Molecular basis of the CRAC channel - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Molecular basis of the CRAC channel
Michael D Cahalan et al. Cell Calcium. 2007 Aug.
Abstract
Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) channels, located in the plasma membrane, are opened upon release of Ca(2+) from intracellular stores, permitting Ca(2+) entry and sustained [Ca(2+)](i) signaling that replenishes the store in numerous cell types. This mechanism is particularly important in T lymphocytes of the immune system, providing the missing link in the signal transduction cascade that is initiated by T cell receptor engagement and leads to altered expression of genes that results ultimately in the production of cytokines and cell proliferation. In the past three years, RNA interference screens together with over-expression and site-directed mutagenesis have identified the triggering molecule (Stim) that links store depletion to CRAC channel-mediated Ca(2+) influx and the pore subunit (Orai) of the CRAC channel that allows highly selective entry of Ca(2+) ions into cells.
Figures
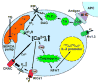
Fig. 1
Ion channels and signaling pathways in T cells.
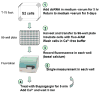
Fig. 2
Candidate RNAi screening protocol.
Fig. 3
Stim1 sequences and motifs.
Fig. 4
Genome-wide RNAi screening protocol.
Fig. 5
Fly and human Orai-related sequences and motifs.
Similar articles
- The CRAC channel consists of a tetramer formed by Stim-induced dimerization of Orai dimers.
Penna A, Demuro A, Yeromin AV, Zhang SL, Safrina O, Parker I, Cahalan MD. Penna A, et al. Nature. 2008 Nov 6;456(7218):116-20. doi: 10.1038/nature07338. Epub 2008 Sep 28. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18820677 Free PMC article. - Molecular identification of the CRAC channel by altered ion selectivity in a mutant of Orai.
Yeromin AV, Zhang SL, Jiang W, Yu Y, Safrina O, Cahalan MD. Yeromin AV, et al. Nature. 2006 Sep 14;443(7108):226-9. doi: 10.1038/nature05108. Epub 2006 Aug 20. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16921385 Free PMC article. - Studies of Structure-Function and Subunit Composition of Orai/STIM Channel.
Fahrner M, Schindl R, Romanin C. Fahrner M, et al. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 2. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 2. PMID: 30299645 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Store-Independent Orai Channels Regulated by STIM.
Zhang X, Gueguinou M, Trebak M. Zhang X, et al. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 11. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 11. PMID: 30299650 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Orai1 is an essential pore subunit of the CRAC channel.
Prakriya M, Feske S, Gwack Y, Srikanth S, Rao A, Hogan PG. Prakriya M, et al. Nature. 2006 Sep 14;443(7108):230-3. doi: 10.1038/nature05122. Epub 2006 Aug 20. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16921383
Cited by
- 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 modulates calcium transport in goat mammary epithelial cells in a dose- and energy-dependent manner.
Sun F, Cao Y, Yu C, Wei X, Yao J. Sun F, et al. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2016 Jul 28;7:41. doi: 10.1186/s40104-016-0101-0. eCollection 2016. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27471592 Free PMC article. - Essential role for STIM1/Orai1-mediated calcium influx in PDGF-induced smooth muscle migration.
Bisaillon JM, Motiani RK, Gonzalez-Cobos JC, Potier M, Halligan KE, Alzawahra WF, Barroso M, Singer HA, Jourd'heuil D, Trebak M. Bisaillon JM, et al. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):C993-1005. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00325.2009. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20107038 Free PMC article. - Choreography of cell motility and interaction dynamics imaged by two-photon microscopy in lymphoid organs.
Cahalan MD, Parker I. Cahalan MD, et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:585-626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.24.021605.090620. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18173372 Free PMC article. Review. - Complex role of STIM1 in the activation of store-independent Orai1/3 channels.
Zhang X, Zhang W, González-Cobos JC, Jardin I, Romanin C, Matrougui K, Trebak M. Zhang X, et al. J Gen Physiol. 2014 Mar;143(3):345-59. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201311084. J Gen Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24567509 Free PMC article. - RNA interference targeting STIM1 suppresses vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointima formation in the rat.
Aubart FC, Sassi Y, Coulombe A, Mougenot N, Vrignaud C, Leprince P, Lechat P, Lompré AM, Hulot JS. Aubart FC, et al. Mol Ther. 2009 Mar;17(3):455-62. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.291. Epub 2008 Dec 23. Mol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19107116 Free PMC article.
References
- Miller MJ, Wei SH, Parker I, Cahalan MD. Two-photon imaging of lymphocyte motility and antigen response in intact lymph node. Science. 2002;296:1869–1873. - PubMed
- DeCoursey TE, Chandy KG, Gupta S, Cahalan MD. Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: a role in mitogenesis? Nature. 1984;307:465–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous