CodonO: codon usage bias analysis within and across genomes - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W132-6.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm392. Epub 2007 May 30.
Affiliations
- PMID: 17537810
- PMCID: PMC1933134
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm392
CodonO: codon usage bias analysis within and across genomes
Michael C Angellotti et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul.
Abstract
Synonymous codon usage biases are associated with various biological factors, such as gene expression level, gene length, gene translation initiation signal, protein amino acid composition, protein structure, tRNA abundance, mutation frequency and patterns, and GC compositions. Quantification of codon usage bias helps understand evolution of living organisms. A codon usage bias pipeline is demanding for codon usage bias analyses within and across genomes. Here we present a CodonO webserver service as a user-friendly tool for codon usage bias analyses across and within genomes in real time. The webserver is available at http//www.sysbiology.org/CodonO.
Contact: wanhenry@yahoo.com.
Figures
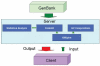
Figure 1.
Simplified CodonO webserver infrastructure.
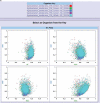
Figure 2.
(A) Visualization of the correlation between synonymous codon usage bias and GC compositions; (B) Visualization of synonymous codon usage bias for each gene in a specific genome; (C) Statistical analysis of synonymous codon usage bias.
Figure 2.
(A) Visualization of the correlation between synonymous codon usage bias and GC compositions; (B) Visualization of synonymous codon usage bias for each gene in a specific genome; (C) Statistical analysis of synonymous codon usage bias.
Similar articles
- Quantitative relationship between synonymous codon usage bias and GC composition across unicellular genomes.
Wan XF, Xu D, Kleinhofs A, Zhou J. Wan XF, et al. BMC Evol Biol. 2004 Jun 28;4:19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-4-19. BMC Evol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15222899 Free PMC article. - The mystery of two straight lines in bacterial genome statistics.
Gorban AN, Zinovyev AY. Gorban AN, et al. Bull Math Biol. 2007 Oct;69(7):2429-42. doi: 10.1007/s11538-007-9229-6. Epub 2007 Jun 19. Bull Math Biol. 2007. PMID: 17577600 - Constraint on di-nucleotides by codon usage bias in bacterial genomes.
Satapathy SS, Powdel BR, Dutta M, Buragohain AK, Ray SK. Satapathy SS, et al. Gene. 2014 Feb 15;536(1):18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.11.098. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24333347 - Codon usage bias: causative factors, quantification methods and genome-wide patterns: with emphasis on insect genomes.
Behura SK, Severson DW. Behura SK, et al. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2013 Feb;88(1):49-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2012.00242.x. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2013. PMID: 22889422 Review. - Codon usage bias.
Parvathy ST, Udayasuriyan V, Bhadana V. Parvathy ST, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jan;49(1):539-565. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06749-4. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34822069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Evolutionary rates and gene dispensability associate with replication timing in the archaeon Sulfolobus islandicus.
Flynn KM, Vohr SH, Hatcher PJ, Cooper VS. Flynn KM, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2010;2:859-69. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evq068. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Genome Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20978102 Free PMC article. - Codon usage vis-a-vis start and stop codon context analysis of three dicot species.
Paul P, Malakar AK, Chakraborty S. Paul P, et al. J Genet. 2018 Mar;97(1):97-107. J Genet. 2018. PMID: 29666329 - Codon Deviation Coefficient: a novel measure for estimating codon usage bias and its statistical significance.
Zhang Z, Li J, Cui P, Ding F, Li A, Townsend JP, Yu J. Zhang Z, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Mar 22;13:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-43. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22435713 Free PMC article. - COUSIN (COdon Usage Similarity INdex): A Normalized Measure of Codon Usage Preferences.
Bourret J, Alizon S, Bravo IG. Bourret J, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2019 Dec 1;11(12):3523-3528. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz262. Genome Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 31800035 Free PMC article. - Comparative investigation of the various determinants that influence the codon and amino acid usage patterns in the genus Bifidobacterium.
Roy A, Mukhopadhyay S, Sarkar I, Sen A. Roy A, et al. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Jun;31(6):959-81. doi: 10.1007/s11274-015-1850-1. Epub 2015 Apr 5. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25842224
References
- Bains W. Codon distribution in vertebrate genes may be used to predict gene length. J. Mol. Biol. 1987;197:379–388. - PubMed
- D’Onofrio G, Ghosh TC, Bernardi G. The base composition of the genes is correlated with the secondary structures of the encoded proteins. Gene. 2002;300:179–187. - PubMed
- Bernardi G, Bernardi G. Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 1986;24:1–11. - PubMed
- Gu W, Zhou T, Ma J, Sun X, Lu Z. The relationship between synonymous codon usage and protein structure in Escherichia coli and Homo sapiens. Biosystems. 2004;73:89–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous