miR-200b mediates post-transcriptional repression of ZFHX1B - PubMed (original) (raw)
miR-200b mediates post-transcriptional repression of ZFHX1B
Nanna Rønbjerg Christoffersen et al. RNA. 2007 Aug.
Abstract
MicroRNAs have important functions during animal development and homeostasis through post-transcriptional regulation of their cognate mRNA targets. ZFHX1B is a transcriptional repressor involved in the TGFbeta signaling pathway and in processes of epithelial to mesenchymal transition via regulation of E-cadherin. We show that Zfhx1b and miR-200b are regionally coexpressed in the adult mouse brain and that miR-200b represses the expression of Zfhx1b via multiple sequence elements present in the 3'-untranslated region. Overexpression of miR-200b leads to repression of endogenous ZFHX1B, and inhibition of miR-200b relieves the repression of ZFHX1B. In accordance with these findings, miR-200b regulates the activity of the E-cadherin promoter.
Figures
FIGURE 1.
miR-200b binding sites in the Zfhx1b 3′-UTR are conserved across species. Schematic representation of the mouse Zfhx1b 3′-UTR containing five potential binding sites for miR-200b (S1–S5), based on occurrence of the complementary miR-200b seed region, CAGUAUU. Numbers refer to positions in Ensembl transcript ENSMUST00000076836. Alignment of a predicted miR-200b binding site (S3) in the ZFHX1B 3′-UTR with complete conservation across three mammalian species is shown as an example. The mature sequence of miR-200b is conserved across the shown species. The seed region of miR-200b is shown in bold.
FIGURE 2.
Expression of miR-200b and Zfhx1b mRNA in the brain. (Top panel) Sagittal section of adult mouse brain hybridized with an antisense RNA probe for Zfhx1b (Allen Brain Atlas 2004). (Bottom panel) Sagittal section of adult mouse brain hybridized with an antisense LNA-modified oligonucleotide probe for miR-200b. Both genes are expressed in the neocortex, pyramidal cell layer, and dentate gyrus of the hippocampal formation as well as in the granular layer of cerebellum. (Py) Pyramidal cell layer; (DG) Dentate gyrus.
FIGURE 3.
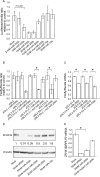
miR-200b regulates the 3′ UTR of Zfhx1b. (A) A luciferase reporter construct containing five miR-200b binding sites was cotransfected into HEK293 cells along with miR-200b, mutated miR-200b, or miR-10a. Five to 30 nM miR-200b represssed the reporter (*P < 0.001, Student's _t_-test). (Mock) Cells transfected with the luciferase reporter construct alone. Data are shown as mean ± SD of six or seven replicates and are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Analysis of individual miR-200b binding sites. Luciferase reporter constructs containing miR-200b binding sites 1–5, 1–2, or 3–5 were cotransfected into HEK293 cells with 10 nM miR-200b or mutated miR-200b. As a control, the empty pGL3 vector was cotransfected with 10 nM miR-200b. miR-200b repressed all of the reporters containing miR-200b binding sites (*P < 0.001, Student's _t_-test) but not the empty vector. Data are shown as mean ± SD of six or seven replicates and are representative of three independent experiments. (C) miR-200b reduces luciferase reporter mRNA levels. Luciferase reporter constructs containing miR-200b binding sites 1–5, 1–2, or 3–5 were cotransfected into HEK293 cells with 10 nM miR-200b. miR-200b caused a significant decrease in the mRNA level of all reporter constructs (*P < 0.001, Student's _t_-test). Data are shown as mean ± SD of three replicates and are representative of five independent experiments. (D) Endogenous ZFHX1B protein is regulated by miR-200b. MDA-MB-435S cells were transfected with 30 nM ZFHX1B siRNA, miR-200b, mutated miR-200b, miR-10a, or an LNA inhibitor of miR-200b. Mock transfected cells were treated with transfection reagent alone. Forty-eight hours later, ZFHX1B levels were analyzed by Western blotting and the same blot was probed for Vincullin as a loading control. Quantification of the ZFHX1B expression relative to Vincullin is shown between the panels and referenced to the expression level in mock transfected cells. The blot is representative of three independent experiments. (E) miR-200b causes degradation of endogenous ZFHX1B mRNA. MDA-MB-435S cells were transfected with 30 nM ZFHX1B siRNA, miR-200b, or mutated miR-200b. Mock transfected cells were treated with transfection reagent alone. miR-200b significantly reduced ZFHX1B mRNA levels as determined by quantitative PCR 48 h after transfection (*P < 0.001, Student's _t_-test). ZFHX1B levels are shown relative to RPLP0 and referenced to the ZFHX1B/RPLP0 ratio in mock transfected cells. Data are shown as mean ± SD of three replicates and are representative of three independent experiments.
FIGURE 4.
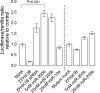
miR-200b increases E-cadherin promoter activity. A luciferase construct containing part of the human E-cadherin promoter, including the E-boxes, was cotransfected into HEK293 cells with Zfhx1b, siRNA against ZFHX1B, miR-200b, or miR-10a. miR-200b derepressed the E-cadherin promoter construct (P < 0.001, Student's _t_-test) whereas miR-10a did not. (Mock) cells transfected with the luciferase construct alone. As a control, a pGL2 construct with point mutations in the E-boxes of the E-cadherin promoter was cotransfected with Zfhx1b or miR-200b (right part of figure). (Mutant mock) cells transfected with the mutated luciferase construct alone. Data are shown as mean ± SD of six or seven replicates and are representative of three independent experiments.
Similar articles
- Genome-wide microRNA expression profiling in renal cell carcinoma: significant down-regulation of miR-141 and miR-200c.
Nakada C, Matsuura K, Tsukamoto Y, Tanigawa M, Yoshimoto T, Narimatsu T, Nguyen LT, Hijiya N, Uchida T, Sato F, Mimata H, Seto M, Moriyama M. Nakada C, et al. J Pathol. 2008 Dec;216(4):418-27. doi: 10.1002/path.2437. J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18925646 - miR-205 Exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human prostate through down-regulation of protein kinase Cepsilon.
Gandellini P, Folini M, Longoni N, Pennati M, Binda M, Colecchia M, Salvioni R, Supino R, Moretti R, Limonta P, Valdagni R, Daidone MG, Zaffaroni N. Gandellini P, et al. Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 15;69(6):2287-95. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2894. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19244118 - Target identification of microRNAs expressed highly in human embryonic stem cells.
Li SS, Yu SL, Kao LP, Tsai ZY, Singh S, Chen BZ, Ho BC, Liu YH, Yang PC. Li SS, et al. J Cell Biochem. 2009 Apr 15;106(6):1020-30. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22084. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19229866 - Dual mechanism of deltaEF1 expression regulated by bone morphogenetic protein-6 in breast cancer.
Yang S, Du J, Wang Z, Yan J, Yuan W, Zhang J, Zhu T. Yang S, et al. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;41(4):853-61. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.08.030. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18805502 - Hedgehog signaling, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and miRNA (review).
Katoh Y, Katoh M. Katoh Y, et al. Int J Mol Med. 2008 Sep;22(3):271-5. Int J Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18698484 Review.
Cited by
- MicroRNA and cancer.
Jansson MD, Lund AH. Jansson MD, et al. Mol Oncol. 2012 Dec;6(6):590-610. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.09.006. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Mol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23102669 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of non-coding RNAs in the regulation of stem cells and progenitors in the normal mammary gland and in breast tumors.
Tordonato C, Di Fiore PP, Nicassio F. Tordonato C, et al. Front Genet. 2015 Feb 27;6:72. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00072. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25774169 Free PMC article. Review. - Molecular mechanisms controlling E-cadherin expression in breast cancer.
Baranwal S, Alahari SK. Baranwal S, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Jun 19;384(1):6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.051. Epub 2009 Apr 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19379710 Free PMC article. Review. - A microRNA circuit mediates transforming growth factor-β1 autoregulation in renal glomerular mesangial cells.
Kato M, Arce L, Wang M, Putta S, Lanting L, Natarajan R. Kato M, et al. Kidney Int. 2011 Aug;80(4):358-68. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.43. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Kidney Int. 2011. PMID: 21389977 Free PMC article. - MicroRNAs in normal and psoriatic skin.
Xia J, Zhang W. Xia J, et al. Physiol Genomics. 2014 Feb 15;46(4):113-22. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00157.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Physiol Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24326350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Allen Brain Atlas. Seattle, WA: Allen Institute for Brain Science. 2004. http://www.brain-map.org.
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
- Bagga, S., Bracht, J., Hunter, S., Massirer, K., Holtz, J., Eachus, R., Pasquinelli, A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
- Bassez, G., Camand, O.J., Cacheux, V., Kobetz, A., Dastot-Le Moal, F., Marchant, D., Catala, M., Abitbol, M., Goossens, M. Pleiotropic and diverse expression of ZFHX1B gene transcripts during mouse and human development supports the various clinical manifestations of the “Mowat–Wilson” syndrome. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004;15:240–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials