Herpes simplex virus type 1 cytoplasmic envelopment requires functional Vps4 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Herpes simplex virus type 1 cytoplasmic envelopment requires functional Vps4
Colin M Crump et al. J Virol. 2007 Jul.
Abstract
The assembly and egress of herpesviruses are complex processes that require the budding of viral nucleocapsids into the lumen of cytoplasmic compartments to form mature infectious virus. This envelopment stage shares many characteristics with the formation of luminal vesicles in multivesicular endosomes. Through expression of dominant-negative Vps4, an enzyme that is essential for the formation of luminal vesicles in multivesicular endosomes, we now show that Vps4 function is required for the cytoplasmic envelopment of herpes simplex virus type 1. This is the first example of a large enveloped DNA virus engaging the multivesicular endosome sorting machinery to enable infectious virus production.
Figures
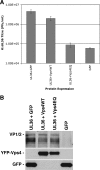
FIG. 1.
The effect of transient Vps4EQ expression on the production of infectious HSV-1. Cells transfected with a UL36 expression plasmid in the presence of GFP, YFP-Vps4WT, or YFP-Vps4EQ expression plasmids or cells transfected with a GFP expression plasmid alone were infected with HSV-1ΔUL36. (A) Progeny viral titers were determined by plaque assay on a UL36-complementing cell line. Bars represent mean PFU/ml, and error bars represent 1 standard deviation from the mean of triplicate samples. (B) Protein extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with VP1/2- and GFP-specific antibodies.
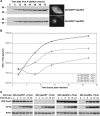
FIG. 2.
Single-step growth curves of HSV-1 in Vps4WT- and Vps4EQ-expressing cell lines. Clonal 293 cell lines expressing GFP-Vps4WT or GFP-Vps4EQ under the control of the ecdysone response element were isolated. (A) Cells were treated with 1 μM ponA for various times, and protein extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with a GFP-specific antibody. Fluorescence microscope images were collected at 16 h after ponA addition. Numbers at left are molecular masses in kilodaltons. (B) Cells were treated with or without ponA for 16 h and infected with HSV-1, and progeny virus was harvested at various times. Infectious viral titers were determined by plaque assay. Data represent mean PFU/ml, and error bars represent 1 standard deviation from the mean of triplicate samples. (C) Protein extracts were harvested from infected cells at various times postinfection and analyzed by Western blotting with GFP-, VP16-, and actin-specific antibodies.
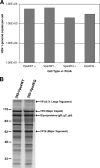
FIG. 3.
HSV-1 genome and protein synthesis. 293-Vps4WT and 293-Vps4EQ cells were treated with 1 μM ponA or not and infected with HSV-1. (A) DNA samples were harvested at 16 hpi, and the copy numbers of HSV-1 and cellular genomes were determined by real-time PCR. Data are shown as mean numbers of HSV-1 genome copies per cell. (B) Infected cells were labeled with [35S]methionine, and protein samples were harvested at 24 hpi. Radiolabeled proteins were detected by autoradiography following SDS-PAGE. The positions of various viral proteins, as expected from previous publications, are shown. Numbers at left are molecular masses in kilodaltons.
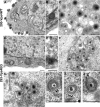
FIG. 4.
EM analysis of infected cells. 293-Vps4WT and 293-Vps4EQ cells were induced with ponA and infected with HSV-1. At 15 hpi, cells were fixed, processed, and analyzed by transmission EM. Bars, 500 nm (A) or 200 nm (B to J).
Similar articles
- HSV-1 Cytoplasmic Envelopment and Egress.
Ahmad I, Wilson DW. Ahmad I, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 19;21(17):5969. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175969. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32825127 Free PMC article. Review. - Herpes simplex virus type 1 production requires a functional ESCRT-III complex but is independent of TSG101 and ALIX expression.
Pawliczek T, Crump CM. Pawliczek T, et al. J Virol. 2009 Nov;83(21):11254-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00574-09. Epub 2009 Aug 19. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19692479 Free PMC article. - Herpes Simplex Virus Capsid Localization to ESCRT-VPS4 Complexes in the Presence and Absence of the Large Tegument Protein UL36p.
Kharkwal H, Smith CG, Wilson DW. Kharkwal H, et al. J Virol. 2016 Jul 27;90(16):7257-7267. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00857-16. Print 2016 Aug 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27252536 Free PMC article. - The herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D (gD) cytoplasmic terminus and full-length gE are not essential and do not function in a redundant manner for cytoplasmic virion envelopment and egress.
Lee HC, Chouljenko VN, Chouljenko DV, Boudreaux MJ, Kousoulas KG. Lee HC, et al. J Virol. 2009 Jun;83(12):6115-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00128-09. Epub 2009 Apr 8. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19357164 Free PMC article. - Involvement of Terminase Complex in Herpes Simplex Virus Mature Virion Egress.
Rao AM, Balireddy S, Mohammad FS, Somashekara DM, Hariharapura RC. Rao AM, et al. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2022;23(2):105-113. doi: 10.2174/1389203723666220217144432. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2022. PMID: 35176987 Review.
Cited by
- Consecutive Inhibition of ISG15 Expression and ISGylation by Cytomegalovirus Regulators.
Kim YJ, Kim ET, Kim YE, Lee MK, Kwon KM, Kim KI, Stamminger T, Ahn JH. Kim YJ, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2016 Aug 26;12(8):e1005850. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005850. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27564865 Free PMC article. - Dysregulation of autophagy in murine fibroblasts resistant to HSV-1 infection.
Le Sage V, Banfield BW. Le Sage V, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042636. Epub 2012 Aug 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22900036 Free PMC article. - Human Cytomegalovirus UL135 and UL136 Genes Are Required for Postentry Tropism in Endothelial Cells.
Bughio F, Umashankar M, Wilson J, Goodrum F. Bughio F, et al. J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(13):6536-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00284-15. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25878111 Free PMC article. - HSV-1 Cytoplasmic Envelopment and Egress.
Ahmad I, Wilson DW. Ahmad I, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 19;21(17):5969. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175969. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32825127 Free PMC article. Review. - Biogenesis of Extracellular Vesicles during Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection: Role of the CD63 Tetraspanin.
Dogrammatzis C, Deschamps T, Kalamvoki M. Dogrammatzis C, et al. J Virol. 2019 Jan 4;93(2):e01850-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01850-18. Print 2019 Jan 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30355691 Free PMC article.
References
- Bieniasz, P. D. 2006. Late budding domains and host proteins in enveloped virus release. Virology 344:55-63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources