Structure of the PTB domain of tensin1 and a model for its recruitment to fibrillar adhesions - PubMed (original) (raw)
Structure of the PTB domain of tensin1 and a model for its recruitment to fibrillar adhesions
Clare J McCleverty et al. Protein Sci. 2007 Jun.
Abstract
Tensin is a cytoskeletal protein that links integrins to the actin cytoskeleton at sites of cell-matrix adhesion. Here we describe the crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain of tensin1, and show that it binds integrins in an NPxY-dependent fashion. Alanine mutagenesis of both the PTB domain and integrin tails supports a model of integrin binding similar to that of the PTB-like domain of talin. However, we also show that phosphorylation of the NPxY tyrosine, which disrupts talin binding, has a negligible effect on tensin binding. This suggests that tyrosine phosphorylation of integrin, which occurs during the maturation of focal adhesions, could act as a switch to promote the migration of tensin-integrin complexes into fibronectin-mediated fibrillar adhesions.
Figures
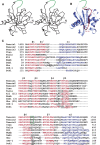
Figure 1.
Structure of the tensin PTB domain. (A) Stereo Cα plot of the tensin1 PTB domain with every 10th residue, and N and C termini, labeled. The unstructured β6-β7 loop is shown schematically in green. (B) Ribbon diagram of the tensin1 PTB domain, with secondary structural elements labeled. A model of the integrin peptide is also shown (in red), including the side-chains of the NPxY tyrosine and the tryptophan residue at the –8 position. (C) Structure-based sequence alignment of the PTB domains of tensin family members, the talin PTB-like domain (Garcia-Alvarez et al. 2003), and other PTB domains (X11 [Zhang et al. 1997], Numb [Li et al. 1998], Dab1 [Stolt et al. 2003], Shc [Zhou et al. 1995b], IRS-1 [Eck et al. 1996; Zhou et al. 1996], and Dok1 [Shi et al. 2004]). β-strands are colored red; α-helices are blue. Residues involved in peptide binding are underlined, and those that directly bind phosphotyrosine are boxed. In the tensin homologs, two basic residues from the β6-β7 loop proposed to engage the phosphotyrosine are boxed in green. Numbers in parentheses for X11, Dab1, and Shc indicate the size of sequence insertions that have been removed for clarity. The asterisk in the X11 sequence marks a 19-residue insertion that is also not shown.
Figure 2.
PTB-integrin models. Surface representations of the tensin1-integrin model (A) and the talin-integrin crystal structure (B) (Garcia-Alvarez et al. 2003), colored by electrostatic potential (blue for positive, red for negative). The integrin peptides are shown as sticks and colored by atom type. Integrin residue numbers are in black (and numbered with respect to the NPxY tyrosine in parentheses); in A, tensin residue numbers are given in green. Figures were generated with MOLSCRIPT (Kraulis 1991), RASTER3D (Kraulis 1991; Merritt and Murphy 1994), and PyMol (
).
Similar articles
- Integrin beta cytoplasmic domain interactions with phosphotyrosine-binding domains: a structural prototype for diversity in integrin signaling.
Calderwood DA, Fujioka Y, de Pereda JM, García-Alvarez B, Nakamoto T, Margolis B, McGlade CJ, Liddington RC, Ginsberg MH. Calderwood DA, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Mar 4;100(5):2272-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.262791999. Epub 2003 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12606711 Free PMC article. - Tensin.
Lo SH. Lo SH. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Jan;36(1):31-4. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(03)00171-7. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14592531 Review. - The PTB domain of tensin: NMR solution structure and phosphoinositides binding studies.
Leone M, Yu EC, Liddington RC, Pasquale EB, Pellecchia M. Leone M, et al. Biopolymers. 2008 Jan;89(1):86-92. doi: 10.1002/bip.20862. Biopolymers. 2008. PMID: 17922498 - The phosphotyrosine binding-like domain of talin activates integrins.
Calderwood DA, Yan B, de Pereda JM, Alvarez BG, Fujioka Y, Liddington RC, Ginsberg MH. Calderwood DA, et al. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):21749-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111996200. Epub 2002 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11932255 - Integrating actin dynamics, mechanotransduction and integrin activation: the multiple functions of actin binding proteins in focal adhesions.
Ciobanasu C, Faivre B, Le Clainche C. Ciobanasu C, et al. Eur J Cell Biol. 2013 Oct-Nov;92(10-11):339-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Eur J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24252517 Review.
Cited by
- Tensin links energy metabolism to extracellular matrix assembly.
Dornier E, Norman JC. Dornier E, et al. J Cell Biol. 2017 Apr 3;216(4):867-869. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201702025. Epub 2017 Mar 21. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28325807 Free PMC article. - TNS1: Emerging Insights into Its Domain Function, Biological Roles, and Tumors.
Wang Z, Ye J, Dong F, Cao L, Wang M, Sun G. Wang Z, et al. Biology (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;11(11):1571. doi: 10.3390/biology11111571. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358270 Free PMC article. Review. - Tensin1 expression and function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Stylianou P, Clark K, Gooptu B, Smallwood D, Brightling CE, Amrani Y, Roach KM, Bradding P. Stylianou P, et al. Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 12;9(1):18942. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55405-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31831813 Free PMC article. - Tensin-4-dependent MET stabilization is essential for survival and proliferation in carcinoma cells.
Muharram G, Sahgal P, Korpela T, De Franceschi N, Kaukonen R, Clark K, Tulasne D, Carpén O, Ivaska J. Muharram G, et al. Dev Cell. 2014 May 27;29(4):421-36. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.03.024. Epub 2014 May 8. Dev Cell. 2014. PMID: 24814316 Free PMC article. - Phosphotyrosine recognition domains: the typical, the atypical and the versatile.
Kaneko T, Joshi R, Feller SM, Li SS. Kaneko T, et al. Cell Commun Signal. 2012 Nov 7;10(1):32. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-10-32. Cell Commun Signal. 2012. PMID: 23134684 Free PMC article.
References
- Auger K.R., Songyang, Z., Lo, S.H., Roberts, T.M., and Chen, L.B. 1996. Platelet-derived growth factor-induced formation of tensin and phosphoinositide 3-kinase complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 23452–23457. - PubMed
- Brünger A.T., Adams, P.D., Clore, G.M., DeLano, W.L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W., Jiang, J.S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N.S., et al. 1998. Crystallography and NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 54: 905–921. - PubMed
- Calderwood D.A., Zent, R., Grant, R., Rees, D.J.G., Hynes, R.O., and Ginsberg, M.H. 1999. The talin head domain binds to integrin β subunit cytoplasmic tails and regulates integrin activation. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 28071–28074. - PubMed
- Calderwood D.A., Yan, B., de Pereda, J.M., Garcia-Alvarez, B., Fujioka, Y., Liddington, R.C., and Ginsberg, M.H. 2002. The phosphotyrosine binding (PTB)-like domain of talin activates integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 21749–21758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases