphine on paw withdrawal threshold in the paw pressure test in MIA-treated animals on (a) day 3, (b) day 7 and (c) day 14 after arthritis induction. Rats were tested 45 to 60 minutes post-drug. Data from 12 animals/group are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 Dunnett's test versus MIA/vehicle treated animals.
Figure 6
Effect of diclofenac on mechanical hyperalgesia after monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) injection. Effect of diclofenac on paw withdrawal threshold in the paw pressure test in MIA-treated animals on days 3, 7 and 14 after arthritis induction. Rats were tested 45 to 60 minutes post-drug. Data from 12 animals/group are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 Dunnett's test versus MIA/vehicle treated animals.
Similar articles
- Antinociceptive effects of lacosamide on spinal neuronal and behavioural measures of pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis.
Rahman W, Dickenson AH. Rahman W, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Dec 23;16(6):509. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0509-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25533381 Free PMC article. - Pre-treatment with capsaicin in a rat osteoarthritis model reduces the symptoms of pain and bone damage induced by monosodium iodoacetate.
Kalff KM, El Mouedden M, van Egmond J, Veening J, Joosten L, Scheffer GJ, Meert T, Vissers K. Kalff KM, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Sep 1;641(2-3):108-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.05.022. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20538089 - Effect of alcoholic extract of Entada pursaetha DC on monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis pain in rats.
Kumari RR, More AS, Gupta G, Lingaraju MC, Balaganur V, Kumar P, Kumar D, Sharma AK, Mishra SK, Tandan SK. Kumari RR, et al. Indian J Med Res. 2015 Apr;141(4):454-62. doi: 10.4103/0971-5916.159296. Indian J Med Res. 2015. PMID: 26112847 Free PMC article. - Beyond rodent models of pain: non-human primate models for evaluating novel analgesic therapeutics and elaborating pain mechanisms.
Hama AT, Toide K, Takamatsu H. Hama AT, et al. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013 Dec;12(8):1257-70. doi: 10.2174/18715273113129990111. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 24111837 Review. - Interest of animal models in the preclinical screening of anti-osteoarthritic drugs.
Jouzeau JY, Gillet P, Netter P. Jouzeau JY, et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2000;67(6):565-9. doi: 10.1016/s1297-319x(00)00214-1. Joint Bone Spine. 2000. PMID: 11195325 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Effects of Low-Level Laser Therapy, 660 nm, in Experimental Septic Arthritis.
Araujo BF, Silva LI, Meireles A, Rosa CT, Gioppo NM, Jorge AS, Kunz RI, Ribeiro Lde F, Brancalhão RM, Bertolini GR. Araujo BF, et al. ISRN Rheumatol. 2013 Aug 12;2013:341832. doi: 10.1155/2013/341832. eCollection 2013. ISRN Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23997964 Free PMC article. - Effects of Tribulus terrestris on monosodium iodoacetate‑induced osteoarthritis pain in rats.
Park YJ, Cho YR, Oh JS, Ahn EK. Park YJ, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):5303-5311. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7296. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28849084 Free PMC article. - Osteoarthritis pain: nociceptive or neuropathic?
Thakur M, Dickenson AH, Baron R. Thakur M, et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014 Jun;10(6):374-80. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.47. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24686507 Review. - Animal models of osteoarthritis: characterization of a model induced by Mono-Iodo-Acetate injected in rabbits.
Rebai MA, Sahnoun N, Abdelhedi O, Keskes K, Charfi S, Slimi F, Frikha R, Keskes H. Rebai MA, et al. Libyan J Med. 2020 Dec;15(1):1753943. doi: 10.1080/19932820.2020.1753943. Libyan J Med. 2020. PMID: 32281500 Free PMC article. - Antinociceptive effects of lacosamide on spinal neuronal and behavioural measures of pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis.
Rahman W, Dickenson AH. Rahman W, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Dec 23;16(6):509. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0509-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25533381 Free PMC article.
References
- Bendele AM. Animal models of osteoarthritis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2001;1:363–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials