Role of PD-1 and its ligand, B7-H1, in early fate decisions of CD8 T cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2007 Jul 1;110(1):186-92.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-062422. Epub 2007 Mar 28.
Charles H Maris, Edward L Hipkiss, Andrew S Flies, Lijie Zhen, Rubin M Tuder, Joseph F Grosso, Timothy J Harris, Derese Getnet, Katharine A Whartenby, Dirk G Brockstedt, Thomas W Dubensky Jr, Lieping Chen, Drew M Pardoll, Charles G Drake
Affiliations
- PMID: 17392506
- PMCID: PMC1896112
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-062422
Role of PD-1 and its ligand, B7-H1, in early fate decisions of CD8 T cells
Monica V Goldberg et al. Blood. 2007.
Abstract
Expression of the PD-1 receptor on T cells has been shown to provide an important inhibitory signal that down-modulates peripheral effector responses in normal tissues and tumors. Furthermore, PD-1 up-regulation on chronically activated T cells can maintain them in a partially reversible inactive state. The function of PD-1 in the very early stages of T-cell response to antigen in vivo has not been fully explored. In this study, we evaluate the role of PD-1 and its 2 B7 family ligands, B7-H1 (PD-L1) and B7-DC (PD-L2), in early fate decisions of CD8 T cells. We show that CD8 T cells specific for influenza hemagglutinin (HA) expressed as a self-antigen become functionally tolerized and express high levels of surface PD-1 by the time of their first cell division. Blockade of PD-1 or B7-H1, but not B7-DC, at the time of self-antigen encounter mitigates tolerance induction and results in CD8 T-cell differentiation into functional cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTLs). These findings demonstrate that, in addition to modulating effector functions in the periphery, B7-H1:PD-1 interactions regulate early T-cell-fate decisions.
Figures
Figure 1
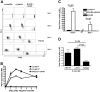
Early induction of PD-1 on CD8 T cells responding to self-antigen. (A, B) Unsorted Thy1.1-marked HA-specific CD8 T cells from clone 4 TCR transgenic mice were CFSE-labeled and adoptively transferred into animals that express HA as a self-antigen in different amounts (C3-HAlow and C3-HAhigh) or to WT mice infected with an attenuated L monocytogenes strain that expresses HA (LM-HA). Plots shown are gated on CD8+ Thy1.1+ lymphocytes (clone 4 donor cells). (A) PD-1 expression on clone 4 CD8 T cells as a function of division (CFSE dilution). Horizontal line represents isotype control. (B) PD-1 expression on clone 4 T cells transferred to mice that express high levels (C3-HAhigh, inverted triangles) or low levels (C3-HAlow, squares) of HA. Mean ± SEM shown. (C) Unlabeled clone 4 T cells transferred as above, total cell number in spleen is shown. For a-c, 5 animals per group, data representative at least 2 experiments. (D) Adoptive transfer into C3-HAlow mice was performed in the presence of 100 μg of the indicated blocking antibody (administered intraperitoneally on day 0). Total number of clone 4 cells per spleen on day 4 is shown. n = 5.
Figure 2
Blockade of PD-1 and its ligands at the time of antigen recognition renders self-antigen-specific T cells competent to produce effector cytokines. (A) Thy1.1-marked clone 4 cells were adoptively transferred into indicated hosts and harvested on day 4. Intracellular cytokine staining for IFN-γ was performed after 5-hour in vitro stimulation with the HA class I peptide in the presence of a blocking antibody cocktail (α-PD-1, α-B7-H1, and α-B7-DC, 30 μg/mL each, middle row) or isotype antibodies (top row). Gated on Thy1.1, 5 animals per group. (B,C) Clone 4 cells were adoptively transferred into C3-HAlow animals as above and PD-1, B7-H1 or B7-DC were blocked in vivo with 100 μg of indicated antibody administered at the time of adoptive transfer. Intracellular staining for IFN-γ was performed on day 4 after transfer. (B) Representative FACS plots, gated on CD8+ Thy1.1+ clone 4 lymphocytes. (C) Summary data of panel B, mean ± SEM n = 5, representative of 2 experiments.
Figure 3
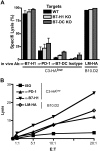
In vivo blockade of PD-1 and B7-H1 at the time of antigen encounter by self-antigen-specific CD8 T cells results in the development of functional CTL. (A) Clone 4 cells were adoptively transferred into C3-HAlow mice with the indicated blocking antibodies administered intraperitoneally on day 0. Specific lysis in vivo was assayed by transfer of CFSE- or PKH26-labeled, HA peptide-pulsed targets on day 6. Targets from WT, B7-H1 KO, and B7-DC KO animals were differentially labeled (see “Materials and methods”) and injected simultaneously. Percentage specific lysis calculated as described previously, n = 5. No significant differences in target lysis within the antibody treatment groups were detected by ANOVA. (B) In vitro CTL. clone 4 T cells were adoptively transferred as above, harvested on day 4 and sorted by FACS to < 95% purity. CTL were coincubated with HA peptide pulsed targets for at 37° for 4 hours, and percentage target lysis was calculated as described previously.
Figure 4
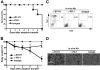
In vivo blockade of PD-1 and B7-H1 at the time of antigen encounter abrogates tolerance and results in autoimmunity. (A-D) C3-HAhigh mice were adoptively transferred with clone 4 cells and anti-PD-1 or anti-B7-H1 blocking antibodies or isotype control on day 0. (A) Survival of antibody-treated treated C3-HAhigh mice, n = 5. (B) Mean body weight relative to isotype control. Data are mean ± SEM. (C) FACS analysis of lung-infiltrating lymphocytes, gated on lymphocytes. Percentage shows the gated clone 4 T cells per total lymphocytes. (D) Pulmonary histology: 8-μm frozen sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, 100× magnification shown.
Similar articles
- Target-dependent B7-H1 regulation contributes to clearance of central nervous system infection and dampens morbidity.
Phares TW, Ramakrishna C, Parra GI, Epstein A, Chen L, Atkinson R, Stohlman SA, Bergmann CC. Phares TW, et al. J Immunol. 2009 May 1;182(9):5430-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803557. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19380790 Free PMC article. - The programmed death-1 ligand 1:B7-1 pathway restrains diabetogenic effector T cells in vivo.
Paterson AM, Brown KE, Keir ME, Vanguri VK, Riella LV, Chandraker A, Sayegh MH, Blazar BR, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. Paterson AM, et al. J Immunol. 2011 Aug 1;187(3):1097-105. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003496. Epub 2011 Jun 22. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21697456 Free PMC article. - Cutting Edge: Programmed death (PD) ligand-1/PD-1 interaction is required for CD8+ T cell tolerance to tissue antigens.
Martin-Orozco N, Wang YH, Yagita H, Dong C. Martin-Orozco N, et al. J Immunol. 2006 Dec 15;177(12):8291-5. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.12.8291. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17142723 - PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity.
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. Keir ME, et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:677-704. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090331. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18173375 Free PMC article. Review. - The right place at the right time: novel B7 family members regulate effector T cell responses.
Liang L, Sha WC. Liang L, et al. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002 Jun;14(3):384-90. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(02)00342-4. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11973139 Review.
Cited by
- Blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 promotes adoptive T-cell immunotherapy in a tolerogenic environment.
Blake SJ, Ching AL, Kenna TJ, Galea R, Large J, Yagita H, Steptoe RJ. Blake SJ, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 5;10(3):e0119483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119483. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25741704 Free PMC article. - Programmed death-1 ligands-transfected dendritic cells loaded with glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 (GAD65) inhibit both the alloresponse and the GAD65-reactive lymphocyte response.
He FR, Zhu HF, Huang H, Dai YD, Shen X, Wang M, Li L, Xing W, Shen GX. He FR, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008 Jan;151(1):86-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03546.x. Epub 2007 Nov 15. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18005363 Free PMC article. - The role of long non-coding RNA FGD5-AS1 in cancer.
He N, Xiang L, Chen L, Tong H, Wang K, Zhao J, Song F, Yang H, Wei X, Jiao Z. He N, et al. Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):11026-11041. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2067292. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35475392 Free PMC article. Review. - Anti-tumor effects of endogenous prostate cancer-specific CD8 T cells in a murine TCR transgenic model.
Bruno TC, Rothwell C, Grosso JF, Getnet D, Yen HR, Durham NM, Netto G, Pardoll DM, Drake CG. Bruno TC, et al. Prostate. 2012 Apr;72(5):514-22. doi: 10.1002/pros.21453. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Prostate. 2012. PMID: 21761425 Free PMC article. - B7-h1 expressed by activated CD8 T cells is essential for their survival.
Pulko V, Harris KJ, Liu X, Gibbons RM, Harrington SM, Krco CJ, Kwon ED, Dong H. Pulko V, et al. J Immunol. 2011 Dec 1;187(11):5606-14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003976. Epub 2011 Oct 24. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22025548 Free PMC article.
References
- Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:515–548. - PubMed
- Zhu B, Guleria I, Khosroshahi A, et al. Differential role of programmed death-ligand 1 [corrected] and programmed death-ligand 2 [corrected] in regulating the susceptibility and chronic progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis [published erratum appears in J Immunol. 2006;176:5683]. J Immunol. 2006;176:3480–3489. - PubMed
- Curiel TJ, Wei S, Dong H, et al. Blockade of B7-H1 improves myeloid dendritic cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Nat Med. 2003;9:562–567. - PubMed
- Hirano F, Kaneko K, Tamura H, et al. Blockade of B7-H1 and PD-1 by monoclonal antibodies potentiates cancer therapeutic immunity. Cancer Res. 2005;65:1089–1096. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials