Ancient biomolecules from deep ice cores reveal a forested southern Greenland - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2007 Jul 6;317(5834):111-4.
doi: 10.1126/science.1141758.
Enrico Cappellini, Wouter Boomsma, Rasmus Nielsen, Martin B Hebsgaard, Tina B Brand, Michael Hofreiter, Michael Bunce, Hendrik N Poinar, Dorthe Dahl-Jensen, Sigfus Johnsen, Jørgen Peder Steffensen, Ole Bennike, Jean-Luc Schwenninger, Roger Nathan, Simon Armitage, Cees-Jan de Hoog, Vasily Alfimov, Marcus Christl, Juerg Beer, Raimund Muscheler, Joel Barker, Martin Sharp, Kirsty E H Penkman, James Haile, Pierre Taberlet, M Thomas P Gilbert, Antonella Casoli, Elisa Campani, Matthew J Collins
Affiliations
- PMID: 17615355
- PMCID: PMC2694912
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1141758
Ancient biomolecules from deep ice cores reveal a forested southern Greenland
Eske Willerslev et al. Science. 2007.
Abstract
It is difficult to obtain fossil data from the 10% of Earth's terrestrial surface that is covered by thick glaciers and ice sheets, and hence, knowledge of the paleoenvironments of these regions has remained limited. We show that DNA and amino acids from buried organisms can be recovered from the basal sections of deep ice cores, enabling reconstructions of past flora and fauna. We show that high-altitude southern Greenland, currently lying below more than 2 kilometers of ice, was inhabited by a diverse array of conifer trees and insects within the past million years. The results provide direct evidence in support of a forested southern Greenland and suggest that many deep ice cores may contain genetic records of paleoenvironments in their basal sections.
Figures
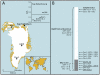
Fig. 1
Sample location and core schematics. (A) Map showing the locations of the Dye 3 (65°11′N, 45°50′W) and GRIP (72°34′N, 37°37′W) drilling sites and the Kap København Formation (82° 22′ N, W21°14′ W) in Greenland as well as the John Evans Glacier (JEG; 79°49′ N, 74°30′ W) on Ellesmere Island (Canada). The insert shows the ratio of D to L aspartic acid, a measure of the extent of protein degradation; more highly degraded samples (above the line) failed to yield amplifiable DNA. (B) Schematic drawing of ice core/icecap cross-section, with depth (in meters below surface, m.b.s.) indicating the depth of the cores and the positions of the Dye 3, GRIP, and JEG samples analyzed for DNA, DNA/amino acid racemization/luminescence (underlined), and 10Be / 36Cl (italic, the control GRIP samples are not shown). The lengths (in meters) of the silty sections are also shown.
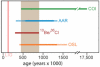
Fig. 2
Summary of dating results for the silty ice from Dye 3. From top to bottom, the bars indicate: maximum likelihood estimates for the branch length of the invertebrate COI sequences (COI); amino acid racemization results using alternative activation energies, models of racemization behavior, and basal temperature histories (AAR); age estimate from 10Be/36Cl measurements in silty ice; minimum ages based on single grain luminescence results (OSL). The time span covered by all dating methods (450-800Ka) is marked in gray. LIG = Last Interglacial. Stippled lines represent the results of less likely models. It should be noted that the maximum age estimate for the invertebrate COI sequences is based on an unlikely slow substitution rate. For details see main text and (6).
Comment in
- Profile: Eske Willerslev. Ancient DNA's intrepid explorer.
Curry A. Curry A. Science. 2007 Jul 6;317(5834):36-7. doi: 10.1126/science.317.5834.36. Science. 2007. PMID: 17615317 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Profile: Eske Willerslev. Ancient DNA's intrepid explorer.
Curry A. Curry A. Science. 2007 Jul 6;317(5834):36-7. doi: 10.1126/science.317.5834.36. Science. 2007. PMID: 17615317 No abstract available. - Understanding global climate change: paleoclimate perspective from the world's highest mountains.
Thompson LG. Thompson LG. Proc Am Philos Soc. 2010 Jun;154(2):133-57. Proc Am Philos Soc. 2010. PMID: 21553594 - Islands in the ice: detecting past vegetation on Greenlandic nunataks using historical records and sedimentary ancient DNA meta-barcoding.
Jørgensen T, Kjaer KH, Haile J, Rasmussen M, Boessenkool S, Andersen K, Coissac E, Taberlet P, Brochmann C, Orlando L, Gilbert MT, Willerslev E. Jørgensen T, et al. Mol Ecol. 2012 Apr;21(8):1980-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05278.x. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Mol Ecol. 2012. PMID: 21951625 - Ice sheets and nitrogen.
Wolff EW. Wolff EW. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 May 27;368(1621):20130127. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0127. Print 2013 Jul 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23713125 Free PMC article. Review. - Past changes in Arctic terrestrial ecosystems, climate and UV radiation.
Callaghan TV, Björn LO, Chernov Y, Chapin T, Christensen TR, Huntley B, Ims RA, Johansson M, Jolly D, Jonasson S, Matveyeva N, Panikov N, Oechel W, Shaver G. Callaghan TV, et al. Ambio. 2004 Nov;33(7):398-403. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447-33.7.398. Ambio. 2004. PMID: 15573568 Review.
Cited by
- Improving ancient DNA read mapping against modern reference genomes.
Schubert M, Ginolhac A, Lindgreen S, Thompson JF, Al-Rasheid KA, Willerslev E, Krogh A, Orlando L. Schubert M, et al. BMC Genomics. 2012 May 10;13:178. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-178. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22574660 Free PMC article. - Palaeogenetics: Icy resolve.
Dalton R. Dalton R. Nature. 2010 Feb 11;463(7282):724-5. doi: 10.1038/463724a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20148008 No abstract available. - A mitochondrial genome sequence of a hominin from Sima de los Huesos.
Meyer M, Fu Q, Aximu-Petri A, Glocke I, Nickel B, Arsuaga JL, Martínez I, Gracia A, de Castro JM, Carbonell E, Pääbo S. Meyer M, et al. Nature. 2014 Jan 16;505(7483):403-6. doi: 10.1038/nature12788. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24305051 - Microbial analyses of ancient ice core sections from greenland and antarctica.
Knowlton C, Veerapaneni R, D'Elia T, Rogers SO. Knowlton C, et al. Biology (Basel). 2013 Jan 25;2(1):206-32. doi: 10.3390/biology2010206. Biology (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24832659 Free PMC article. - South Greenland ice-sheet collapse during Marine Isotope Stage 11.
Reyes AV, Carlson AE, Beard BL, Hatfield RG, Stoner JS, Winsor K, Welke B, Ullman DJ. Reyes AV, et al. Nature. 2014 Jun 26;510(7506):525-8. doi: 10.1038/nature13456. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24965655
References
- Bennike O. Meddelelser om Grønland, Geoscience. 1990;23:85.
- Funder S, et al. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Denmark. 2001;48:117.
- Francis JE, Hill RS. Palaios. 1996;11:389.
- Dansgaard W, et al. Science. 1982;218:1273. - PubMed
- Dansgaard W, et al. Nature. 1993;364:218.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous