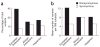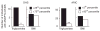Population-based resequencing of ANGPTL4 uncovers variations that reduce triglycerides and increase HDL - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
doi: 10.1038/ng1984. Epub 2007 Feb 25.
Affiliations
- PMID: 17322881
- PMCID: PMC2762948
- DOI: 10.1038/ng1984
Multicenter Study
Population-based resequencing of ANGPTL4 uncovers variations that reduce triglycerides and increase HDL
Stefano Romeo et al. Nat Genet. 2007 Apr.
Abstract
Resequencing genes provides the opportunity to assess the full spectrum of variants that influence complex traits. Here we report the first application of resequencing to a large population (n = 3,551) to examine the role of the adipokine ANGPTL4 in lipid metabolism. Nonsynonymous variants in ANGPTL4 were more prevalent in individuals with triglyceride levels in the lowest quartile than in individuals with levels in the highest quartile (P = 0.016). One variant (E40K), present in approximately 3% of European Americans, was associated with significantly lower plasma levels of triglyceride and higher levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in European Americans from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study and in Danes from the Copenhagen City Heart Study. The ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous variants was higher in European Americans than in African Americans (4:1 versus 1.3:1), suggesting population-specific relaxation of purifying selection. Thus, resequencing of ANGPTL4 in a multiethnic population allowed analysis of the phenotypic effects of both rare and common variants while taking advantage of genetic variation arising from ethnic differences in population history.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
Figure 1
Schematic of the ANGPTL4 gene with location of nonsynonymous sequence variations identified in the upper and lower quartiles of Dallas Heart Study. The 406-residue protein comprises a signal sequence (SP), a coiled-coil domain (CC) and a fibrinogen-like domain. Sequence variants found among individuals in the low-triglyceride group (plasma triglyceride levels less than or equal to the 25th percentile) but not in individuals in the high-triglyceride group (plasma triglyceride levels greater than or equal to the 75th percentile) are shown below the protein. Sequence variants found in the high-triglyceride group but not in the low-triglyceride group are shown above the protein. Sequence variants found in African Americans are indicated by boxes. All variants were found in separate individuals in each group, except for R336C, which was found in three individuals in the low group (asterisk indicates n = 3). Thus, the number of individuals with nonsynonymous sequence variants in the bottom quartile (n = 13) was significantly greater than the number in the highest quartile (n = 2; P = 0.016). fs, frameshift.
Figure 2
Proportion of nonsynonymous and synonymous sequence variants in European Americans, African Americans and Hispanics in the Dallas Heart Study. (a) Number of nonsynonymous and synonymous variants expressed as a percentage of the total number of variants identified in the three ethnic groups in the DHS. (b) Number of nonsynonymous and synonymous variants identified per 596 individuals in each population. To adjust for the different numbers of individuals in each group, five subsamples of 596 individuals (corresponding to the total number of Hispanics from whom sequence data were obtained) were drawn at random from the 1,045 European Americans and from the 1,830 African Americans in the sample. The number of nonsynonymous and synonymous variants was determined in each subsample, and the average number across the five subsamples was calculated. This random selection process was repeated once, with essentially identical results.
Figure 3
Prevalence of the _ANGPTL4_[E40K] allele among individuals with low and high plasma triglyceride levels in the Dallas Heart Study and ARIC study. European American participants in the DHS were stratified by plasma triglyceride level (which was significantly associated with the E40K variant in all three populations) and by BMI (which was not associated with the variant in any of the three populations). The number of _ANGPTL4_[E40K] carriers in the upper and lower quartiles for each trait was determined. A corresponding analysis was performed in the ARIC study using the upper and lower 5% of the population distribution for the two traits. *P = 0.008; **P = 1.1 × 10 −9.
Comment in
- The resequencing imperative.
Topol EJ, Frazer KA. Topol EJ, et al. Nat Genet. 2007 Apr;39(4):439-40. doi: 10.1038/ng0407-439. Nat Genet. 2007. PMID: 17392801 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- ANGPTL4 variants E40K and T266M are associated with lower fasting triglyceride levels in Non-Hispanic White Americans from the Look AHEAD Clinical Trial.
Smart-Halajko MC, Kelley-Hedgepeth A, Montefusco MC, Cooper JA, Kopin A, McCaffrey JM, Balasubramanyam A, Pownall HJ, Nathan DM, Peter I, Talmud PJ, Huggins GS; Look AHEAD Study. Smart-Halajko MC, et al. BMC Med Genet. 2011 Jun 29;12:89. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-12-89. BMC Med Genet. 2011. PMID: 21714923 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Carbohydrate intake modifies associations between ANGPTL4[E40K] genotype and HDL-cholesterol concentrations in White men from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study.
Nettleton JA, Volcik KA, Hoogeveen RC, Boerwinkle E. Nettleton JA, et al. Atherosclerosis. 2009 Mar;203(1):214-20. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.05.037. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Atherosclerosis. 2009. PMID: 18599063 Free PMC article. - Association of blood lipids with common DNA sequence variants at 19 genetic loci in the multiethnic United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III.
Keebler ME, Sanders CL, Surti A, Guiducci C, Burtt NP, Kathiresan S. Keebler ME, et al. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009 Jun;2(3):238-43. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.108.829473. Epub 2009 Apr 14. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009. PMID: 20031591 Free PMC article. - Differential association of plasma angiopoietin-like proteins 3 and 4 with lipid and metabolic traits.
Mehta N, Qamar A, Qu L, Qasim AN, Mehta NN, Reilly MP, Rader DJ. Mehta N, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 May;34(5):1057-63. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302802. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24626437 Free PMC article. - Impacts of angiopoietin-like proteins on lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular events.
Miida T, Hirayama S. Miida T, et al. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2010 Feb;21(1):70-5. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e328333269e. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2010. PMID: 19851103 Review.
Cited by
- Distinct roles of angiopoietin-like 4 in the regulation of central and peripheral lipid metabolism?
Blüher M. Blüher M. Mol Metab. 2014 Dec 13;4(2):79-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.12.003. eCollection 2015 Feb. Mol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25685694 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Inhibition of Angiopoietin-Like Protein 3 or 3/8 Complex and ApoC-III in Severe Hypertriglyceridemia.
Larouche M, Khoury E, Brisson D, Gaudet D. Larouche M, et al. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2023 Dec;25(12):1101-1111. doi: 10.1007/s11883-023-01179-y. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2023. PMID: 38095804 Review. - Resequencing candidate genes implicates rare variants in asthma susceptibility.
Torgerson DG, Capurso D, Mathias RA, Graves PE, Hernandez RD, Beaty TH, Bleecker ER, Raby BA, Meyers DA, Barnes KC, Weiss ST, Martinez FD, Nicolae DL, Ober C. Torgerson DG, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2012 Feb 10;90(2):273-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.01.008. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22325360 Free PMC article. - Quantitation of serum angiopoietin-like proteins 3 and 4 in a Finnish population sample.
Robciuc MR, Tahvanainen E, Jauhiainen M, Ehnholm C. Robciuc MR, et al. J Lipid Res. 2010 Apr;51(4):824-31. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M002618. Epub 2009 Oct 13. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 19826106 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association studies for atherosclerotic vascular disease and its risk factors.
Ding K, Kullo IJ. Ding K, et al. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009 Feb;2(1):63-72. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.108.816751. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009. PMID: 19750184 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
- Rondinone CM. Adipocyte-derived hormones, cytokines, and mediators. Endocrine. 2006;29:81–90. - PubMed
- Li C. Genetics and regulation of angiopoietin-like proteins 3 and 4. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2006;17:152–156. - PubMed
- Koster A, et al. Transgenic angiopoietin-like (angptl)4 overexpression and targeted disruption of angptl4 and angptl3: regulation of triglyceride metabolism. Endocrinology. 2005;146:4943–4950. - PubMed
- Yoshida K, Shimizugawa T, Ono M, Furukawa H. Angiopoietin-like protein 4 is a potent hyperlipidemia-inducing factor in mice and inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res. 2002;43:1770–1772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RL1 HL092550/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 HL092550-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066681/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL066681/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases