The hormonal control of food intake - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The hormonal control of food intake
Anthony P Coll et al. Cell. 2007.
Abstract
Numerous circulating peptides and steroids produced in the body influence appetite through their actions on the hypothalamus, the brain stem, and the autonomic nervous system. These hormones come from three major sites-fat cells, the gastrointestinal tract, and the pancreas. In this Review we provide a synthesis of recent evidence concerning the actions of these hormones on food intake.
Figures
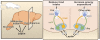
Figure 1
Control of Food Intake by the Hypothalamic Leptin-Melanocortin Pathway The hypothalamus receives and integrates neural, metabolic, and hormonal signals to regulate energy homeostasis. In particular, the adipocyte-derived hormone leptin and the melanocortin pathway have a critical role in the control of food intake. AgRP, Agouti-related protein; Arc, arcuate nucleus; MC4R, melanocortin 4 receptor; POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin; PVN, paraventricular nucleus.
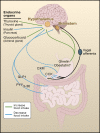
Figure 2
Hormones from the Gut and Endocrine Organs Affect Food Intake Hormonal signals derived from the gut and classical endocrine organs, such as the pancreas, thyroid, and adrenal glands act in synergy to effect changes in feeding behavior. CCK, cholecystokinin; OXM, oxyntomodulin; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; PYY3–36, peptide YY3–36.
Similar articles
- Hormonal regulation of food intake.
Stanley S, Wynne K, McGowan B, Bloom S. Stanley S, et al. Physiol Rev. 2005 Oct;85(4):1131-58. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2004. Physiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16183909 Review. - Gut peptides in the control of food intake.
Moran TH. Moran TH. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009 Apr;33 Suppl 1:S7-10. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2009.9. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009. PMID: 19363513 Review. - Afferent signals regulating food intake.
Bray GA. Bray GA. Proc Nutr Soc. 2000 Aug;59(3):373-84. doi: 10.1017/s0029665100000422. Proc Nutr Soc. 2000. PMID: 10997653 Review. - [Peptides regulating food intake and body weight].
Stasiūniene N, Praskevicius A. Stasiūniene N, et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2005;41(12):989-1001. Medicina (Kaunas). 2005. PMID: 16401955 Review. Lithuanian. - Gut hormones and the control of appetite.
Small CJ, Bloom SR. Small CJ, et al. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Aug;15(6):259-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2004.06.002. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15358278 Review.
Cited by
- The Unrestrained Overeating Behavior and Clinical Perspective.
Engin A. Engin A. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:167-198. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287852 Review. - Tanycytic transcytosis inhibition disrupts energy balance, glucose homeostasis and cognitive function in male mice.
Duquenne M, Deligia E, Folgueira C, Bourouh C, Caron E, Pfrieger F, Schwaninger M, Nogueiras R, Annicotte JS, Imbernon M, Prévot V. Duquenne M, et al. Mol Metab. 2024 Sep;87:101996. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101996. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39047908 Free PMC article. - Decreased islet amyloid polypeptide staining in the islets of insulinoma patients.
Ishibashi C, Yoneda S, Fujita Y, Fujita S, Mitsushio K, Ozawa H, Baden MY, Nammo T, Kozawa J, Eguchi H, Shimomura I. Ishibashi C, et al. Islets. 2024 Dec 31;16(1):2379650. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2024.2379650. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Islets. 2024. PMID: 39028826 Free PMC article. - The effects of COVID-19 quarantine on eating and sleeping behaviors.
da Silva FR, Junior AHL, Brant VM, Lôbo ILB, Lancha LOP, Silva A, de Mello MT. da Silva FR, et al. Nutrire. 2020;45(2):25. doi: 10.1186/s41110-020-00128-y. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Nutrire. 2020. PMID: 38624453 Free PMC article. Review. - Aging and Adiposity-Focus on Biological Females at Midlife and Beyond.
Rehman A, Lathief S, Charoenngam N, Pal L. Rehman A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 4;25(5):2972. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052972. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Alharbi K.K., Spanakis E., Tan K., Smith M.J., Aldahmesh M.A., O'Dell S.D., Sayer A.A., Lawlor D.A., Ebrahim S., Smith G.D. Prevalence and functionality of paucimorphic and private MC4R mutations in a large, unselected European British population, scanned by meltMADGE. Hum. Mutat. 2007;28:294–302. - PubMed
- Balthasar N., Dalgaard L.T., Lee C.E., Yu J., Funahashi H., Williams T., Ferreira M., Tang V., McGovern R.A., Kenny C.D. Divergence of melanocortin pathways in the control of food intake and energy expenditure. Cell. 2005;123:493–505. - PubMed
- Balthasar N., Coppari R., McMinn J., Liu S.M., Lee C.E., Tang V., Kenny C.D., McGovern R.A., Chua S.C., Elmquist J.K., Lowell B.B. Leptin receptor signaling in POMC neurons is required for normal body weight homeostasis. Neuron. 2004;42:983–991. - PubMed
- Bates S.H., Myers M.G., Jr. The role of leptin receptor signaling in feeding and neuroendocrine function. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003;14:447–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 068086/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G108/617/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G108/617(73637)/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9824984/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical