MAGMA: analysis of two-channel microarrays made easy - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W86-90.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm302. Epub 2007 May 21.
Affiliations
- PMID: 17517778
- PMCID: PMC1933123
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm302
MAGMA: analysis of two-channel microarrays made easy
Hubert Rehrauer et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul.
Abstract
The web application MAGMA provides a simple and intuitive interface to identify differentially expressed genes from two-channel microarray data. While the underlying algorithms are not superior to those of similar web applications, MAGMA is particularly user friendly and can be used without prior training. The user interface guides the novice user through the most typical microarray analysis workflow consisting of data upload, annotation, normalization and statistical analysis. It automatically generates R-scripts that document MAGMA's entire data processing steps, thereby allowing the user to regenerate all results in his local R installation. The implementation of MAGMA follows the model-view-controller design pattern that strictly separates the R-based statistical data processing, the web-representation and the application logic. This modular design makes the application flexible and easily extendible by experts in one of the fields: statistical microarray analysis, web design or software development. State-of-the-art Java Server Faces technology was used to generate the web interface and to perform user input processing. MAGMA's object-oriented modular framework makes it easily extendible and applicable to other fields and demonstrates that modern Java technology is also suitable for rather small and concise academic projects. MAGMA is freely available at www.magma-fgcz.uzh.ch.
Figures
Figure 1.
Structural representation of MAGMA's architecture. MAGMA implements the Model-View-Controller paradigm and has the HTML pages (View), the rules for the HTML page flow (Controller) and the actual data processing (Model) decoupled. This allows for independent modification or extension of MAGMA.
Figure 2.
MAGMA's result navigation panel. For each analyzed experiment, the results are organized in an explorer-like hierarchy. Each folder of the tree represents a single processing step and clicking on it, displays the corresponding result in the lower part of the page. More processing steps can be added after the current processing step by selecting a step from the Next box.
Figure 3.
Graphs visualizing diagnostic statistics. In the example, the percentage of flagged and negative probes as well as the median log ratio is shown for six uploaded arrays. These overview plots allow for the identification of outliers as well as general trends.
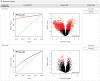
Figure 4.
Result of a statistical analysis that included two comparisons. Each comparison is shown as a row with two plots. The first plot shows the number of significantly differentially expressed genes (red) selected using the current _P_-value threshold and compares it to results expected from random data. The second figure shows a Volcano plot displaying the _P_-values and fold changes of all genes with significant genes highlighted in red. The results can be retrieved in tabular form from the links in the rightmost column.
Similar articles
- MARS: microarray analysis, retrieval, and storage system.
Maurer M, Molidor R, Sturn A, Hartler J, Hackl H, Stocker G, Prokesch A, Scheideler M, Trajanoski Z. Maurer M, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr 18;6:101. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-101. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15836795 Free PMC article. - MILANO--custom annotation of microarray results using automatic literature searches.
Rubinstein R, Simon I. Rubinstein R, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Jan 20;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-12. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15661078 Free PMC article. - JCell--a Java-based framework for inferring regulatory networks from time series data.
Spieth C, Supper J, Streichert F, Speer N, Zell A. Spieth C, et al. Bioinformatics. 2006 Aug 15;22(16):2051-2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl322. Epub 2006 Jun 16. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16782725 - Software packages for quantitative microarray-based gene expression analysis.
Dresen IM, Hüsing J, Kruse E, Boes T, Jöckel KH. Dresen IM, et al. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2003 Dec;4(6):417-37. doi: 10.2174/1389201033377436. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 14683435 Review. - Recent developments of the chemistry development kit (CDK) - an open-source java library for chemo- and bioinformatics.
Steinbeck C, Hoppe C, Kuhn S, Floris M, Guha R, Willighagen EL. Steinbeck C, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(17):2111-20. doi: 10.2174/138161206777585274. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 16796559 Review.
Cited by
- The transcriptional response to encystation stimuli in Giardia lamblia is restricted to a small set of genes.
Morf L, Spycher C, Rehrauer H, Fournier CA, Morrison HG, Hehl AB. Morf L, et al. Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Oct;9(10):1566-76. doi: 10.1128/EC.00100-10. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 20693303 Free PMC article. - EzArray: a web-based highly automated Affymetrix expression array data management and analysis system.
Zhu Y, Zhu Y, Xu W. Zhu Y, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Jan 24;9:46. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-46. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18218103 Free PMC article. - D-MaPs - DNA-microarray projects: Web-based software for multi-platform microarray analysis.
Carazzolle MF, Herig TS, Deckmann AC, Pereira GA. Carazzolle MF, et al. Genet Mol Biol. 2009 Jul;32(3):634-9. doi: 10.1590/S1415-47572009000300030. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Genet Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 21637530 Free PMC article. - Pomelo II: finding differentially expressed genes.
Morrissey ER, Diaz-Uriarte R. Morrissey ER, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(Web Server issue):W581-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp366. Epub 2009 May 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19435879 Free PMC article. - RIP-chip-SRM--a new combinatorial large-scale approach identifies a set of translationally regulated bantam/miR-58 targets in C. elegans.
Jovanovic M, Reiter L, Clark A, Weiss M, Picotti P, Rehrauer H, Frei A, Neukomm LJ, Kaufman E, Wollscheid B, Simard MJ, Miska EA, Aebersold R, Gerber AP, Hengartner MO. Jovanovic M, et al. Genome Res. 2012 Jul;22(7):1360-71. doi: 10.1101/gr.133330.111. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22454234 Free PMC article.