Concentrations of urinary phthalate metabolites are associated with increased waist circumference and insulin resistance in adult U.S. males - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
. 2007 Jun;115(6):876-82.
doi: 10.1289/ehp.9882. Epub 2007 Mar 14.
Affiliations
- PMID: 17589594
- PMCID: PMC1892109
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.9882
Comparative Study
Concentrations of urinary phthalate metabolites are associated with increased waist circumference and insulin resistance in adult U.S. males
Richard W Stahlhut et al. Environ Health Perspect. 2007 Jun.
Erratum in
- Environ Health Perspect. 2007 Sep;115(9):A443
Abstract
Background: Phthalates impair rodent testicular function and have been associated with anti-androgenic effects in humans, including decreased testosterone levels. Low testosterone in adult human males has been associated with increased prevalence of obesity, insulin resistance, and diabetes.
Objectives: Our objective in this study was to investigate phthalate exposure and its associations with abdominal obesity and insulin resistance.
Methods: Subjects were adult U.S. male participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999-2002. We modeled six phthalate metabolites with prevalent exposure and known or suspected antiandrogenic activity as predictors of waist circumference and log-transformed homeostatic model assessment (HOMA; a measure of insulin resistance) using multiple linear regression, adjusted for age, race/ethnicity, fat and total calorie consumption, physical activity level, serum cotinine, and urine creatinine (model 1); and adjusted for model 1 covariates plus measures of renal and hepatic function (model 2). Metabolites were mono-butyl phthalates (MBP), mono-ethyl phthalate (MEP), mono-(2-ethyl)-hexyl phthalate (MEHP), mono-benzyl phthalate (MBzP), mono-(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate (MEHHP), and mono-(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate (MEOHP).
Results: In model 1, four metabolites were associated with increased waist circumference (MBzP, MEHHP, MEOHP, and MEP; p-values </= 0.013) and three with increased HOMA (MBP, MBzP, and MEP; p-values </= 0.011). When we also adjusted for renal and hepatic function, parameter estimates declined but all significant results remained so except HOMA-MBP.
Conclusions: In this national cross-section of U.S. men, concentrations of several prevalent phthalate metabolites showed statistically significant correlations with abdominal obesity and insulin resistance. If confirmed by longitudinal studies, our findings would suggest that exposure to these phthalates may contribute to the population burden of obesity, insulin resistance, and related clinical disorders.
Figures
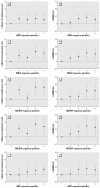
Figure 1
Fully-adjusted associations (adjusted model 1) between changes in outcomes and exposure quintiles (quintile 1 is reference) for metabolites with significant/near-significant (p ≤ 0.10) continuous regression coefficients. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals.
Similar articles
- Biomonitoring of phthalate metabolites in the Canadian population through the Canadian Health Measures Survey (2007-2009).
Saravanabhavan G, Guay M, Langlois É, Giroux S, Murray J, Haines D. Saravanabhavan G, et al. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2013 Nov;216(6):652-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2012.12.009. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2013. PMID: 23419587 - Phthalates and the diets of U.S. children and adolescents.
Trasande L, Sathyanarayana S, Jo Messito M, S Gross R, Attina TM, Mendelsohn AL. Trasande L, et al. Environ Res. 2013 Oct;126:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Environ Res. 2013. PMID: 24041780 - Occurrence and daily variation of phthalate metabolites in the urine of an adult population.
Fromme H, Bolte G, Koch HM, Angerer J, Boehmer S, Drexler H, Mayer R, Liebl B. Fromme H, et al. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2007 Jan;210(1):21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2006.09.005. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2007. PMID: 17182278 - Urinary phthalate metabolites and semen quality: a review of a potential biomarker of susceptibility.
Hauser R. Hauser R. Int J Androl. 2008 Apr;31(2):112-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2007.00844.x. Epub 2007 Dec 6. Int J Androl. 2008. PMID: 18067563 Review. - Possible impact of phthalates on infant reproductive health.
Lottrup G, Andersson AM, Leffers H, Mortensen GK, Toppari J, Skakkebaek NE, Main KM. Lottrup G, et al. Int J Androl. 2006 Feb;29(1):172-80; discussion 181-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2005.00642.x. Int J Androl. 2006. PMID: 16466537 Review.
Cited by
- Occupational exposure to phthalates in relation to gender, consumer practices and body composition.
Petrovičová I, Kolena B, Šidlovská M, Pilka T, Wimmerová S, Trnovec T. Petrovičová I, et al. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Dec;23(23):24125-24134. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7394-6. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27640056 - Role of environmental chemicals in diabetes and obesity: a National Toxicology Program workshop review.
Thayer KA, Heindel JJ, Bucher JR, Gallo MA. Thayer KA, et al. Environ Health Perspect. 2012 Jun;120(6):779-89. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1104597. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Environ Health Perspect. 2012. PMID: 22296744 Free PMC article. Review. - The Impact of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Male Fertility: Focus on the Action of Obesogens.
Rato L, Sousa ACA. Rato L, et al. J Xenobiot. 2021 Nov 29;11(4):163-196. doi: 10.3390/jox11040012. J Xenobiot. 2021. PMID: 34940512 Free PMC article. Review. - Relationship between housing characteristics, lifestyle factors and phthalates exposure: the first Korean National Environmental Health Survey (2009-2011).
Jung K, Oh H, Ryu JY, Kim DH, Lee S, Son BC, Lee CK. Jung K, et al. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2015 Dec 23;27:33. doi: 10.1186/s40557-015-0078-8. eCollection 2015. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2015. PMID: 26705476 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Phthalates and other additives in plastics: human exposure and associated health outcomes.
Meeker JD, Sathyanarayana S, Swan SH. Meeker JD, et al. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009 Jul 27;364(1526):2097-113. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0268. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19528058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Adams KF, Schatzkin A, Harris TB, Kipnis V, Mouw T, Ballard-Barbash R, et al. Overweight, obesity, and mortality in a large prospective cohort of persons 50 to 71 years old. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(8):763–778. - PubMed
- Andrade AJ, Grande SW, Talsness CE, Grote K, Chahoud I. A dose-response study following in utero and lactational exposure to di-(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate (DEHP): non-monotonic dose-response and low dose effects on rat brain aromatase activity. Toxicology. 2006;227(3):185–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous