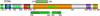TRPC channels as STIM1-regulated store-operated channels - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
TRPC channels as STIM1-regulated store-operated channels
Paul F Worley et al. Cell Calcium. 2007 Aug.
Abstract
Receptor-activated Ca(2+) influx is mediated largely by store-operated channels (SOCs). TRPC channels mediate a significant portion of the receptor-activated Ca(2+) influx. However, whether any of the TRPC channels function as a SOC remains controversial. Our understanding of the regulation of TRPC channels and their function as SOCs is being reshaped with the discovery of the role of STIM1 in the regulation of Ca(2+) influx channels. The findings that STIM1 is an ER resident Ca(2+) binding protein that regulates SOCs allow an expanded and molecular definition of SOCs. SOCs can be considered as channels that are regulated by STIM1 and require the clustering of STIM1 in response to depletion of the ER Ca(2+) stores and its translocation towards the plasma membrane. TRPC1 and other TRPC channels fulfill these criteria. STIM1 binds to TRPC1, TRPC2, TRPC4 and TRPC5 but not to TRPC3, TRPC6 and TRPC7, and STIM1 regulates TRPC1 channel activity. Structure-function analysis reveals that the C-terminus of STIM1 contains the binding and gating function of STIM1. The ERM domain of STIM1 binds to TRPC channels and a lysine-rich region participates in the gating of SOCs and TRPC1. Knock-down of STIM1 by siRNA and prevention of its translocation to the plasma membrane inhibit the activity of native SOCs and TRPC1. These findings support the conclusion that TRPC1 is a SOC. Similar studies with other TRPC channels demonstrate their regulation by STIM1 and indicate that all TRPC channels, except TRPC7, function as SOCs.
Figures
Fig. 1
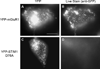
Majority of the YFP-STIM1 D76A punctae are not on the plasma membrane. HEK293 cells were transfected with YFPmGluR1 together with Homer1 and Shank3 to get the YFP-mGluR1 to the plasma membrane (A, B) or YFP-STIM1 D76A (C, D). A and C are intrinsic YFP signals. B and D are images of surface live staining with an anti- GFP rabbit polyclonal antibody. The intense signal in A is from Golgi. Scale bar, 10 µm.
Fig. 2
STIM1 and its domains
Fig. 3
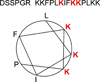
The predicted two-turn helix of the C-terminal tail of STIM1.
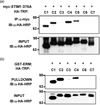
Fig. 4. Interaction of STIM1 with TRPC channels
Panel (a) shows to co-IP of STIM1 and the indicated TRPC channels expressed in HEK cells. Panel (b) shows the pull-down of the indicated TRPC channels by GST-ERM domain of STIM1.
Similar articles
- TRPC channels as STIM1-regulated SOCs.
Yuan JP, Kim MS, Zeng W, Shin DM, Huang G, Worley PF, Muallem S. Yuan JP, et al. Channels (Austin). 2009 Jul-Aug;3(4):221-5. doi: 10.4161/chan.3.4.9198. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Channels (Austin). 2009. PMID: 19574740 Review. - STIM1 heteromultimerizes TRPC channels to determine their function as store-operated channels.
Yuan JP, Zeng W, Huang GN, Worley PF, Muallem S. Yuan JP, et al. Nat Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;9(6):636-45. doi: 10.1038/ncb1590. Epub 2007 May 7. Nat Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17486119 Free PMC article. - Molecular determinants mediating gating of Transient Receptor Potential Canonical (TRPC) channels by stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1).
Lee KP, Choi S, Hong JH, Ahuja M, Graham S, Ma R, So I, Shin DM, Muallem S, Yuan JP. Lee KP, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):6372-6382. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.546556. Epub 2014 Jan 24. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24464579 Free PMC article. - STIM1 carboxyl-terminus activates native SOC, I(crac) and TRPC1 channels.
Huang GN, Zeng W, Kim JY, Yuan JP, Han L, Muallem S, Worley PF. Huang GN, et al. Nat Cell Biol. 2006 Sep;8(9):1003-10. doi: 10.1038/ncb1454. Epub 2006 Aug 13. Nat Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16906149 - The TRPCs-STIM1-Orai interaction.
Choi S, Maleth J, Jha A, Lee KP, Kim MS, So I, Ahuja M, Muallem S. Choi S, et al. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;223:1035-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-05161-1_13. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24961979 Review.
Cited by
- The synthetic triterpenoid, RTA 405, increases the glomerular filtration rate and reduces angiotensin II-induced contraction of glomerular mesangial cells.
Ding Y, Stidham RD, Bumeister R, Trevino I, Winters A, Sprouse M, Ding M, Ferguson DA, Meyer CJ, Wigley WC, Ma R. Ding Y, et al. Kidney Int. 2013 May;83(5):845-54. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.393. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23235569 Free PMC article. - Store-operated channels regulate intracellular calcium in mammalian rods.
Molnar T, Barabas P, Birnbaumer L, Punzo C, Kefalov V, Križaj D. Molnar T, et al. J Physiol. 2012 Aug 1;590(15):3465-81. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.234641. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22674725 Free PMC article. - On the role of endothelial TRPC3 channels in endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular disease.
Smedlund K, Bah M, Vazquez G. Smedlund K, et al. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2012 Sep;10(3):265-74. doi: 10.2174/187152512802651051. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22827251 Free PMC article. Review. - Calcium homeostasis and cone signaling are regulated by interactions between calcium stores and plasma membrane ion channels.
Szikra T, Barabas P, Bartoletti TM, Huang W, Akopian A, Thoreson WB, Krizaj D. Szikra T, et al. PLoS One. 2009 Aug 21;4(8):e6723. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006723. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19696927 Free PMC article. - The closing and opening of TRPC channels by Homer1 and STIM1.
Yuan JP, Lee KP, Hong JH, Muallem S. Yuan JP, et al. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012 Feb;204(2):238-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02319.x. Epub 2011 May 27. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012. PMID: 21518270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Parekh AB, Putney JW., Jr Store-operated calcium channels. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:757–810. - PubMed
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:517–529. - PubMed
- Parekh AB, Penner R. Store depletion and calcium influx. Physiol Rev. 1997;77:901–930. - PubMed
- Feske S, Gwack Y, Prakriya M, Srikanth S, Puppel SH, Tanasa B, Hogan PG, Lewis RS, Daly M, Rao A. A mutation in Orai1 causes immune deficiency by abrogating CRAC channel function. Nature. 2006;441:179–185. - PubMed
- Prakriya M, Feske S, Gwack Y, Srikanth S, Rao A, Hogan PG. Orai1 is an essential pore subunit of the CRAC channel. Nature. 2006;443:230–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK038938-16/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-03/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA010309-05/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-21/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA010309/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH068830-040002/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA010309-09/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA000266-370017/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-08/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA010309-06/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-15/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH068830-020002/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-20/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA010309-04/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH068830-050002/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA010309-08/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA010309/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA010309-07/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-10/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-11/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-22/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-05/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH068830-010002/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-18/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-23/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-09/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-14/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-19/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-12/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-06/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH068830-030002/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA000266/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA000266-360017/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-17/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-07/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-13/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH068830/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA000266-310015/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938-24/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012309-04/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038938/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous