Mutant prevention concentrations of fluoroquinolones for Enterobacteriaceae expressing the plasmid-carried quinolone resistance determinant qnrA1 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Mutant prevention concentrations of fluoroquinolones for Enterobacteriaceae expressing the plasmid-carried quinolone resistance determinant qnrA1
J M Rodríguez-Martínez et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jun.
Abstract
The influence of qnrA1 on the development of quinolone resistance in Enterobacteriaceae was evaluated by using the mutant prevention concentration parameter. The expression of qnrA1 considerably increased the mutant prevention concentration compared to strains without this gene. In the presence of qnrA1, mutations in gyrA and parC genes were easily selected to produce high levels of quinolone resistance.
Figures
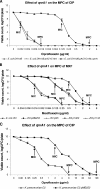
FIG. 1.
MPC assays. MIC and MPC values are indicated on figures by arrows. CIP, ciprofloxacin; MXF, moxifloxacin.
Similar articles
- Prevalence and expression of the plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinant qnrA1.
Xu X, Wu S, Ye X, Liu Y, Shi W, Zhang Y, Wang M. Xu X, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Nov;51(11):4105-10. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00616-07. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17724159 Free PMC article. - [Prevalence of qnr genes in clinical Enterobacteriaceae non-susceptible to fluoroquinolone in Poland].
Piekarska K, Rzeczkowska M, Zacharczuk K, Chróst A, Januszkiewicz A, Bareja E, Olak M, Gierczyński R. Piekarska K, et al. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 2012;64(3):211-9. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 2012. PMID: 23285775 Polish. - Prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants in Enterobacteriaceae strains isolated in North-East Italy.
Kocsis B, Mazzariol A, Kocsis E, Koncan R, Fontana R, Cornaglia G. Kocsis B, et al. J Chemother. 2013 Feb;25(1):36-40. doi: 10.1179/1120009X12Z.00000000078. J Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23433443 - Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance.
Martínez-Martínez L, Eliecer Cano M, Manuel Rodríguez-Martínez J, Calvo J, Pascual A. Martínez-Martínez L, et al. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008 Oct;6(5):685-711. doi: 10.1586/14787210.6.5.685. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008. PMID: 18847406 Review. - New fluoroquinolones: a class of potent antibiotics.
De Souza MV. De Souza MV. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005 Nov;5(11):1009-17. doi: 10.2174/138955705774575246. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16307530 Review.
Cited by
- Aquatic Environments as Hotspots of Transferable Low-Level Quinolone Resistance and Their Potential Contribution to High-Level Quinolone Resistance.
Miranda CD, Concha C, Godoy FA, Lee MR. Miranda CD, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Oct 27;11(11):1487. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111487. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358142 Free PMC article. Review. - Mechanisms of reduced susceptibility to ciprofloxacin in Escherichia coli isolates from Canadian hospitals.
Baudry-Simner PJ, Singh A, Karlowsky JA, Hoban DJ, Zhanel GG; Canadian Antimicrobial Resistance Alliance. Baudry-Simner PJ, et al. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2012 Fall;23(3):e60-4. doi: 10.1155/2012/569093. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23997786 Free PMC article. - Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: a systematic review with a focus on Mediterranean countries.
Yanat B, Rodríguez-Martínez JM, Touati A. Yanat B, et al. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017 Mar;36(3):421-435. doi: 10.1007/s10096-016-2847-x. Epub 2016 Nov 26. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 27889879 Review. - In vitro effect of qnrA1, qnrB1, and qnrS1 genes on fluoroquinolone activity against isogenic Escherichia coli isolates with mutations in gyrA and parC.
Briales A, Rodríguez-Martínez JM, Velasco C, Díaz de Alba P, Domínguez-Herrera J, Pachón J, Pascual A. Briales A, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Mar;55(3):1266-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00927-10. Epub 2010 Dec 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21173174 Free PMC article. - Resistance determinants and mobile genetic elements of an NDM-1-encoding Klebsiella pneumoniae strain.
Hudson CM, Bent ZW, Meagher RJ, Williams KP. Hudson CM, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Jun 6;9(6):e99209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099209. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24905728 Free PMC article.
References
- Baquero, F., and M. C. Negri. 1997. Strategies to minimize the development of antibiotic resistance. J. Chemother. 9(Suppl. 3):29-37. - PubMed
- Bertino, J., Jr., and D. Fish. 2000. The safety profile of the fluoroquinolones. Clin. Ther. 22:798-817. - PubMed
- Boy, D., M. Well, M. Kinzig-Schippers, F. Sorgel, D. Nkel-Fuchs, and K. G. Naber. 2004. Urinary bactericidal activity, urinary excretion and plasma concentrations of gatifloxacin (400 mg) versus ciprofloxacin (500 mg) in healthy volunteers after a single oral dose. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 23(Suppl. 1):S6-S16. - PubMed
- CLSI. 2005. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 15th informational supplement. Document M100-S15. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
- Drlica, K. 2003. The mutant selection window and antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 52:11-17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical