Longitudinal MRI findings from the vitamin E and donepezil treatment study for MCI - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Longitudinal MRI findings from the vitamin E and donepezil treatment study for MCI
Clifford R Jack Jr et al. Neurobiol Aging. 2008 Sep.
Abstract
The vitamin E and donepezil trial for the treatment of amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) was conducted at 69 centers in North America; 24 centers participated in an MRI sub study. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of treatment on MRI atrophy rates; and validate rate measures from serial MRI as indicators of disease progression in multi center therapeutic trials for MCI. Annual percent change (APC) from baseline to follow-up was measured for hippocampus, entorhinal cortex, whole brain, and ventricle in the 131 subjects who remained in the treatment study and completed technically satisfactory baseline and follow-up scans. Although a non-significant trend toward slowing of hippocampal atrophy rates was seen in APOE is an element of 4 carriers treated with donepezil; no treatment effect was confirmed for any MRI measure in either treatment group. For each of the four brain atrophy rate measures, APCs were greater in subjects who converted to AD than non-converters, and were greater in APOE is an element of 4 carriers than non-carriers. MRI APCs and changes in cognitive test performance were uniformly correlated in the expected direction (all p<0.000). Results of this study support the feasibility of using MRI as an outcome measure of disease progression in multi center therapeutic trials for MCI.
Figures
Figure 1. Volume Measures
Image on the readers right illustrates tracing of the hippocampal and entorhinal cortex outlines. The image on the left illustrates computation of volume change with the boundary shift integral. Red demarcates pixels at the brain- CSF boundary where volume was lost from the baseline to follow up scan. The ventricular BSI is calculated by creating a hand drawn mask of the ventricle.
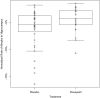
Figure 2. Hippocampal APC in APOE ∈4 Carriers: Donepezil vs. Placebo
Hippocampal APC of all APOE ∈4 carriers treated with donepezil (n=23) vs. placebo (n=36) with superimposed box plot (bar = median; box = inter-quartile range; whiskers = 1.5X inter-quartile range).
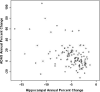
Figure 3. Correlation between Change in MRI and Change in Cognition
Scatter plot illustrating the correlation between annualized percent change in hippocampal volume and annualized percent change in ADAS-Cog 13.
Similar articles
- Donepezil treatment of patients with MCI: a 48-week randomized, placebo-controlled trial.
Doody RS, Ferris SH, Salloway S, Sun Y, Goldman R, Watkins WE, Xu Y, Murthy AK. Doody RS, et al. Neurology. 2009 May 5;72(18):1555-61. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000344650.95823.03. Epub 2009 Jan 28. Neurology. 2009. PMID: 19176895 Clinical Trial. - Donepezil decreases annual rate of hippocampal atrophy in suspected prodromal Alzheimer's disease.
Dubois B, Chupin M, Hampel H, Lista S, Cavedo E, Croisile B, Louis Tisserand G, Touchon J, Bonafe A, Ousset PJ, Ait Ameur A, Rouaud O, Ricolfi F, Vighetto A, Pasquier F, Delmaire C, Ceccaldi M, Girard N, Dufouil C, Lehericy S, Tonelli I, Duveau F, Colliot O, Garnero L, Sarazin M, Dormont D; “Hippocampus Study Group”; Hippocampus Study Group. Dubois B, et al. Alzheimers Dement. 2015 Sep;11(9):1041-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2014.10.003. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Alzheimers Dement. 2015. PMID: 25596420 Clinical Trial. - Hippocampal and entorhinal atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: prediction of Alzheimer disease.
Devanand DP, Pradhaban G, Liu X, Khandji A, De Santi S, Segal S, Rusinek H, Pelton GH, Honig LS, Mayeux R, Stern Y, Tabert MH, de Leon MJ. Devanand DP, et al. Neurology. 2007 Mar 13;68(11):828-36. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000256697.20968.d7. Neurology. 2007. PMID: 17353470 - Donepezil delays progression to AD in MCI subjects with depressive symptoms.
Lu PH, Edland SD, Teng E, Tingus K, Petersen RC, Cummings JL; Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study Group. Lu PH, et al. Neurology. 2009 Jun 16;72(24):2115-21. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181aa52d3. Neurology. 2009. PMID: 19528519 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Comparison of different MRI brain atrophy rate measures with clinical disease progression in AD.
Jack CR Jr, Shiung MM, Gunter JL, O'Brien PC, Weigand SD, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Ivnik RJ, Smith GE, Cha RH, Tangalos EG, Petersen RC. Jack CR Jr, et al. Neurology. 2004 Feb 24;62(4):591-600. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000110315.26026.ef. Neurology. 2004. PMID: 14981176 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Automated and manual hippocampal segmentation techniques: Comparison of results, reproducibility and clinical applicability.
Hurtz S, Chow N, Watson AE, Somme JH, Goukasian N, Hwang KS, Morra J, Elashoff D, Gao S, Petersen RC, Aisen PS, Thompson PM, Apostolova LG. Hurtz S, et al. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;21:101574. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.10.012. Epub 2018 Oct 14. Neuroimage Clin. 2019. PMID: 30553759 Free PMC article. - Reduced sample sizes for atrophy outcomes in Alzheimer's disease trials: baseline adjustment.
Schott JM, Bartlett JW, Barnes J, Leung KK, Ourselin S, Fox NC; Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative investigators. Schott JM, et al. Neurobiol Aging. 2010 Aug;31(8):1452-62, 1462.e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.04.011. Neurobiol Aging. 2010. PMID: 20620665 Free PMC article. - Whole-brain analysis reveals increased neuroanatomical asymmetries in dementia for hippocampus and amygdala.
Wachinger C, Salat DH, Weiner M, Reuter M; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Wachinger C, et al. Brain. 2016 Dec;139(Pt 12):3253-3266. doi: 10.1093/brain/aww243. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Brain. 2016. PMID: 27913407 Free PMC article. - Bias in estimation of hippocampal atrophy using deformation-based morphometry arises from asymmetric global normalization: an illustration in ADNI 3 T MRI data.
Yushkevich PA, Avants BB, Das SR, Pluta J, Altinay M, Craige C; Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Yushkevich PA, et al. Neuroimage. 2010 Apr 1;50(2):434-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.007. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20005963 Free PMC article. - Reduction of basal forebrain cholinergic system parallels cognitive impairment in patients at high risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
Grothe M, Zaborszky L, Atienza M, Gil-Neciga E, Rodriguez-Romero R, Teipel SJ, Amunts K, Suarez-Gonzalez A, Cantero JL. Grothe M, et al. Cereb Cortex. 2010 Jul;20(7):1685-95. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhp232. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Cereb Cortex. 2010. PMID: 19889714 Free PMC article.
References
- Adak S, Illouz K, Gorman W, Tandon R, Zimmerman EA, Moore MM, Kaye JA. Predicting the rate of cognitive decline in aging and early Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2004;63:108–114. - PubMed
- Berg L. Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) Psychopharmacol Bull. 1988;24:637–639. - PubMed
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;261:921–923. - PubMed
- den Heijer T, Oudkerk M, Launer LJ, van Duijn CM, Hofman A, Breteler MB. Hippocampal, amygdalar, and global brain atrophy in different apolipoprotein E genotypes. Neurology. 2002;59:746–748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous