microRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
microRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder
Diana O Perkins et al. Genome Biol. 2007.
Abstract
Background: microRNAs (miRNAs) are small, noncoding RNA molecules that are now thought to regulate the expression of many mRNAs. They have been implicated in the etiology of a variety of complex diseases, including Tourette's syndrome, Fragile x syndrome, and several types of cancer.
Results: We hypothesized that schizophrenia might be associated with altered miRNA profiles. To investigate this possibility we compared the expression of 264 human miRNAs from postmortem prefrontal cortex tissue of individuals with schizophrenia (n = 13) or schizoaffective disorder (n = 2) to tissue of 21 psychiatrically unaffected individuals using a custom miRNA microarray. Allowing a 5% false discovery rate, we found that 16 miRNAs were differentially expressed in prefrontal cortex of patient subjects, with 15 expressed at lower levels (fold change 0.63 to 0.89) and 1 at a higher level (fold change 1.77) than in the psychiatrically unaffected comparison subjects. The expression levels of 12 selected miRNAs were also determined by quantitative RT-PCR in our lab. For the eight miRNAs distinguished by being expressed at lower microarray levels in schizophrenia samples versus comparison samples, seven were also expressed at lower levels with quantitative RT-PCR.
Conclusion: This study is the first to find altered miRNA profiles in postmortem prefrontal cortex from schizophrenia patients.
Figures
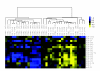
Figure 1
An miRNA expression map shows differentiated genes as determined by SAM analysis. Yellow indicates low expression and blue indicates high expression, relative to the median.
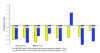
Figure 2
miRNA microarray fold changes can be compared with delta-delta C(t) functions of qRT-PCR data (see Materials and methods). The comparisons are over four samples from schizophrenia patients and four samples from psychiatrically unaffected comparison subjects. Seven of the eight comparisons are consistent.
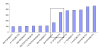
Figure 3
Regarding the 11 isolated miRNAs distinguished in schizophrenia, this figure shows the distances (numbers of bases) from shared 5' motifs we discovered (two 8 nt and two 12 nt motif sequences in the pri-miRNA) to the ssRNA-dsRNA junctions at starts of pre-miRNAs. Pre-miR-30a and -9-1 have double motif instances; second instances are in the rectangle. Ignoring the second instances as redundant leaves some motif distances in sharp clusters.
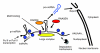
Figure 4
Transcription yields a continuous supply of some types of pri-miRNA transcripts, capped and polyadenylated. hnRNPs are hypothesized to shape the pri-miRNA into linear and hairpin sections. A signaling system somehow recruits and activates unknown factors that select particular pre-miRNA hairpins on a particular pri-miRNA for excision and processing in the miRNA pathway. We hypothesize that this system might include a binding motif. RNASEN and DGCR8 are products of genes 29102 and 54487.
Similar articles
- Upregulation of dicer and microRNA expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex Brodmann area 46 in schizophrenia.
Santarelli DM, Beveridge NJ, Tooney PA, Cairns MJ. Santarelli DM, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Jan 15;69(2):180-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.030. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21111402 - Expression of microRNAs and other small RNAs in prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depressed subjects.
Smalheiser NR, Lugli G, Zhang H, Rizavi H, Cook EH, Dwivedi Y. Smalheiser NR, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e86469. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086469. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475125 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA expression profiling in the prefrontal cortex of individuals affected with schizophrenia and bipolar disorders.
Kim AH, Reimers M, Maher B, Williamson V, McMichael O, McClay JL, van den Oord EJ, Riley BP, Kendler KS, Vladimirov VI. Kim AH, et al. Schizophr Res. 2010 Dec;124(1-3):183-91. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.07.002. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Schizophr Res. 2010. PMID: 20675101 Free PMC article. - The emerging role of MicroRNA in schizophrenia.
Caputo V, Ciolfi A, Macri S, Pizzuti A. Caputo V, et al. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015;14(2):208-21. doi: 10.2174/1871527314666150116124253. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25613509 Review. - 'Whole-Body' Perspectives of Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Illness: miRNA-143 as an Exemplary Molecule Implicated across Multi-System Dysfunctions.
Waddington JL, Wang X, Zhen X. Waddington JL, et al. Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 20;14(9):1185. doi: 10.3390/biom14091185. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Role of MicroRNAs in Human Diseases.
Ardekani AM, Naeini MM. Ardekani AM, et al. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2010 Oct;2(4):161-79. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 23407304 Free PMC article. - MiRNAs in Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes as Possible Mediators of Neuronal Plasticity.
Lafourcade C, Ramírez JP, Luarte A, Fernández A, Wyneken U. Lafourcade C, et al. J Exp Neurosci. 2016 Aug 8;10(Suppl 1):1-9. doi: 10.4137/JEN.S39916. eCollection 2016. J Exp Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27547038 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA as Biomarkers and Diagnostics.
Wang J, Chen J, Sen S. Wang J, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2016 Jan;231(1):25-30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25056. J Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26031493 Free PMC article. Review. - miRNA cargo in circulating vesicles from neurons is altered in individuals with schizophrenia and associated with severe disease.
Barnett MM, Reay WR, Geaghan MP, Kiltschewskij DJ, Green MJ, Weidenhofer J, Glatt SJ, Cairns MJ. Barnett MM, et al. Sci Adv. 2023 Dec;9(48):eadi4386. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi4386. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38019909 Free PMC article. - MicroRNAs, stem cells and cancer stem cells.
Garg M. Garg M. World J Stem Cells. 2012 Jul 26;4(7):62-70. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.62. World J Stem Cells. 2012. PMID: 22993663 Free PMC article.
References
- Prabakaran S, Swatton JE, Ryan MM, Huffaker SJ, Huang JT, Griffin JL, Wayland M, Freeman T, Dudbridge F, Lilley KS, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in schizophrenia: evidence for compromised brain metabolism and oxidative stress. Mol Psychiatry. 2004;9:684–697. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001532. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MH-01752/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 MH001752/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5-P20-RR020751-01-02/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM070674/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020751/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM070674/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 MH068855/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous