Synteny and chromosome evolution in the lepidoptera: evidence from mapping in Heliconius melpomene - PubMed (original) (raw)
Synteny and chromosome evolution in the lepidoptera: evidence from mapping in Heliconius melpomene
Elizabeth G Pringle et al. Genetics. 2007 Sep.
Abstract
The extent of conservation of synteny and gene order in the Lepidoptera has been investigated previously only by comparing a small subset of linkage groups between the moth Bombyx mori and the butterfly Heliconius melpomene. Here we report the mapping of 64 additional conserved genes in H. melpomene, which contributed 47 markers to a comparative framework of 72 orthologous loci spanning all 21 H. melpomene chromosomes and 27 of the 28 B. mori chromosomes. Comparison of the maps revealed conserved synteny across all chromosomes for the 72 loci, as well as evidence for six cases of chromosome fusion in the Heliconius lineage that contributed to the derived 21-chromosome karyotype. Comparisons of gene order on these fused chromosomes revealed two instances of colinearity between H. melpomene and B. mori, but also one instance of likely chromosomal rearrangement. B. mori is the first lepidopteran species to have its genome sequenced, and the finding that there is conserved synteny and gene order among Lepidoptera indicates that the genomic tools developed in B. mori will be broadly useful in other species.
Figures
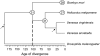
Figure 1.—
Phylogeny used to estimate time of divergence between B. mori and H. melpomene. The dashed line indicates the approximate age of divergence between these lineages (∼103 MY). Arrows indicate constrained nodes (see
materials and methods
). Numbers in circles indicate the haploid number of chromosomes for B. mori, H. melpomene, and basal taxa.
Figure 2.—
Linkage maps of putatively fused chromosomes in H. melpomene with comparison to maps of conserved markers in B. mori (A–F, corresponding to the six different putatively fused chromosomes in H. melpomene). Note the difference in scale between the maps. The lack of position bars for RpL13, ptc, and _Ef1_α in B. mori LG5 indicates that these markers were mapped using BAC–FISH instead of recombination linkage mapping (see Y
asukochi
et al. 2006). The lack of position bars for RpS16 in B. mori LG14 and H. melpomene LG13 indicates the lack of recombination mapping in B. mori and recombination mapping in a different brood (brood 44 as opposed to brood 33; see
materials and methods
) in H. melpomene.
Figure 2.—
Linkage maps of putatively fused chromosomes in H. melpomene with comparison to maps of conserved markers in B. mori (A–F, corresponding to the six different putatively fused chromosomes in H. melpomene). Note the difference in scale between the maps. The lack of position bars for RpL13, ptc, and _Ef1_α in B. mori LG5 indicates that these markers were mapped using BAC–FISH instead of recombination linkage mapping (see Y
asukochi
et al. 2006). The lack of position bars for RpS16 in B. mori LG14 and H. melpomene LG13 indicates the lack of recombination mapping in B. mori and recombination mapping in a different brood (brood 44 as opposed to brood 33; see
materials and methods
) in H. melpomene.
Similar articles
- Highly conserved gene order and numerous novel repetitive elements in genomic regions linked to wing pattern variation in Heliconius butterflies.
Papa R, Morrison CM, Walters JR, Counterman BA, Chen R, Halder G, Ferguson L, Chamberlain N, Ffrench-Constant R, Kapan DD, Jiggins CD, Reed RD, McMillan WO. Papa R, et al. BMC Genomics. 2008 Jul 22;9:345. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-345. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18647405 Free PMC article. - Extensive conserved synteny of genes between the karyotypes of Manduca sexta and Bombyx mori revealed by BAC-FISH mapping.
Yasukochi Y, Tanaka-Okuyama M, Shibata F, Yoshido A, Marec F, Wu C, Zhang H, Goldsmith MR, Sahara K. Yasukochi Y, et al. PLoS One. 2009 Oct 15;4(10):e7465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007465. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19829706 Free PMC article. - A second-generation integrated map of the silkworm reveals synteny and conserved gene order between lepidopteran insects.
Yasukochi Y, Ashakumary LA, Baba K, Yoshido A, Sahara K. Yasukochi Y, et al. Genetics. 2006 Jul;173(3):1319-28. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.055541. Epub 2006 Mar 17. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16547103 Free PMC article. - A gene-based linkage map for Bicyclus anynana butterflies allows for a comprehensive analysis of synteny with the lepidopteran reference genome.
Beldade P, Saenko SV, Pul N, Long AD. Beldade P, et al. PLoS Genet. 2009 Feb;5(2):e1000366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000366. Epub 2009 Feb 6. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19197358 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide identification and characterization of Fox genes in the silkworm, Bombyx mori.
Song J, Li Z, Tong X, Chen C, Chen M, Meng G, Chen P, Li C, Xin Y, Gai T, Dai F, Lu C. Song J, et al. Funct Integr Genomics. 2015 Sep;15(5):511-22. doi: 10.1007/s10142-015-0440-5. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Funct Integr Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25893708 Review.
Cited by
- Suppression of _Wolbachia_-mediated male-killing in the butterfly Hypolimnas bolina involves a single genomic region.
Reynolds LA, Hornett EA, Jiggins CD, Hurst GDD. Reynolds LA, et al. PeerJ. 2019 Oct 1;7:e7677. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7677. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31592190 Free PMC article. - A telomere-to-telomere assembly of Oscheius tipulae and the evolution of rhabditid nematode chromosomes.
Gonzalez de la Rosa PM, Thomson M, Trivedi U, Tracey A, Tandonnet S, Blaxter M. Gonzalez de la Rosa PM, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Jan 18;11(1):jkaa020. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaa020. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 33561231 Free PMC article. - Convergent evolution in the genetic basis of Müllerian mimicry in heliconius butterflies.
Baxter SW, Papa R, Chamberlain N, Humphray SJ, Joron M, Morrison C, ffrench-Constant RH, McMillan WO, Jiggins CD. Baxter SW, et al. Genetics. 2008 Nov;180(3):1567-77. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.082982. Epub 2008 Sep 14. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18791259 Free PMC article. - Chromosomal rearrangements maintain a polymorphic supergene controlling butterfly mimicry.
Joron M, Frezal L, Jones RT, Chamberlain NL, Lee SF, Haag CR, Whibley A, Becuwe M, Baxter SW, Ferguson L, Wilkinson PA, Salazar C, Davidson C, Clark R, Quail MA, Beasley H, Glithero R, Lloyd C, Sims S, Jones MC, Rogers J, Jiggins CD, ffrench-Constant RH. Joron M, et al. Nature. 2011 Aug 14;477(7363):203-6. doi: 10.1038/nature10341. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21841803 Free PMC article. - The evolution of sex ratio distorter suppression affects a 25 cM genomic region in the butterfly Hypolimnas bolina.
Hornett EA, Moran B, Reynolds LA, Charlat S, Tazzyman S, Wedell N, Jiggins CD, Hurst GD. Hornett EA, et al. PLoS Genet. 2014 Dec 4;10(12):e1004822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004822. eCollection 2014 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25474676 Free PMC article.
References
- Behura, S. K., 2006. Molecular marker systems in insects: current trends and future avenues. Mol. Ecol. 15: 3087–3113. - PubMed
- Blaxter, M., 2003. Comparative genomics: two worms are better than one. Nature 426: 395–396. - PubMed
- Brown, K. S., T. C. Emmel, P. J. Eliazar and E. Suomalainen, 1992. Evolutionary patterns in chromosome-numbers in neotropical Lepidoptera.1. Chromosomes of the Heliconiini (family Nymphalidae, subfamily Nymphalinae). Hereditas 117: 109–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources