LIPID MAPS online tools for lipid research - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W606-12.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm324. Epub 2007 Jun 21.
Affiliations
- PMID: 17584797
- PMCID: PMC1933166
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm324
LIPID MAPS online tools for lipid research
Eoin Fahy et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul.
Abstract
The LIPID MAPS consortium has developed a number of online tools for performing tasks such as drawing lipid structures and predicting possible structures from mass spectrometry (MS) data. A simple online interface has been developed to enable an end-user to rapidly generate a variety of lipid chemical structures, along with corresponding systematic names and ontological information. The structure-drawing tools are available for six categories of lipids: (i) fatty acyls, (ii) glycerolipids, (iii) glycerophospholipids, (iv) cardiolipins, (v) sphingolipids and (vi) sterols. Within each category, the structure-drawing tools support the specification of various parameters such as chain lengths at a specific sn position, head groups, double bond positions and stereochemistry to generate a specific lipid structure. The structure-drawing tools have also been integrated with a second set of online tools which predict possible lipid structures from precursor-ion and product-ion MS experimental data. The MS prediction tools are available for three categories of lipids: (i) mono/di/triacylglycerols, (ii) glycerophospholipids and (iii) cardiolipins. The LIPID MAPS online tools are publicly available at www.lipidmaps.org/tools/.
Figures
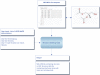
Figure 1.
Schematic demonstrating the principle of using molfile templates and a list of lipid abbreviations as input for structure-drawing tools.
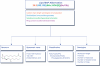
Figure 2.
Online structure-drawing tool for glycerophospholipids.
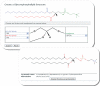
Figure 3.
Flowchart showing structure/name/ontology generation from an abbreviation of a lipid. This example demonstrates the conversion of a text abbreviation for a prostaglandin into a dataset containing structure (MDL Molfile), systematic name, classification and various molecular attributes such as formula, molecular weight, number of functional groups, double bonds and rings.
Figure 4.
Online MS prediction tools for glycerophospholipids.
Similar articles
- LMSD: LIPID MAPS structure database.
Sud M, Fahy E, Cotter D, Brown A, Dennis EA, Glass CK, Merrill AH Jr, Murphy RC, Raetz CR, Russell DW, Subramaniam S. Sud M, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D527-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl838. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17098933 Free PMC article. - Shorthand notation for lipid structures derived from mass spectrometry.
Liebisch G, Vizcaíno JA, Köfeler H, Trötzmüller M, Griffiths WJ, Schmitz G, Spener F, Wakelam MJO. Liebisch G, et al. J Lipid Res. 2013 Jun;54(6):1523-1530. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M033506. Epub 2013 Apr 2. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23549332 Free PMC article. - Lipid classification, structures and tools.
Fahy E, Cotter D, Sud M, Subramaniam S. Fahy E, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov;1811(11):637-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.06.009. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21704189 Free PMC article. Review. - Update of the LIPID MAPS comprehensive classification system for lipids.
Fahy E, Subramaniam S, Murphy RC, Nishijima M, Raetz CR, Shimizu T, Spener F, van Meer G, Wakelam MJ, Dennis EA. Fahy E, et al. J Lipid Res. 2009 Apr;50 Suppl(Suppl):S9-14. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800095-JLR200. Epub 2008 Dec 19. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19098281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Hepatic lipid signatures of little brown bats (Myotis lucifugus) and big brown bats (Eptesicus fuscus) at early stages of white-nose syndrome.
Pannkuk EL, Dorville NAS, Dzal YA, Fletcher QE, Norquay KJO, Willis CKR, Fornace AJ Jr, Laiakis EC. Pannkuk EL, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 2;11(1):11581. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90828-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34078939 Free PMC article. - Targeting of the hydrophobic metabolome by pathogens.
Helms JB, Kaloyanova DV, Strating JR, van Hellemond JJ, van der Schaar HM, Tielens AG, van Kuppeveld FJ, Brouwers JF. Helms JB, et al. Traffic. 2015 May;16(5):439-60. doi: 10.1111/tra.12280. Traffic. 2015. PMID: 25754025 Free PMC article. Review. - Succession of rumen microbiota and metabolites across different reproductive periods in different sheep breeds and their impact on the growth and development of offspring lambs.
Sha Y, Liu X, Li X, Wang Z, Shao P, Jiao T, He Y, Zhao S. Sha Y, et al. Microbiome. 2024 Sep 12;12(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01892-z. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39267132 Free PMC article. - Metabolic changes in response to varying whole-grain wheat and rye intake.
Koistinen VM, Haldar S, Tuomainen M, Lehtonen M, Klåvus A, Draper J, Lloyd A, Beckmann M, Bal W, Ross AB, Brandt K, Fawcett L, Seal C, Hanhineva K. Koistinen VM, et al. NPJ Sci Food. 2024 Jan 30;8(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41538-024-00247-0. NPJ Sci Food. 2024. PMID: 38291073 Free PMC article. - IDSL_MINT: a deep learning framework to predict molecular fingerprints from mass spectra.
Baygi SF, Barupal DK. Baygi SF, et al. J Cheminform. 2024 Jan 18;16(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13321-024-00804-5. J Cheminform. 2024. PMID: 38238779 Free PMC article.
References
- Weininger D. SMILES, a chemical language and information system. 1. Introduction to methodology and encoding rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1988;28(1):31–36.
- Watanabe K, Yasugi E, Ohshima M. How to search the glycolipid data in “Lipidbank for web”, the newly-developed lipid database in Japan. Trends Gycosci. Glycotechnol. 2000;12:175–184.
- Caffrey M, Hogan J. LIPIDAT: a database of lipid phase transition temperatures and enthalpy changes. DMPC data subset analysis. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 1992;61:1–109. - PubMed
- Fahy E, Subramaniam S, Brown HA, Glass CK, Merrill A.H., Jr, Murphy RC, Raetz CR, Russell, D.W. Seyama Y, et al. A comprehensive classification system for lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2005;46:839–862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources