Polo-like kinase 1 regulates RhoA during cytokinesis exit in human cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Polo-like kinase 1 regulates RhoA during cytokinesis exit in human cells
B N Dai et al. Cell Prolif. 2007 Aug.
Abstract
Objective: Both RhoA (Rho1) and polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) are implicated in the regulation of cytokinesis, a cellular process that marks the division of cytoplasm of a parent cell into daughter cells after nuclear division. Cytokinesis failure is often accompanied by the generation of cells with an unstable tetraploid content, which predisposes it to chromosomal instability and oncogenic transformation. Several studies using lower eukaryotic systems demonstrate that RhoA and Plk1 are essential for mitotic progression and cytokinesis.
Materials and methods: Physical and functional interactions between RhoA and Plk-1 were analyzed using subcellular localization of RhoA and Plk1 in HeLa cells by immunofluorescence and co-precipitation techniques, followed by Western blotting in RhoA transfected cells.
Results: Plk1 localizes to kinetochores as well as to spindle poles during prophase and metaphase; it translocates to the midbody during telophase. RhoA is also enriched at the midbody region during telophase and colocalizes with Plk1. Recombinant RhoA, expressed as a GFP fusion protein, is enriched in the nucleus of HeLa and U2OS cells. Ectopically expressed GFP-RhoA does not cause significant cell death, although there exist a group of cells that appear to exhibit a delay in mitotic exit or in impaired cytokinesis.
Conclusion: Co-immunoprecipitation reveals that RhoA and Plk1 physically interact and that their interaction appears to be enhanced during mitosis. Given the role of RhoA and Plk1 in cytokinesis, our findings suggest that regulated activation of RhoA is important for cytokinesis and that Plk1 may alter activation of RhoA during mitotic cytokinesis.
Figures
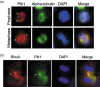
Figure 1
Subcellular localization of Plk1 and RhoA during mitosis. (a) HeLa cells were fixed and stained with antibodies to Plk1 and α‐tubulin. DNA was stained with DAPI. The stained cells were then examined by fluorescence microscopy. Representative prophase and metaphase cells are shown. Arrows indicate the positions of spindle poles. (b) HeLa cells were fixed and stained with antibodies to RhoA and Plk1. DNA was stained with DAPI. A representative telophase cell was shown. Arrow indicates the position of the midbody.
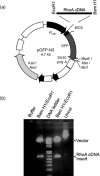
Figure 2
Cloning of RhoA cDNA into pGFP plasmid. (a) RhoA cDNA amplified using a pair of primers was cloned at BamH1 and EcoR1 sites of pGFP‐N3 plasmid. (b) Plasmid DNA of pGFP‐RhoA digested with _Bam_H1 and _Eco_R1 was analysed by agarose gel electrophoresis.
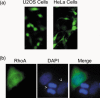
Figure 3
Expression of GFP‐RhoA. (a) U2OS and HeLa cells were transfected with pGFP‐RhoA expression plasmid for 48 h. Transfected cells were directly examined by fluorescence microscopy. Representative images are shown. No fluorescence was detected with parental cells (data not shown). (b) HeLa cells transfected with pGFP‐RhoA for 24 h were fixed and stained with the antibody to GFP. DNA was stained with DAPI. An anaphase cell and an interphase cell expressing no transfected protein are also shown (arrows).
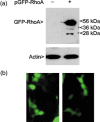
Figure 4
Analysis of cells ectopically expressing GFP‐RhoA. (a) HeLa cells transfected with or without pGFP‐RhoA for 48 h was lysed. Equal amounts of proteins were blotted for GFP‐RhoA and β‐actin. (b) HeLa cells expressing transfected GFP‐RhoA were directly examined for their morphology using fluorescence microscopy. Cells with apparent defects in cytokinesis are shown.
Figure 5
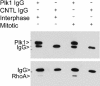
RhoA interacts with Plk1. Interphase and mitotic cells were collected and lysed. Equal amounts (1 mg) of proteins were immnoprecipitated with anti‐Plk1 antibody or with a control antibody (CNTL IgG). After overnight incubation, immunoprecipitates were blotted for Plk1 and RhoA. The relative positions of IgGs were also indicated.
Similar articles
- Polo-like kinase 1 regulates activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) at the mitotic apparatus.
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Cufí S, Menendez JA. Vazquez-Martin A, et al. Cell Cycle. 2011 Apr 15;10(8):1295-302. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.8.15342. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21474997 - A Non-canonical BRCT-Phosphopeptide Recognition Mechanism Underlies RhoA Activation in Cytokinesis.
Gómez-Cavazos JS, Lee KY, Lara-González P, Li Y, Desai A, Shiau AK, Oegema K. Gómez-Cavazos JS, et al. Curr Biol. 2020 Aug 17;30(16):3101-3115.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.05.090. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32619481 Free PMC article. - Cytokinesis and cancer: Polo loves ROCK'n' Rho(A).
Li J, Wang J, Jiao H, Liao J, Xu X. Li J, et al. J Genet Genomics. 2010 Mar;37(3):159-72. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(09)60034-5. J Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20347825 Review. - Choice of Plk1 docking partners during mitosis and cytokinesis is controlled by the activation state of Cdk1.
Neef R, Gruneberg U, Kopajtich R, Li X, Nigg EA, Sillje H, Barr FA. Neef R, et al. Nat Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;9(4):436-44. doi: 10.1038/ncb1557. Epub 2007 Mar 11. Nat Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17351640 - Polo on the Rise-from Mitotic Entry to Cytokinesis with Plk1.
Petronczki M, Lénárt P, Peters JM. Petronczki M, et al. Dev Cell. 2008 May;14(5):646-59. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.04.014. Dev Cell. 2008. PMID: 18477449 Review.
Cited by
- Phosphorylation of MyoGEF on Thr-574 by Plk1 promotes MyoGEF localization to the central spindle.
Asiedu M, Wu D, Matsumura F, Wei Q. Asiedu M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 17;283(42):28392-400. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801801200. Epub 2008 Aug 11. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18694934 Free PMC article. - Induction of Mitotic Catastrophe via Inhibition of Aurora B by Ionizing Radiation With Additive of Mulberry Water Extract in Human Bladder Cancer Cells.
Su CC, Chen NC, Chyau CC, Tseng HC, Chou FP. Su CC, et al. Integr Cancer Ther. 2019 Jan-Dec;18:1534735418808586. doi: 10.1177/1534735418808586. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Integr Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 30428726 Free PMC article. - Serum inducible kinase is a positive regulator of cortical dendrite development and is required for BDNF-promoted dendritic arborization.
Guo SL, Tan GH, Li S, Cheng XW, Zhou Y, Jia YF, Xiong H, Tao J, Xiong ZQ. Guo SL, et al. Cell Res. 2012 Feb;22(2):387-98. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.100. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 21691298 Free PMC article. - PLK1 Regulates MicroRNA Biogenesis through Drosha Phosphorylation.
Fletcher CE, Taylor MA, Bevan CL. Fletcher CE, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 19;24(18):14290. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814290. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762595 Free PMC article. - Constitutively active RhoA inhibits proliferation by retarding G(1) to S phase cell cycle progression and impairing cytokinesis.
Morin P, Flors C, Olson MF. Morin P, et al. Eur J Cell Biol. 2009 Sep;88(9):495-507. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2009.04.005. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Eur J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19515453 Free PMC article.
References
- Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA (2004) Polo‐like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 429–440. - PubMed
- Elia AE, Cantley LC, Yaffe MB (2003) Proteomic screen finds pSer/pThr‐binding domain localizing Plk1 to mitotic substrates. Science 299, 1228–1231. - PubMed
- Fujiwara T, Bandi M, Nitta M, Ivanova EV, Bronson RT, Pellman D (2005) Cytokinesis failure generating tetraploids promotes tumorigenesis in p53‐null cells. Nature 437, 1043–1047. - PubMed
- Glotzer M (2005) The molecular requirements for cytokinesis. Science 307, 1735–1739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous