Tryptase haplotype in mastocytosis: relationship to disease variant and diagnostic utility of total tryptase levels - PubMed (original) (raw)
Tryptase haplotype in mastocytosis: relationship to disease variant and diagnostic utility of total tryptase levels
Cem Akin et al. Clin Immunol. 2007 Jun.
Abstract
Serum mast cell tryptase levels are used as a diagnostic criterion and surrogate marker of disease severity in mastocytosis. Approximately 29% of the healthy population lacks alpha tryptase genes; however, it is not known whether lack of alpha tryptase genes leads to variability in tryptase levels or impacts on disease severity in mastocytosis. We have thus analyzed tryptase haplotype in patients with mastocytosis, computing correlations between haplotype and plasma total and mature tryptase levels; and disease category. We found: (1) the distribution of tryptase haplotype in patients with mastocytosis appeared consistent with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and the distribution in the general population; (2) the disease severity and plasma tryptase levels were not affected by the number of alpha or beta tryptase alleles in this study; and (3) information about the tryptase haplotype did not provide any prognostic value about the severity of disease. Total and mature tryptase levels positively correlated with disease severity, as well as prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time, and negatively correlated with the hemoglobin concentration.
Figures
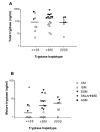
Figure 1
Total (A) and mature (B) tryptase levels in patients with mastocytosis according to tryptase haplotype. Lines indicate median values for each category. CM, cutaneous mastocytosis; ISM, indolent systemic mastocytosis; SSM, smoldering systemic mastocytosis; SM-AHNMD, systemic mastocytosis with an associated hematologic clonal non-mast cell lineage disease; ASM, aggressive systemic mastocytosis.
Figure 2
Correlations of total (A-C) and mature (D-F) tryptase levels with prothrombin time (PT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and hemoglobin levels. Prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time values were not available for all patients.
Similar articles
- Tryptase detection in bone-marrow blood: a new diagnostic tool in systemic mastocytosis.
Proelss J, Wenzel J, Ko Y, Bieber T, Bauer R. Proelss J, et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007 Mar;56(3):453-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2006.09.020. Epub 2006 Oct 30. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17317486 - Assessment of clinical findings, tryptase levels, and bone marrow histopathology in the management of pediatric mastocytosis.
Carter MC, Clayton ST, Komarow HD, Brittain EH, Scott LM, Cantave D, Gaskins DM, Maric I, Metcalfe DD. Carter MC, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Dec;136(6):1673-1679.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.04.024. Epub 2015 Jun 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26044856 Free PMC article. - Serum tryptase and SCORMA (SCORing MAstocytosis) Index as disease severity parameters in childhood and adult cutaneous mastocytosis.
Heide R, van Doorn K, Mulder PG, van Toorenenbergen AW, Beishuizen A, de Groot H, Tank B, Oranje AP. Heide R, et al. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009 Jun;34(4):462-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.03005.x. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19077102 - Diagnostic value of tryptase in anaphylaxis and mastocytosis.
Schwartz LB. Schwartz LB. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2006 Aug;26(3):451-63. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2006.05.010. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2006. PMID: 16931288 Review. - Childhood mastocytosis.
Torrelo A, Alvarez-Twose I, Escribano L. Torrelo A, et al. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2012 Aug;24(4):480-6. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e328355b248. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 22790101 Review.
Cited by
- Alpha-Tryptase as a Risk-Modifying Factor for Mast Cell-Mediated Reactions.
Shin H, Lyons JJ. Shin H, et al. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Apr;24(4):199-209. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01136-y. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 38460022 Review. - Acute Urticaria and Anaphylaxis: Differences and Similarities in Clinical Management.
Ensina LF, Min TK, Félix MMR, de Alcântara CT, Costa C. Ensina LF, et al. Front Allergy. 2022 Apr 15;3:840999. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2022.840999. eCollection 2022. Front Allergy. 2022. PMID: 35958944 Free PMC article. Review. - Case Report: Hereditary Alpha Tryptasemia in Children: A Pediatric Case Series and a Brief Overview of Literature.
Zama D, Muratore E, Giannetti A, Neri I, Conti F, Magini P, Ferrari S, Pession A. Zama D, et al. Front Pediatr. 2021 Aug 20;9:716786. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.716786. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34490168 Free PMC article. - Hereditary Alpha-Tryptasemia: a Commonly Inherited Modifier of Anaphylaxis.
Wu R, Lyons JJ. Wu R, et al. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021 May 10;21(5):33. doi: 10.1007/s11882-021-01010-1. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021. PMID: 33970354 Review. - Hereditary α tryptasemia is a valid genetic biomarker for severe mediator-related symptoms in mastocytosis.
Greiner G, Sprinzl B, Górska A, Ratzinger F, Gurbisz M, Witzeneder N, Schmetterer KG, Gisslinger B, Uyanik G, Hadzijusufovic E, Esterbauer H, Gleixner KV, Krauth MT, Pfeilstöcker M, Keil F, Gisslinger H, Nedoszytko B, Niedoszytko M, Sperr WR, Valent P, Hoermann G. Greiner G, et al. Blood. 2021 Jan 14;137(2):238-247. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006157. Blood. 2021. PMID: 32777817 Free PMC article.
References
- Valent P, Horny H, Escribano L, Longley BJ, Li CY, Schwartz LB, Marone G, Nunez R, Akin C, Sotlar K, Sperr WR, Wolff K, Brunning RD, Parwaresch RM, Austen KF, Lennert K, Metcalfe DD, Vardiman JW, Bennett JM. Diagnostic criteria and classification of mastocytosis: a consensus proposal. Leuk Res. 2001;25:603–25. - PubMed
- Schwartz LB, Irani AM. Serum tryptase and the laboratory diagnosis of systemic mastocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000;14:641–57. - PubMed
- Schwartz LB. Diagnostic value of tryptase in anaphylaxis and mastocytosis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2006;26:451–63. - PubMed
- Pallaoro M, Fejzo MS, Shayesteh L, Blount JL, Caughey GH. Characterization of genes encoding known and novel human mast cell tryptases on chromosome 16p13.3. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:3355–62. - PubMed
- Wong GW, Yasuda S, Madhusudhan MS, Li L, Yang Y, Krilis SA, Sali A, Stevens RL. Human tryptase epsilon (PRSS22), a new member of the chromosome 16p13.3 family of human serine proteases expressed in airway epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:49169–82. Epub 2001 Oct 15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL024136-190014/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI20487/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI020487-19/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI020487/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL024136/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI020487/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL024136/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI020487/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AI000249-26/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources