Adiponectin as an anti-inflammatory factor - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Adiponectin as an anti-inflammatory factor
Noriyuki Ouchi et al. Clin Chim Acta. 2007.
Abstract
Obesity is characterized by low-grade systemic inflammation. Adiponectin is an adipose tissue-derived hormone, which is downregulated in obesity. Adiponectin displays protective actions on the development of various obesity-linked diseases. Several clinical studies demonstrate the inverse relationship between plasma adiponectin levels and several inflammatory markers including C-reactive protein. Adiponectin attenuates inflammatory responses to multiple stimuli by modulating signaling pathways in a variety of cell types. The anti-inflammatory properties of adiponectin may be a major component of its beneficial effects on cardiovascular and metabolic disorders including atherosclerosis and insulin resistance. In this review, we focus on the role of adiponectin in regulation of inflammatory response and discuss its potential as an anti-inflammatory marker.
Figures
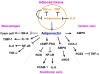
Figure
Adiponectin-mediated regulation of inflammatory responses in different cell types. Adiponectin negatively regulates CRP and TNF-α expression in adipose tissue, whereas adiponectin expression is inhibited by TNF-α and IL-6. Adiponectin inhibits IL-8, VCAM-1 and ROS production in endothelial cells through cAMP-PKA-dependent signaling. Adiponectin also stimulates AMPK activation in endothelial cells, leading to activation of eNOS. Adiponectin suppresses TNF-α production in cardiac cells through its ability to stimulate the COX-2-PGE2 pathway. In macrophages, adiponectin attenuates TNF-α and IL-6 production through its ability to suppress NF-κB activation, and enhances IL-10 expression resulting in increase in TIMP-1 production. Adiponectin inhibits foam cell formation by reducing SR-A expression.
Similar articles
- Association between adiponectin and mediators of inflammation in obese women.
Engeli S, Feldpausch M, Gorzelniak K, Hartwig F, Heintze U, Janke J, Möhlig M, Pfeiffer AF, Luft FC, Sharma AM. Engeli S, et al. Diabetes. 2003 Apr;52(4):942-7. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.4.942. Diabetes. 2003. PMID: 12663465 - Role of adiponectin and PBEF/visfatin as regulators of inflammation: involvement in obesity-associated diseases.
Tilg H, Moschen AR. Tilg H, et al. Clin Sci (Lond). 2008 Feb;114(4):275-88. doi: 10.1042/CS20070196. Clin Sci (Lond). 2008. PMID: 18194136 Review. - Adiponectin: a key fat-derived molecule regulating inflammation.
Tilg H, Wolf AM. Tilg H, et al. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005 Apr;9(2):245-51. doi: 10.1517/14728222.9.2.245. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005. PMID: 15934913 Review. - Clinical review: adiponectin biology and its role in inflammation and critical illness.
Robinson K, Prins J, Venkatesh B. Robinson K, et al. Crit Care. 2011 Apr 20;15(2):221. doi: 10.1186/cc10021. Crit Care. 2011. PMID: 21586104 Free PMC article. Review. - Adiponectin and cardiovascular inflammatory responses.
Takemura Y, Walsh K, Ouchi N. Takemura Y, et al. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2007 Sep;9(3):238-43. doi: 10.1007/s11883-007-0025-4. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2007. PMID: 18241619 Review.
Cited by
- Distinct Influence of Hypercaloric Diets Predominant with Fat or Fat and Sucrose on Adipose Tissue and Liver Inflammation in Mice.
Fonseca CSM, Basford JE, Kuhel DG, Konaniah ES, Cash JG, Lima VLM, Hui DY. Fonseca CSM, et al. Molecules. 2020 Sep 23;25(19):4369. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194369. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32977558 Free PMC article. - A comprehensive analysis of adiponectin QTLs using SNP association, SNP cis-effects on peripheral blood gene expression and gene expression correlation identified novel metabolic syndrome (MetS) genes with potential role in carcinogenesis and systemic inflammation.
Zhang Y, Kent JW Jr, Olivier M, Ali O, Cerjak D, Broeckel U, Abdou RM, Dyer TD, Comuzzie A, Curran JE, Carless MA, Rainwater DL, Göring HH, Blangero J, Kissebah AH. Zhang Y, et al. BMC Med Genomics. 2013 Apr 29;6:14. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-6-14. BMC Med Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23628382 Free PMC article. - Adiponectin, Insulin Sensitivity and Diabetic Retinopathy in Latinos With Type 2 Diabetes.
Kuo JZ, Guo X, Klein R, Klein BE, Genter P, Roll K, Hai Y, Goodarzi MO, Rotter JI, Chen YD, Ipp E. Kuo JZ, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Sep;100(9):3348-55. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-1221. Epub 2015 May 28. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26020763 Free PMC article. - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and psoriasis: So far, so near.
Ganzetti G, Campanati A, Offidani A. Ganzetti G, et al. World J Hepatol. 2015 Mar 27;7(3):315-26. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.315. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25848461 Free PMC article. Review. - Browning of White Fat: Novel Insight Into Factors, Mechanisms, and Therapeutics.
Jeremic N, Chaturvedi P, Tyagi SC. Jeremic N, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2017 Jan;232(1):61-8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25450. Epub 2016 Jun 21. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27279601 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Walsh K. Obesity, adiponectin and vascular inflammatory disease. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2003;14:561–566. - PubMed
- Berg AH, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2005;96:939–949. - PubMed
- Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman BM. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:10697–10703. - PubMed
- Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K. cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript 1) Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;221:286–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL77774/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AR40197/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015052/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG15052/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG015052/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL66957/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL066957/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR040197/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077774/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials